AP US History
advertisement

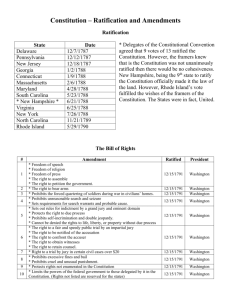
AP US History Founding & Constitution Test Study Guide Founding & the Constitutional Convention Declaration of Independence Announces disunion with Great Britain; statements include “All men are created equal,” & “Life, liberty & the pursuit of happiness…” Virginia/Randolph Plan Calls for a 2 House legislature; Lower House (House of Representatives) representation based on population, Upper House (Senate) members voted on by Lower House New Jersey/Patterson Plan Calls for 1 House legislature; Representation equal between states Connecticut Compromise Created a 2 House legislature; Lower House (House of Representatives) representation based on population, Upper House (Senate) representation equal between states 3/5 Clause Slaves counted as 3/5 person for representation and taxation purposes Preamble Gives 6 goals of the new government; statements include “We the People of the United States of America…” Article I Duties & powers of the Legislative Branch Article II Duties & powers of the Executive Branch Article III Duties & powers of the Judicial Branch Article IV Rules and powers for our federal form of gov’t Article V Procedures for making amendments Article VI Oath of allegiance for elected officials Article VII Descriptions and rules for Constitution’s ratification Strict Interpretation Laws cannot be passed regarding items or situations not specifically detailed in the Constitution (based on 10 th Amendment) Loose Interpretation Laws can be passed if item or situation not specifically detailed in the Constitution (based on Elastic Clause (Article I, Section 8) Constitutional Amendments 1 Freedom of religion, speech, press, assembly and to petition the government (1791) 2 Right to bear arms (in order for states to keep militias (1791) 3 No quartering of troops in private homes (1791) 4 Specific search warrants required (1791) 5 Rights of the accused; indictments are required; due process & justified compensation (1791) 6 Speedy and public trial; call of witnesses (1791) 7 Trial by jury allowed in civil suits over $20 (1791) 8 Excessive bail; cruel and unusual punishment (1791) 9 All rights not listed are retained by the people (1791) 10 All powers not delegated are retained by the states (1791) 11 Citizens of one state cannot sue another state; foreigners cannot sue states (1798) 12 Electors to cast separate ballots for President and VP (1804) 13 Slavery abolished (1865) 14 Blacks are citizens; Confederate leaders ineligible for office (1868) 15 16 17 18 19 Black suffrage guaranteed (1870) Federal income tax legalized (1913) Direct election of US Senators (1913) Alcohol illegal; establishes national Prohibition (1919) Women’s suffrage (1920) 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Congressional and presidential inauguration dates changed (1933) Repeal of Prohibition (1933) Two term/10 year limit on presidential term (1951) Presidential electoral votes for Washington DC (1961) Prohibition of poll taxes (1964) Presidential ability/disability and succession defined (1967) 18 year old suffrage (1971) Congressional pay raises (1992)