Acids, Bases and Salts
advertisement
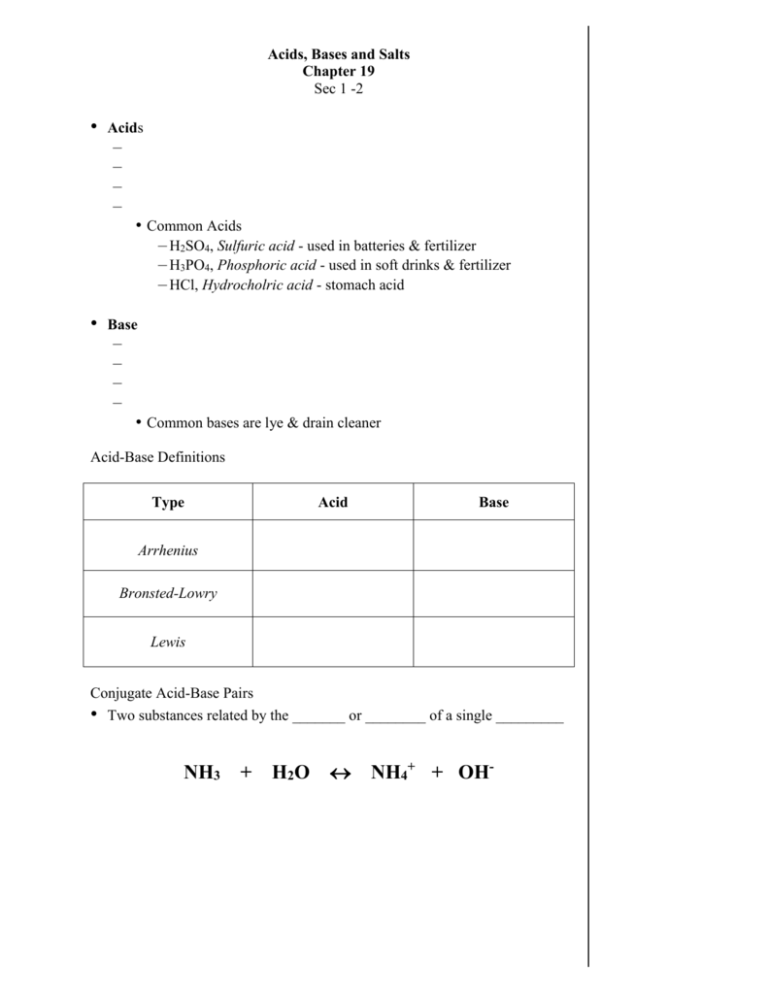
Acids, Bases and Salts Chapter 19 Sec 1 -2 • Acids – – – – • Common Acids – H2SO4, Sulfuric acid - used in batteries & fertilizer – H3PO4, Phosphoric acid - used in soft drinks & fertilizer – HCl, Hydrocholric acid - stomach acid • Base – – – – • Common bases are lye & drain cleaner Acid-Base Definitions Type Acid Base Arrhenius Bronsted-Lowry Lewis Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs • Two substances related by the _______ or ________ of a single _________ NH3 + H2 O NH4+ + OH- Naming Acids • Use the template below to name acids: Example Acid Anion ending Example Examples: • Name the following acids – HBr – HNO2 • – H2SO4 Write the formula for the following acids – Hydrofluoric acid – Phosphorous acid pH and pOH • The conc. of H+ and OH- ions determines the pH (or) pOH of a solution • • • In aq. solutions, Note: pH = If and pH = pH < pH > Examples: • Find the pH of . . . • [H+] = 1.0 x 10-4 M • [H+] = 1.0 x 10-8 M • [H+] = 2.0 x 10-7 M • • [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-6 M [OH-] = 4.5 x 10-11 M pOH = Example: • • • What is the [H+] of a solution if the pH = 4.98? – Use the inverse log button, 10x or yx key – Plug in the negative value of pH [H+] = or + [H ] = pH is logarithmic pH=3 is ten times more acidic than a pH=4 – A little change in pH is a BIG change in concentration. If the concentration of H+ is… 0.000 000 1 M = 1 x 10-7 M – The pH is 7 0.001 M = 1 x 10-3 M – The pH is 3 • • Water is unique b/c… – Sometimes it _____________ a H+ ion, ________ – Sometimes it _____________ a H+ ion, ________ Water can act both as an acid and base, which is defined as amphoteric Acid-Base Indicators • – Examples • •