File
advertisement

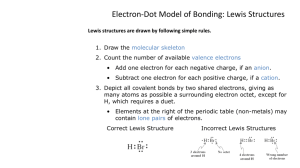
GOOD MORNING! Today we will: Turn Covalent Bond Practice Problems & Quiz Revisions • Ionic/Covalent Naming Quiz • Continue Lewis Structures – Atoms – Ions – Molecules • Start Practicing! • HW: DUE Fri 2/12 Start Lewis Practice Problems • 2nd Column of Vocab DUE Fri Who the Heck is Gilbert Lewis? Ba: . : • Lewis devised a method for showing how electrons are arranged in elements and compounds. • He used element symbols to represent atoms and dots to show the valence electrons in a structure. • We call them “Lewis Dot Structures” or “Lewis Dot Diagrams” or just “Lewis Structures” • Some examples: :P: :O: Lewis Diagrams / Structures Lewis structures represent electron distribution in atoms, ions, and molecules by showing ALL valence electrons •Atoms Ba: •Ions [Na]+ , •Molecules •Polyatomic ions or Lewis Structures for Atoms and Ions Write the symbol of the atom and show a dot for each valence electron. Si Write the symbol of the ion, show a dot for each valence electron ADDING electrons for a (-) ion and SUBTRACTING electrons for a (+) ion. [Al]+3 [:Ö̤ :]-2 Put brackets [ ] and a charge on the symbol. Lewis Structures for Ionic Compounds : : : : • Arrange ions symmetrically based on charge • Show valence electrons around each atom representing e-’s lost and gained in bonding (none for metals and full octet for nonmetals) • Put brackets and charge on each ion Example: MgBr2 [:Br:]- [Mg]2+ [:Br:]- Lewis Structures for Molecules • Goal: every atom has full octet (8 electrons) • Use the trial and error method of counting valence electrons and distributing them, in pairs, to achieve octet (each atom has 8 e-) • Or, use need / have / share method to determine number of bonds first, then distribute e-’s to achieve octet • Keep e-s in pairs!!! • Only include double or triple bonds if necessary • Exceptions to octet rule: H only gets 2 e-s Be only gets 4 e-s B and Al only get 6 e-s Total e-’s = odd number e-’s on atom exceed 8 Lewis Structure Helpful Hints • Carbon is the middle man, (4 bonding e- pairs) • H is always on perimeter, (1 bonding e- pair) • Halogens share 2 e-’s (one bonding e- pair) • Oxygen: share 4 e-’s (2 bonding e- pairs) • Nitrogen: share 6 e-’s (3 bonding e- pairs) Rules are meant to be broken … except C and H! CH3OH CHOCl NI3 What would Lewis do? Write a Lewis Structure for the following molecules: •OBr2 •CH2F2 •CF2O Describe the electron arrangement on the central atom • # of unshared e- pairs, • # of shared e- pairs (single, double, triple bonds) Lewis Structures for Polyatomic Ions • Anions: anions are negative ions because they have more electrons than protons ADD electrons to equal the charge • Cations: cations are positive ions because they have less electrons than protons REMOVE electrons equal to the charge ClOPO43- Write a Lewis Diagram for each of the following and identify the shape • PCl3 • CH2Br2 • CH2O • BrO3• C2H4