The Circulatory System
advertisement

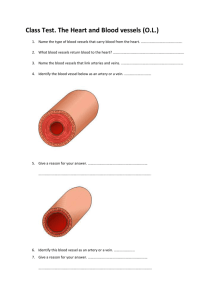
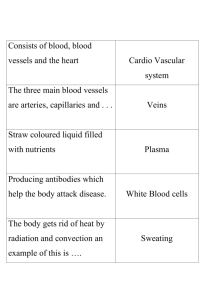
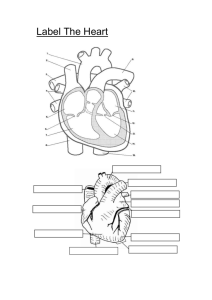
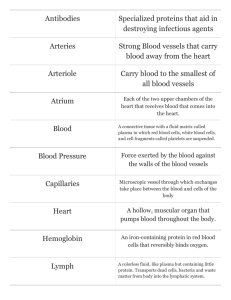
The Circulatory System 1. Using your first two fingers (not your thumb), try to find your pulse. There are several places you can check. 2. Once you have found a good pulse point, have a partner time you for 15 seconds and count the number of times you feel your pulse. ___________ 3. Multiply that number by 4 to get the resting beats per minute _____________ The Circulatory System • Made up of the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system The Cardiovascular System • Made up of (organs): – heart – blood vessels (veins and arteries) – blood The Cardiovascular System • Functions – Carries nutrients, gases, hormones and waste around the body. • carbon dioxide and waste away • oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to – Helps your body maintain a balanced temperature. vocabulary word! • heart – hollow muscular organ that pumps blood around the body. • Size of your fist • Located in the center of your chest • right side pumps oxygen poor blood to the lungs • left side pumps oxygen rich blood to the body. Structure of the Heart • The heart has two sides • Each side has an upper chamber – Atrium • Each side has a lower chamber – Ventricle How the Heart Works • The heart’s action has two phases – The heart relaxes and the atria fill with blood – The atria contract, blood is pumped into the ventricles, then the ventricles contract and send blood out of the heart • Blood only travels in one direction, it cannot flow backwards Regulation of the Heartbeat • The heart contains pacemaker cells that tell the heart when to beat – When you are exercising, excited, scared etc…, your heart beats faster. – When you are relaxed, calm, asleep etc…, your heart beats slower. vocabulary word! • blood – the tissue that carries gases, hormones, nutrients and wastes through the body. • Helps the body maintain homeostasis (balance) FACT: blood is NEVER blue!!!! Oxygen rich blood from an artery Oxygen poor blood from a vein Unless you’re a horseshoe crab. vocabulary word! • blood vessels – the tubes that your blood travels in. – arteries – capillaries – veins vocabulary word! Arteries • arteries - carry oxygen rich blood away from the heart. – Walls are thick, strong and flexible – Contain smooth muscle that can contract and relax Arteries vocabulary word! Capillaries • capillaries - tiny blood vessels where material is exchanged between the blood and the body’s cells. • Oxygen and glucose rich blood from the arteries goes into the capillaries • From the capillaries needed materials pass into the cells and waste material is removed from the cells Capillaries vocabulary word! Veins • veins - carry oxygen poor blood back to the heart. – Veins have 3 layers to their walls too but the wall is much thinner – Muscle contractions, breathing and valves help move blood through veins Veins Create this chart in your notes and complete. artery capillary Blood moves in circuits inside blood vessels. • Oxygen poor blood enters the right atrium. • It is then pumped to the right ventricle, then to the lungs. • It picks up oxygen and goes back to the left atrium • It pumps from the left atrium into the left ventricle. • The left ventricle pumps oxygen rich blood to the rest of the body. Blood moves in two circuits around the body: Maintaining body temperature • Blood circulating through the body helps maintain homeostasis. • When we are hot, blood vessels enlarge to allow more blood close to the surface of our skin where it can be cooled. • When we are cold, blood vessels constrict to keep as much blood close to the chest as possible to keep us warm. The Lymphatic System • Made up of (organs): – lymph nodes – lymph vessels – lymph – spleen – bone marrow – Tonsils – thymus The Lymphatic System • Functions – Carries white blood cells. – Helps remove waste from the blood. – Helps us heal and fight disease. vocabulary word! • lymph – clear to white fluid found in blood that contains white blood cells. • Lymph can move in and out of blood vessels and body tissues. • It helps prevent infection and heals injuries. • lymph nodes – small, bean shaped organs that remove dead cells and pathogens. • Found mostly in the arm pits, neck and groin. • Stores white blood cells that help fight infection. • bone marrow – soft tissue inside of bones where red blood cells are produced. • tonsils – small lymphatic organs at the back of the throat. • Tonsils help defend the body against infection. • spleen – largest lymphatic organ. It stores white blood cells. Working together: • These two systems work together to form the circulatory system. • Blood stays in the blood vessels (closed loop). • Lymph can travel in and out of lymph vessels and into and out of blood vessels (open loop). Working together: Working together: