Brain days-Part I
advertisement

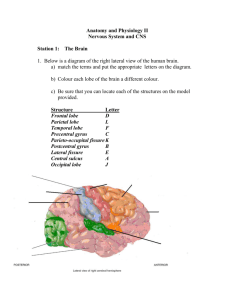
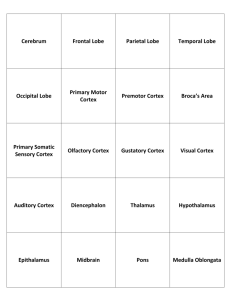
5th Floor Anatomical Drawing Class Room # 937-939 Introduction 16:30-17:15 Telencephalon The rest of the brain 14:00-14:45 16:30-17:15 Limbic System 14:00-14:45 Circuits & functional neuroanatomy 16:30-17:15 Brain Days Kaan Yücel M.D.,Ph.D. Learning Objectives Explain the neuron types and the concepts of axon and dendirite Explain the concepts of “cortex”, “grey matter” and “white matter” Explain the parts of the brain 1. What is inside the skull? Meninges CSF Neuron Cortex Neuroglia Grey matter Axons White matter Tracts Hemispheres Lobes Sulcus & gyrus Arteries & Veins 2. Neuron 100 billion neurons in the brain share a number of common features: Cell body metabolic center of the neuron Dendrites receives connections from other neurons. Axon transmits information to other neurons Presynaptic terminals 2. Neuron Synapse terminal region of the axon where one neuron forms a connection with another and conveys information through the process of synaptic transmission. To communicate with the postsynaptic cell, the presynaptic neuron needs to release a chemical messenger. Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine Memory Adrenaline Dopamine Reward, addiction Histamine Noradrenaline Serotonin Mood 3. Neuroglia Non-neuronal supporting cells Macroglia Microglia Ependymal cells 4. Cortex - Grey matter Grey matter Nerve cells bodies grouped into large aggregates Two types of arrangement 1) Arranged in sheaths as in the cerebral cortex 2) A smaller collection of nerve cell bodies: nucleus 5. White matter - Tracts Processes of neurons Many axons are in a myelin sheathlooks white Fasciculi Axons collected into small bundles Tracts Certain larger fiber bundles Funiculi Large bundles 6. White matter types Association fibres Cingulum Fasciculus longitudinales superior & inferior Fasciculus uncinatus (Uncinate fasciculus) Commissural fibers L Corpus Callosum Commissura anterior R Projection fibers Corona radiata Capsula interna Wakana S, Jiang H, Nagae-Poetscher LM, van Zijl PC, Mori S. Fiber tract-based atlas of human white matter anatomy. Radiology. 2004;230:77-87. 7. Gyrus & Sulcus & Fissure Primary sulci Secondary sulci Tertiary sulci Typically continuous sulci •Interhemispheric fissure (Longitudinal cerebral fissure) •Sylvian fissure (Lateral fissure) •Parieto-occipital fissure •Collateral sulcus •Central sulcus •Calcarine Sulcus 7. Gyrus & Sulcus & Fissure SULCI-depressionsDIVIDE THE BRAIN INTO GYRI -elevationsLOBES are MADE UP BY GYRI 8. Parts of the brain Two hemispheres Interhemispheric fissure -Longitudinal cerebral fissureFalx cerebri Corpus callosum 8. Parts of the brain FOREBRAIN HINDBRAIN Cerebellum+Pons MIDBRAIN PONS MEDULLA OBLONGATA Anterior border Frontal pole Posterior border Central sulcus Inferior border Slyvian [lateral] fissure Anterior 1/3 of the cerebral cortex Anterior border Central sulcus Posterior border Parieto-occipital sulcus Inferior border Slyvian [lateral] fissure Anterior border Temporal pole Posterior border An imaginary line passing through the parietooccipital sulcus from the pre-occipital notch Superior border Slyvian [lateral] fissure Anterior border Parieto-occipital sulcus Posterior border Occipital pole FRONTAL LOBE Primary motor area Broca’s area –speech productionHigher cognitive functioning «executive functions» Problem solving, decision making, abstract thinking, reasoning, working memory, etc. TEMPORAL LOBE PARIETAL LOBE Primary auidotory cortex Wernicke’s area- comphrensionMemory Mood regulation Emotinal memory OCCIPITAL LOBE Primary sensory areas Somatosensory function Visual cortex Midbrain 9. Meninges Dura mater (dura): tough, thick external fibrous layer Arachnoid mater (arachnoid): thin intermediate layer Pia mater (pia): delicate internal vasculated layer Dural sections 10. CSF [Cerebrospinal fluid] Lateral ventricles Third ventricle Fourth ventricle Kaan’s first seminar @ PhD: Telencephalon [in Turkish]