Blood System
advertisement

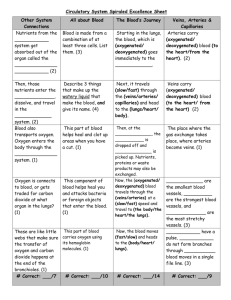
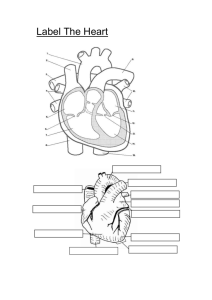
Blood System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Three major types of blood vessels: arteries, capillaries, and veins. Arteries (arteri/o) large blood vessels that carry oxygen rich blood away from the heart to the body, arterial blood is bright red Aorta is the main part of arterial system, begins in the left ventricle Coronary arteries (coron/o) supplies the heart with blood. Arterioles are thinner branches, carry blood to capillaries http://plus.maths.org/issue36/interview/artery.jpg Blood Vessels Cont’d Capillaries (capill/o) Blood vessels that connect arteries and veins to each other Smallest vessels in the body Blood flow is slower through capillaries; allows time for exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between surrounding cells and fluids Veins (phleb/o, ven/o) Responsible for carrying waste-filled blood back to heart Veins have valves that allow for one-way blood flow toward the heart Venules are small veins that join to form larger veins Pulse & Blood Pressure Pulse – expansion and contraction of an artery caused by the pressure of the blood moving through the artery Blood Pressure – measures the amount of pressure applied against the walls of the vessels Example – 124/72 Systolic Pressure – the upper number of a blood pressure reading (124 / __ ) Diastolic Pressure – the lower number of a blood pressure reading ( __ / 72) http://www.stockphotography.com/img/medical/stock_photos/blood_pressure_cuff.jpg Blood The Blood (Hem/o or hemat/o) Blood is composed of 55% liquid plasma and 45% formed elements. Formed elements are red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma Liquid part of blood; contains nutrients, wastes and hormones 91% water, 9% proteins http://www.bloodservices.ca/centreapps/internet/uw_v502_mainengine.nsf/resources/Blood+Process/$file/Step6_150.jpg Fibrinogen & prothrombin are clotting proteins to help blood clot and control bleeding Erythrocytes Erythrocytes (erythr/o = red + -cyte = cell) Also called red blood cells (RBC’s) Contains hemoglobin (hem/o = blood + -globin = protein) which is iron containing portion of erythrocyte Hemoglobin transports oxygen from the lungs to the tissues of the body Live about 120 days Leukocytes Leukocytes (leuk/o = white + -cyte = cell) Also called white blood cells (WBC’s) Protect body against infection There are five types of leukocytes: Neutrophils – majority of WBC’s, fight infection by phagocytosis (engulfing & swallowing germs). Elevated count indicates a bacterial infection (strep, staph, etc..) Basophils – promote inflammatory response, elevated basophil count may indicate an allergic condition (ex. allergic reaction, asthma, etc…) Leukocytes Cont’d. Types of Leukocytes cont’d. Eosinophils – formed in red bone marrow, increase in response to allergic conditions (ex - allergic reaction, asthma, etc…) Lymphocytes – formed in red bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen; protect body against disease Monocytes – Also formed in red bone marrow, lymph nodes and spleen. Help protect against disease, an elevated count usually indicates a chronic (long-term) condition http://www.lymphomation.org/images/leukocytes-normal.gif Thrombocytes Thrombocytes (thromb/o = clot + -cyte = cell) Also known as platelets Smallest formed elements in the blood When blood vessel is damaged, platelets become sticky and clump together to form a clot http://sacs.vetmed.ufl.edu/histo/29b_sm.gif Anatomy Sheet Take out the “Anatomy of the Heart” handout Fill in the blanks using the diagram on the next slide Color the arteries blue Color the veins red THIS IS YOUR TICKET TO LEAVE!!!!!! Blood Flow Through the Heart A. The superior vena cava drains deoxygenated blood from the head, neck, and arms. The inferior vena cava drains deoxygenated blood from the abdomen and the legs into the right atrium. The coronary sinus drains deoxygenated blood from the myocardium into the right atrium. Blood Flow Through the Heart B. C. D. From the right atrium, deoxygenated blood flows through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. From the right ventricle, deoxygenated blood flows through the pulmonary semilunar valve into the pulmonary trunk. The pulmonary trunk branches to form the right and left pulmonary arteries, which take deoxygenated blood to the lungs for gas exchange. Carbon dioxide is released from the blood while oxygen is picked up by the blood. Blood Flow Through the Heart E. F. G. Oxygenated blood returns through the right and left pulmonary veins into the left atrium. From the left atrium, oxygenated blood flows through the bicuspid (mitral) valve into the left ventricle. From the left ventricle, oxygenated blood flows through the aortic semilunar valve into the aorta. Blood Flow Through the Heart H. I. From the aorta, oxygenated blood flows into the arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins, eventually reaching the superior and inferior vena cava once again. The body’s entire blood supply is circulated every minute Pattern of Circulation RED = O2 rich BLUE = O2 poor Blood System Abbreviations – pulse BP – blood pressure RBC – red blood cells WBC – white blood cells P Career Opportunities Hematologist (hemat/o = blood + -ologist = specialist) specializes and treats disorders of the blood Phlebotomist Takes patient blood samples and prepares them for testing in the lab http://healthcare.maricopa.edu/images/PHLEB.jpg Medical Laboratory Technologist (MT) Works under the supervision of pathologist to study tissues, fluids, and cells in the human body Medical Laboratory Assistant Prepares specimens for testing and helps clean and maintain laboratory equipment.