Theme 1 – Investigating population Change Below is the key areas
advertisement
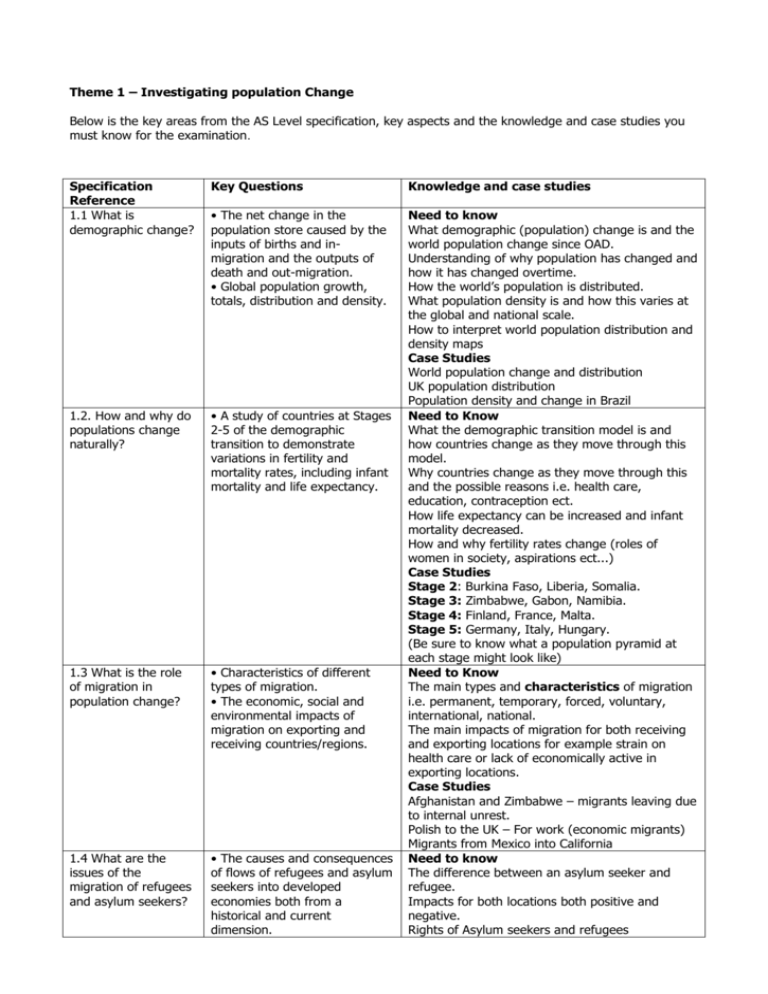
Theme 1 – Investigating population Change Below is the key areas from the AS Level specification, key aspects and the knowledge and case studies you must know for the examination. Specification Reference 1.1 What is demographic change? Key Questions Knowledge and case studies • The net change in the population store caused by the inputs of births and inmigration and the outputs of death and out-migration. • Global population growth, totals, distribution and density. 1.2. How and why do populations change naturally? • A study of countries at Stages 2-5 of the demographic transition to demonstrate variations in fertility and mortality rates, including infant mortality and life expectancy. 1.3 What is the role of migration in population change? • Characteristics of different types of migration. • The economic, social and environmental impacts of migration on exporting and receiving countries/regions. 1.4 What are the issues of the migration of refugees and asylum seekers? • The causes and consequences of flows of refugees and asylum seekers into developed economies both from a historical and current dimension. Need to know What demographic (population) change is and the world population change since OAD. Understanding of why population has changed and how it has changed overtime. How the world’s population is distributed. What population density is and how this varies at the global and national scale. How to interpret world population distribution and density maps Case Studies World population change and distribution UK population distribution Population density and change in Brazil Need to Know What the demographic transition model is and how countries change as they move through this model. Why countries change as they move through this and the possible reasons i.e. health care, education, contraception ect. How life expectancy can be increased and infant mortality decreased. How and why fertility rates change (roles of women in society, aspirations ect...) Case Studies Stage 2: Burkina Faso, Liberia, Somalia. Stage 3: Zimbabwe, Gabon, Namibia. Stage 4: Finland, France, Malta. Stage 5: Germany, Italy, Hungary. (Be sure to know what a population pyramid at each stage might look like) Need to Know The main types and characteristics of migration i.e. permanent, temporary, forced, voluntary, international, national. The main impacts of migration for both receiving and exporting locations for example strain on health care or lack of economically active in exporting locations. Case Studies Afghanistan and Zimbabwe – migrants leaving due to internal unrest. Polish to the UK – For work (economic migrants) Migrants from Mexico into California Need to know The difference between an asylum seeker and refugee. Impacts for both locations both positive and negative. Rights of Asylum seekers and refugees 1.5 What are the causes and impacts of changing gender structures? 1.6 What are the demographic challenges facing countries? • Housing. • Repatriation. • The attitudes and values of immigrants and hosts. • Human rights. • Changing gender structures in populations as countries pass through the demographic transition. • Social, economic and political impacts of gender structures. • The demographic causes and effects of ageing societies including issues such as dependency, workforce and pensions. • The issues of high birth rates and high mortality rates – including AIDS. • Policies to alleviate the ‘demographic challenges’ Case Studies Afghanistan migrants Iraq refugees following invasion Need to know How to interpret a population pyramid and explain why it is the shape it is. How gender inequality within a country can affect it. How passing through the demographic transition model can lead to a change in gender structures. The social (people), economic (monetary) and political impacts that having more females or males can have on places. Case Studies Mexico / California and the impact that it can have for the people in the rural areas of Mexico with a loss of men. For California the impact that it can have on jobs and strains on health care and social housing. Afghanistan and Iraq and how rebuilding the countries economy may be a problem. Need to know The impacts of an ageing population (economically dependents). Think about how countries with a pay as you go system may struggle in economic downturns. What AIDS and HIV are and the problems that are faced by countries with high levels of HIV infection on the development of the country. Population policies used to help stop population growth (China) and help population growth (France). Case studies AIDS – Sub Saharan Africa (SWAZILAND where 40% of population are infected) Ageing population – Japan and USA Population policies – China and its one child policy and France with benefits for having 3 children per family.