Step Up To: Psychology
advertisement

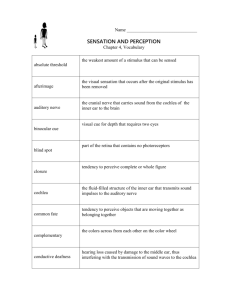
Step Up To: Psychology by John J. Schulte, Psy.D. From Myers, Psychology 8e Worth Publishers Chapter 5: Sensation Sensational Eyes Have It The Better to Hear You With. Basics What’s it Mean? Basics 500 400 300 200 100 Eyes Have It 500 400 300 200 100 Sensational 500 400 300 200 100 The Better to Hear You With 500 400 300 200 100 What’s it Mean? 500 400 300 200 100 1. The absolute threshold is the minimum amount of stimulation that a person needs to detect a stimulus: • A) at the beginning of a sensory experience. • B) on a subliminal level. • C) 50 percent of the time. • D) reliably on any occasion. 2. Psychophysics is best defined as the study of relationships between : • A) sensation and perception. • B) stimulus energies and neural impulses. • C) absolute thresholds and difference thresholds. • D) physical stimuli and psychological experience. 3. Weber’s law is relevant to an understanding of: • • • • A) absolute thresholds. B) difference thresholds. C) sensory adaptation. D) sensory interaction. 4. Sensory adaptation helps us to focus our attention on _______ stimuli. • • • • A) familiar B) subliminal C) novel D) intense 5. Experiencing an apple as being red is _____, whereas recognizing an apple as being a fruit is ____. • A) absolute threshold; difference threshold • B) accommodation; feature detection. • C) sensation; perception • D) feature detection; difference threshold 6. Dilation and constriction of the pupil are controlled by the: • • • • A) optic nerve. B) iris. C) lens. D) cornea. 7. The most light-sensitive receptor cells are the: • • • • A) ganglion cells. B) cones. C) bipolar cells. D) rods. 8. According to the Young-Helmholtz theory: • A) the retina contains three kinds of color receptors. • B) color vision depends on pairs of opposing retinal processes. • C) the size of the difference threshold is proportional to the intensity of the stimulus. • D) certain nerve cells in the brain respond to specific features of a stimulus. 9. When most people stare at a red square and then shift their eyes to a white surface, the afterimage of the square is: • • • • A) yellow. B) red. C) green. D) blue. 10. Damage to the fovea would have the greatest effect on: • • • • A) night vision. B) peripheral vision. C) sensory adaptation. D) visual acuity. 11. Heavy smoking is most likely to interfere with your sense of: • • • • A) vision. B) taste. C) kinesthesis. D) equilibrium. 12. With her eyes closed and her nose plugged, Joan was unable to taste the difference between an onion and a pear. Her experience best illustrates the importance of: • • • • A) sensory interaction. B) sensory transduction. C) sensory adaptation. D) kinesthesis. 13. Areas of the brain involved in memory are located most closely to areas of the brain responsible for our sense of: • • • • A) touch. B) smell. C) vision. D) hearing. 14. With her eyes closed, Sandra can accurately touch her mouth, nose, and chin with her index finger. Her accuracy illustrates the importance of: • • • • A) kinesthesis. B) accommodation. C) sensory interaction. D) parallel processing. 15. There are no specialized receptor neurons devoted solely to the sense of: • • • • A) pressure. B) sight. C) pain. D) smell. 16. The coiled, fluid-filled tube in which sound waves trigger nerve impulses is called the: • • • • A) eustachian tube. B) auditory canal. C) semicircular canal. D) cochlea. 17. Hue is to light as ____ is to sound. • • • • A) wavelength B) loudness C) pitch D) amplitude 18. Small differences in the intensity of a sound received by each ear enable us to identify the _____ of the sound. • • • • A) location B) amplitude C) pitch D) timbre 19. The basilar membrane is located in the: • • • • A) middle ear. B) auditory canal. C) cochlea. D) semicircular canal. 20. Conduction hearing loss is most likely to result from damage to the: • • • • A) cochlea. B) eardrum. C) auditory canal. D) auditory nerve. 21. The area of the retina where the optic nerve leaves the eye is called the: • • • • A) blind spot. B) pupil. C) visual cortex. D) cornea. 22. If the just-noticeable difference for a 10-ounce weight is 1 ounce, the just noticeable difference for an 80-ounce weight would be ____ ounces. • • • • A) 1 B) 2 C) 4 D) 8 23. A subliminal message is one that is presented: • A) while an individual is under hypnosis. • B) below the absolute threshold for awareness. • C) in a manner that is unconsciously persuasive. • D) with very soft background music. 24. The discovery that high-frequency sounds trigger large vibrations near the beginning of the basilar membrane supports the _____ theory. • • • • A) gate-control B) frequency C) place D) opponent-process 25. Our experience of pain may be intensified when we perceive that others are experiencing pain. This best illustrates the importance of: • • • • A) top-down processing. B) sensory adaptation. C) accommodation. D) difference thresholds. Stop here, or continue as a review 1. The absolute threshold is the minimum amount of stimulation that a person needs to detect a stimulus: • A) at the beginning of a sensory experience. • B) on a subliminal level. • C) 50 percent of the time. • D) reliably on any occasion. 2. Psychophysics is best defined as the study of relationships between : • A) sensation and perception. • B) stimulus energies and neural impulses. • C) absolute thresholds and difference thresholds. • D) physical stimuli and psychological experience. 3. Weber’s law is relevant to an understanding of: • • • • A) absolute thresholds. B) difference thresholds. C) sensory adaptation. D) sensory interaction. 4. Sensory adaptation helps us to focus our attention on _______ stimuli. • • • • A) familiar B) subliminal C) novel D) intense 5. Experiencing an apple as being red is _____, whereas recognizing an apple as being a fruit is ____. • A) absolute threshold; difference threshold • B) accommodation; feature detection. • C) sensation; perception • D) feature detection; difference threshold 6. Dilation and constriction of the pupil are controlled by the: • • • • A) optic nerve. B) iris. C) lens. D) cornea. 7. The most light-sensitive receptor cells are the: • • • • A) ganglion cells. B) cones. C) bipolar cells. D) rods. 8. According to the Young-Helmholtz theory: • A) the retina contains three kinds of color receptors. • B) color vision depends on pairs of opposing retinal processes. • C) the size of the difference threshold is proportional to the intensity of the stimulus. • D) certain nerve cells in the brain respond to specific features of a stimulus. 9. When most people stare at a red square and then shift their eyes to a white surface, the afterimage of the square is: • • • • A) yellow. B) red. C) green. D) blue. 10. Damage to the fovea would have the greatest effect on: • • • • A) night vision. B) peripheral vision. C) sensory adaptation. D) visual acuity. 11. Heavy smoking is most likely to interfere with your sense of: • • • • A) vision. B) taste. C) kinesthesis. D) equilibrium. 12. With her eyes closed and her nose plugged, Joan was unable to taste the difference between an onion and a pear. Her experience best illustrates the importance of: • • • • A) sensory interaction. B) sensory transduction. C) sensory adaptation. D) kinesthesis. 13. Areas of the brain involved in memory are located most closely to areas of the brain responsible for our sense of: • • • • A) touch. B) smell. C) vision. D) hearing. 14. With her eyes closed, Sandra can accurately touch her mouth, nose, and chin with her index finger. Her accuracy illustrates the importance of: • • • • A) kinesthesis. B) accommodation. C) sensory interaction. D) parallel processing. 15. There are no specialized receptor neurons devoted solely to the sense of: • • • • A) pressure. B) sight. C) pain. D) smell. 16. The coiled, fluid-filled tube in which sound waves trigger nerve impulses is called the: • • • • A) eustachian tube. B) auditory canal. C) semicircular canal. D) cochlea. 17. Hue is to light as ____ is to sound. • • • • A) wavelength B) loudness C) pitch D) amplitude 18. Small differences in the intensity of a sound received by each ear enable us to identify the _____ of the sound. • • • • A) location B) amplitude C) pitch D) timbre 19. The basilar membrane is located in the: • • • • A) middle ear. B) auditory canal. C) cochlea. D) semicircular canal. 20. Conduction hearing loss is most likely to result from damage to the: • • • • A) cochlea. B) eardrum. C) auditory canal. D) auditory nerve. 21. The area of the retina where the optic nerve leaves the eye is called the: • • • • A) blind spot. B) pupil. C) visual cortex. D) cornea. 22. If the just-noticeable difference for a 10-ounce weight is 1 ounce, the just noticeable difference for an 80-ounce weight would be ____ ounces. • • • • A) 1 B) 2 C) 4 D) 8 23. A subliminal message is one that is presented: • A) while an individual is under hypnosis. • B) below the absolute threshold for awareness. • C) in a manner that is unconsciously persuasive. • D) with very soft background music. 24. The discovery that high-frequency sounds trigger large vibrations near the beginning of the basilar membrane supports the _____ theory. • • • • A) gate-control B) frequency C) place D) opponent-process 25. Our experience of pain may be intensified when we perceive that others are experiencing pain. This best illustrates the importance of: • • • • A) top-down processing. B) sensory adaptation. C) accommodation. D) difference thresholds. Acknowledgements • Step Up Created by: – John J. Schulte, Psy.D. • Based on Psychology, Eighth Edition by • David Myers • Published by • Worth Publishers, 2006 Answers to Chapter 5 1. C 9. C 17. C 2. D 10. D 18. A 3. B 11. B 19. C 4. C 12. A 20. B 5. C 13. B 21. A 6. B 14. A 22. D 7. D 15. C 23. B 8. A 16. D 24. C 25. A