Population Geography: Distribution, Migration, & Demographics

Unit 2- Population
Key Questions guiding the assigned four chapters in this unit:
What is the present day distribution and density of the world’s population and where are people concentrated in particular regions and countries on Earth?
What are some of the significant differences among the four leading areas of population concentrations on Earth – East Asia, South Asia, Europe, and North America – and what geographic, historic, economic, and socio-cultural processes have created these differences?
How do population geographers and demographers analyze population change through
time?
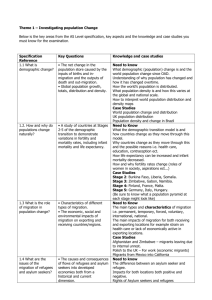
What are the four stages of the demographic transition?
What are some of the lessons learned from the population explosion?
How has the demographic change in developing countries differed from changes in the birth and death rates through time in Europe?
What processes and theories help explain the Earth’s relatively high rates of internal and external migration through time?
What factors account for the high rates of internal mobility in the U.S.?
What major migration streams have occurred during the past five centuries on Earth?
What is the definition of a refugee and why have the total number of refugees increased so dramatically on Earth since the 1970s?
What is the difference between expansive, eugenic, and restrictive population policies?
How have post-World War II population policies in Japan, India, and China differed?
What are some examples of anti-immigration policies that have been passed in countries such as the U.S. and Australia that have attempted to restrict the numbers of incoming legal migrants?
II. Population . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13–17%
A. Geographical analysis of population
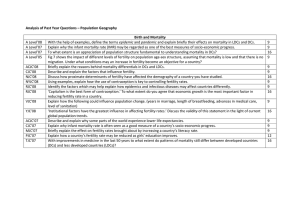
1. Density, distribution, and scale
2. Implications of various densities and distributions
3. Patterns of composition: age, sex, race, and ethnicity
4. Population and natural hazards: past, present, and future
B. Population growth and decline over time and space
1. Historical trends and projections for the future
2. Theories of population growth, including the
Demographic Transition Model
3. Patterns of fertility, mortality, and health
4. Regional variations of demographic transitions
5. Effects of population policies
C. Population movement
1. Migration selectivity
2. Major voluntary and involuntary migrations at different scales
3. Theories of migration, including push and pull factors, human capital, and life course
4. International migration and refugees
5. Socioeconomic consequences of migration
CONCEPTS: UNIT II
Each of the following concepts is discussed in detail in Chapters 4 through 7 of your textbook.
Population: Migration:
Population densities Push-pull factors
Demographic regions Voluntary
Population distributions Forced
Natality Transmigration
Mortality Refugee
Population explosion Migrations patterns
Thomas Malthus -- intercontinental
Demographic Transition model -- interregional
Zero population growth -- rural-urban
Age distribution Place utility
Population pyramid Activity space
Cohort Personal space
Sex ratio Space-time prism
Gendered space Gravity model
Standard of living Distance decay
Infant mortality rate Step migration
Diffusion of fertility control Chain migration
Disease diffusion Interveningopportunity
Maladaptation Cyclic movement
Sustainability Migratory movement
Epidemiological Transition model Periodic movement
Demographic equation Transhumance
Dependency ratio Internal migration
Rate of natural increase
Doubling time
J-curve
S-curve
Ecumene
Overpopulation
Underpopulation
Carrying capacity
Population projection
Neo-Malthusian Demographic momentum