International Trade
advertisement

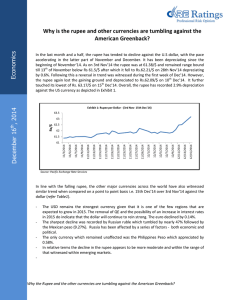
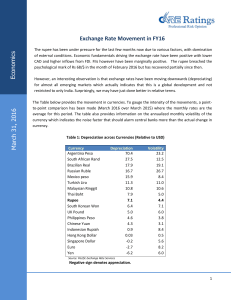
International Trade Class 10 The production possibilities frontier Australia can produce either 100 Agricultural products or 50 electronic products Malaysia can produce either 40 agricultural products or 50 electronic products. World Output The need to specialize! When countries specialize world output increases. Comparative advantage. The ability of a country to price a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country. Absolute Advantage. The ability of a country to produce a good using a fewer resources than another country. Free trade vs Fair Trade Free Trade – The flow of good and services between countries without restrictions. Fair Trade – a county should only reduce its barriers to entry if the other country does not have some sort of “unfair competitive” advantage. And also provided that the other country also reduces its trade barriers. Type of protections Embargo Tariff Quota Common arguments for protection The infant industry argument National Security argument. A nation should not be dependent on other countries for defense. Employment argument. New domestic industries need protection because it is not yet ready to compete. Job increases in protected industries. Cheap foreign labor argument. Other countries have cheaper labour, it is difficult to compete. Free Trade Agreements ASEAN – Association of South Eastern Asian Nations EEC – European Economic Community NAFTA – North American Free Trade Agreement. APEC – Asian Pacific Economic Cooperation. Supply and Demand for foreign exchange. When the SL Rupee is low or depreciates. Sri-Lankan goods and services will cost foreign consumers less. Foreigners will buy more SL products. For Sri-Lankans foreign products become more expensive. When the SL rupee is high or appreciates. SL goods will cost foreign consumers more. Foreigners will buy less SL products Sri-Lankans will buy more foreign products. 4 shifts in supply and demand of a currency. Taste and Preference. Relative Incomes Relative Price levels Relative Real Interest Rates Depreciation – A fall in the price of one currency relative to another Appreciate – A rise in the price of one currency relative to another. THANK YOU!!! THE Well almost END!!!!!!