DCE (distributed computing environment)
advertisement

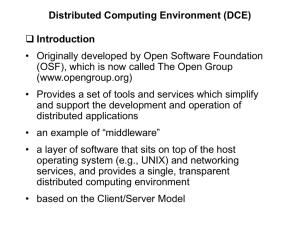
DCE (distributed computing environment) What is DCE distributed computing environment It is defined by the open software foundation(OSF). It is an architecture, a set of standard service, and application programs, built on top of the existing operating system which hides the differences among individual computers. used to support the development and usage of distributed applications in a single distributed system. It use client/server model. Goals of DCE • 1) can run on many different computers, operating systems (Unix, Os/2, VMS,windows) and networks in a distributed system, Provide a coherent seamless platform for running distributed applications. • 2) Provide a mechanism for synchronizing clocks on different machines. • 3) Provide tools to make it easier to write distributed applications in which multiple users at multiple locations can work together. • 4)Provide extensive tools for authentication and access protection DCE architecture • DCE cell: the basic unit of operation in the DCE. A cell is a group of users, systems,and resources that are typically centered around a common purpose and that share a common DCE services. It is an administrative domain that allows users,machines, and resources to be managed through functions distributed within the network in which they are in. Members working on the same project in an organization are likely belong to the same cell. • DCE architecture(cont’d) • DCE threads • DCE remote procedure call • DCE directory service: cell directory service; global directory service • DCE distributed time service • DCE security service • Distributed file service Distributed services provided by the DCE • Thread services; • RPC; • time service; • directory services; • security service. DCE threads • DCE thread package: a collection of userlevel library procedures that allow processes to create,delete, and manipulate threads. multiple tasks could occur at the same time to complete a process(work). It is designed to minimize the impact on the existing software: a single threaded program can be converted into multithreaded one by setting parameter indicating that more threads will be used. All threads in a process share the same address space, file system, and other process resources. Each thread has its own program counter, stack,and registers. Scheduling • determines how long a thread may run and which thread will run next. • Three algorithms: • FIFO: search and locate the priority queue with one or more threads from highest to lowest, run the first thread on this queue until finish by blocking or exiting. • Round robin:the scheduler locates the highest populated queue and runs each thread for a fixed quantum. • Default algorithm: it uses a time-sliced roundrobin algorithm to run the threads on all queues, the higher the priority the larger the quantum a Synchronization Mutexes: prevent multiple threads from accessing the same resource at the same time. • Condition variable: it is used with mutexes to manage synchronization.e.g.: a thread could use mutexes to gain exclusive access to a resource, if this resource is not available, the thread waits on a condition variable that atomically suspends the threads and releases the mutexes. Later, when another thread signals the condition variable, the waiting thread is restarted. RPC • DCE is based on the client/server model. RPC package of DCE allows a client process to call a procedure on a remote computer. It allows application programmer to extend the local procedure call to a distributed environment. The application programmer doesn’t have to be concerned with the detail of the network communications between client and server nodes. • RPC hides communication detail and removes system and hardware dependencies. It can automatically handle data type conversions between the client and the server without considering whether they run on the same or different architecture, or have same or different byte ordering. DCE directory service • Provide up-to-date addressing information by keeping track of where all resources (user, machine, file, server…) are located. So users can identify these resources by names and gain access to them without needing to know where they are located • It’s distributed service--- the information that forms database is stored in different places. • A replicated service: the information is replicated and stored in more than one location which make it more readily Time service • It enables distributed applications on different computers to determine event sequencing, duration, and scheduling. • Keeps clocks on separate computers participating in a distributed system synchronization. • It uses universal coordinated time(UTC) to synchronize DCE host’s time. Security service • Controls interactions between clients and servers. It allows client and servers to authenticate each other and perform authenticated RPC. • Offers integrity and privacy of communications without having password appearing on the network . • Controls access to resources by authorization; • Principal: is a user or process that needs to communicate securely. It could be a server, computers, cells or users. • Authentication: is the process of verifying a principal’s network identity. Distributed file service • It’s a worldwide distributed file system; • Allows users to access and share files stored on a file server anywhere on the network without knowing the physical location of the file; • The physical file system (DCE local file system) is able to do several tasks: Replicate data; log file system data, enable quick recovering after a crash; Simple administration by dividing the file system into easily managed units; Associate access control list with files and directory. Advantages of DCE • 1) The services provided by DCE is much easier to use than the ones found in other computer networking environments: i.e.: the DCE remote procedure call provide a much simpler way for communicating between software modules running on different system than using socket calls. • 2) the DCE security service provides a reliable way to determine if a user in a distributed system should be allowed to perform certain action. Advantages (cont’d) • 3)supports portability and interoperability by hiding differences among the various hardware,software,and networking elements in a large network. • 4) supports distributed file service which means files present on workstation in a network are available to this network. • END • •