Fitness Training Methods II
advertisement

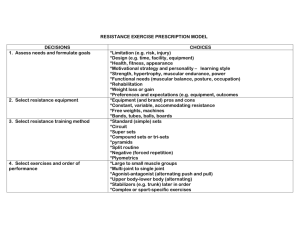
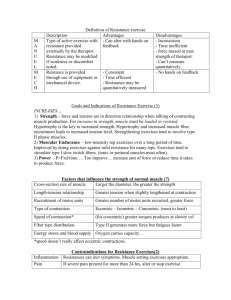
Btec Sport and Leadership Identify 3 types of training to develop muscular endurance, strength & power. Give examples of how to include these in a training program Explain the advantages & disadvantages of each method. In the gym with England Rugby SLTV: England Hit The Gym What does this type of training help to improve?? A weight not attached to a device or machine E.g. barbells/dumb-bells for constant-resistance exercises This means the amount of resistance for a muscle/muscle group is the same throughout the reps. Each time an athlete completes a lifting movement they are working against resistance. ‘One Repetition Maximum’ or ‘1RM’ is the maximum weight a person can lift in a single ‘rep’ of an exercise. Spotters are essential for safety- working with someone who can watch & help with safety. Order of exercises can affect progress Core exercises- work major muscle groups & should be done 1st and help stabilise the spine/pelvis. Assistance exercisesexercise smaller muscles and are sport specific should be 2nd. Examples you need to know! Which is which? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Bicep curls Tricep extensions Upright rows Squats Bent over rows Seated overhead presses Lateral raises Front raises Bench press Deadlift Examples you need to know! Which is which? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 2 6. 3 7. 8. 1 9. 10. Bicep curls Tricep extensions Upright rows Squats Bent over rows Seated overhead presses Lateral raises 10 Front raises Bench press Deadlift 5 4 9 7 6 8 Max Strength Muscular Endurance Elastic Strength Which sports athletes can you think of that would use each different aim? • Low Reps and High Loads • 90% 1RM 1-6 reps • Single movement against high resistance. • High Reps and Low Loads • 50-60% 1RM up to 20 reps • Repetitive movements of a muscle or muscle group • Medium Reps and Loads • 75% 1RM for 12 reps • Movements in very close succession Warm up: _______________ your joints to avoid injury Body alignment: standing- feet shoulder width apart, knees slightly bent, ________ __ _________________movement Breathing technique: do not hold breath as it _________ blood pressure and chance of a heart attack, breathe _____as weight lifted Intensity: not too heavy- should be able to lift at least 6 times. Too heavy can damage skeletal & joint structures- use __________ to judge Number of sets: ________ reps, progressive overloadincrease reps or increase weights and _______ reps Number of exercises: 1-2 _____ of ___ exercises, trying to cover all major muscle groups Order of exercises: focus on core exercises before assistance exercises, _______________ upper/lower body and push/pull exercises After training: perform _______ ______and developmental stretching (hold 15-20 seconds) to help _______ ________, prevent cramps and increase joint range of movement. Missing words: Reduce soreness Sets Alternate 8-12 Slow & controlled Increases %1RM Prepares Out Lower Cool down 6 Extension: You know what free weights are… so what are fixedresistance machines? How could they be used instead of free weights? Are they better? Why/why not? Prepares Warm up: _______________ your joints to avoid injury Body alignment: standing- feet shoulder width apart, knees Slow__ & controlled slightly bent, ________ _________________movement Breathing technique: do not hold breath as it _________ increases blood pressure and chance of a heart attack, breathe out _____as weight lifted Intensity: not too heavy- should be able to lift at least 6 times. Too heavy can damage skeletal & joint structures- use %1RM to judge __________ Number of sets: ________ reps, progressive overload8-12 increase reps or increase weights and _______ lower reps sets of ___ 6 exercises, trying to Number of exercises: 1-2 _____ cover all major muscle groups Order of exercises: focus on core exercises before assistance exercises, _______________ upper/lower body alternate and push/pull exercises cool down After training: perform _______ ______and developmental reduce soreness stretching (hold 15-20 seconds) to help _______ ________, prevent cramps and increase joint range of movement. Missing words: Reduce soreness Sets Alternate 8-12 Slow & controlled Increases %1RM Prepares Out Lower Cool down 6 Extension: You know what free weights are… so what are fixedresistance machines? How could they be used instead of free weights? Are they better? Why/why not? Advantages Disadvantages + training can be made sport specific targeting specific muscle groups + good for both strength & endurance • - Needs careful organisation to ensure correct & safe technique • - May need a gym for specialist equipment • - Equipment can be expensive • - May need a spotter Bootcamp circuit training What do you need to consider before planning a circuit training session? E.g. warm up… Considerations: Training goals How many stations? How long will individuals work for? How will you decide the intensity? E.g. RPE scale… Rest period OR rest station? How many circuits per session? Total work out time? Order of exercises To avoid muscle fatiguemake sure you do not work the same muscle group one after the other. E.g. you would not have a press up and a tricep extension next to each other in the circuit… but you could have press ups then sit ups then steps etc. To improve a component of fitness it is necessary to ‘Progressively Overload’ – To work harder than your body is used to working normally. How could progressive overload be achieved? Reduce time to complete exercise Reduce resting time Increase exercise resistance Increase repetitions Increase number of stations Increase number of circuits done Advantages Disadvantages + training can be made sport specific targeting specific muscle groups + good for both strength & endurance & power + can be varied to keep motivation high + you can use household items so you can complete without specialist equipment! E.g. tins of soup! • - needs careful organisation to include setting up and taking down the circuit. • - need time to demonstrate correct & safe technique of each exercise Introduction to Plyometrics: Beginners Guide What is unique about these types of exercises? Require a maximal force as muscle lengthens (eccentric) before an immediate maximal force as a muscle shortens (concentric). Plyometrics are designed to improve strength and explosive power. This is a training method used by those who wish to jump higher, run faster, throw further or hit harder – such as sprinters and hurdlers, netball, volleyball and basketball players. Plyometric drills are performed at sub-maximal levels in a warm up e.g. skipping, arm swings & jogging drills. Walking & jogging should be done to cool down after. Exercises need to be performed carefully and consideration of performers experience is needed so the right intensity level is used. Be careful though – they can cause muscle soreness! Basic equipment needed: Boxes Benches Hurdles Cones Medicine balls Exercise examples: Standing jumps Incline press ups Jumping Bounding Skipping Hopping Medicine ball exercises for core strength. Advantages Disadvantages + training can be made sport specific targeting specific muscle groups + little cost involved and no need for specialist equipment • - need to be experienced to perform the correct & safe technique of each exercise Complete worksheets on this section. You have completed all sections for the exam! Give these Revision resources a go! Training Methods sort cards Training Methods & Training Principles WIPEOUT! Questions Game: Full module revision game! Practice Exam: Weds 20th / Thursday 4th