F) matching cards for the nervous system
advertisement

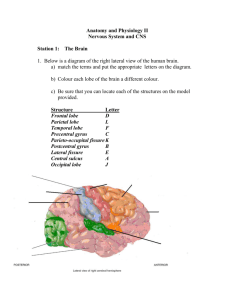
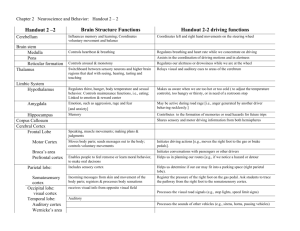
Cerebrum Frontal Lobe Parietal Lobe Temporal Lobe Occipital Lobe Primary Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex Broca’s Area Primary Somatic Sensory Cortex Olfactory Cortex Gustatory Cortex Visual Cortex Auditory Cortex Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus Epithalamus Midbrain Pons Medulla Oblongata Cerebellum Nuclei Tract Corpus Collusum Sulci (Sulcus) Gyri (gyrus) Fissure Wernicke’s Area Brain Stem Longitudinal Fissure Transverse Fissure Central Sulcus Parieto-occipital sulcus Lateral Sulcus Precentral gyrus Postcentral Gyrus Pineal gland Choroid plexus Higher intellectual reasoning, complex memories, language comprehension, primary motor cortex and premotor cortex Primary somatic sensory cortex processes sensory information such as pressure, touch, and pain Primary auditory cortex interprets sounds and primary olfactory cortex interprets smells Primary visual cortex receives visual stimuli and information Allows us to consciously move our skeletal muscles Allows us to control learned motor skills of a patterned nature Special motor speech area that directs muscles involved in speech planning and production Receives information from the cutaneous receptors in the skin and the proprioceptors in the muscles Receives impulses from the olfactory receptors in the nose Receives impulses from the taste receptors Receives impulses from the photoreceptors of the eye Dominant brain structure, composed of two hemispheres and responsible for voluntary and conscious activities Receives impulses from the auditory receptors of the ears Located in the brain’s central area and composed of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus Relay stations for sensory impulses passing upward to the sensory cortex; filters out unnecessary sensory information Controls the autonomic nervous system, the body temperature, thirst, hunger, emotional response, sleep-wake cycles, and the pituitary gland Contains the pineal gland and choroid plexus Startle, visual and auditory reflexes Fibers connect the brain to the spinal cord and control the normal rate of breathing Automatic reflex centers for the heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, swallowing, and vomiting Provides precise timing for skeletal muscle activity, regulates equilibrium and balance, and produces smooth and coordinated skilled skeletal muscle movements Cluster of cell bodies and dendrites located in the brain and spinal cord Cluster of myelinated axons in the brain and spinal cord The tract that connects the two cerebral hemispheres Shallow grooves of tissue Elevated ridges of tissues Deeper grooves of tissue Recognizes spoken words, translates words into thoughts and helps us sound out strange or new words Located between the spinal cord and the cerebrum; composed of the midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata; provides a pathway for tracts, and produces behaviors for survival Separates the cerebral hemispheres in the middle Separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum Separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe Separates the occipital lobe from the parietal lobe Separates the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobe Elevation located just anterior to the central sulcus Elevation located just posterior to the central sulcus Makes the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Secretes melatonin