White Plains High School Anatomy & Physiology I Guided Notes
advertisement

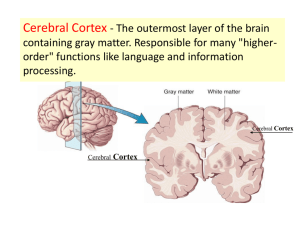
White Plains High School Anatomy & Physiology I Guided Notes: The Brain:Cerebrum 1. Where is the cerebrum located? What are its three major areas? 2. What is the cortex composed of? What is the purpose of the folds? 3. Compare and contrast the gyri and sulci. 4. What is lissencephaly? 5. What are three functional areas of the cerebrum? 6. What is meant by lateralization? 7. Examine the picture of Einstein and Picasso, how do they illustrate lateralization? 8. What is the Precentral Gyrus? Indicate it on the diagram below. 9. Explain why the homunculus appears the way it does? 10. Texting or riding a bike would be controlled in what area of the brain. 11. Describe the location and function of Broca’s area. What condition results when a stroke occurs in this area? 12. Compare the four types of aphasia. 13. What is the sense of proprioception? 14. What are the three multimodal areas and what is their function? 15. Compare and contrast the anterior and posterior association areas. 16. How does the Case of Phineas Gage illustrate the function of the association areas? 17. Why would olfaction be associated with the limbic area? 18. What is the primary function of the cerebral white matter? What cell type is responsible for producing the myelin in the CNS? 19. Compare association fibers with association fibers and projection fibers. 20. What are the functions of the basal nuclei? 21. Label the caudate, putamen and, caudate nucleus globus pallidus on the diagram below. 22. What are some common disorders of the basal nucleus? Let’s Practice! 1) Which of the following best describes the cerebrum? A) motor command center B) visceral command center C) executive suite D) decussation center 2) A shallow groove on the surface of the cortex is called a ________. A) sulcus B) fissure C) gyrus D) furrow 3) Which of the following generalizations does not describe the cerebral cortex? A) The cerebral cortex contains three kinds of functional areas. B) Each hemisphere is chiefly concerned with sensory and motor functions of the contralateral side of the body. C) The hemispheres are exactly equal in function. D) No functional area of the cortex works alone. 4) Ridges of tissue on the surface of the cerebral hemispheres are called ________. A) gyri B) sulci C) fissures D) ganglia 5) The frontal lobe is separated from the temporal lobe by the ________. A) longitudinal fissure B) lateral sulcus C) central sulcus D) cranial fossa 6) Broca's area ________. A) corresponds to Brodmann's area 8 B) is usually found in the right hemisphere C) serves the recognition of complex objects D) is considered a motor speech area 7) Which part of the cerebral cortex is involved in intellect, cognition, recall, and personality? A) prefrontal cortex B) posterior association area C) limbic association area D) combined primary somatosensory cortex and somatosensory association cortex 8) Which of the following is not part of the basal nuclei? A) putamen B) lentiform nucleus C) globus pallidus D) substantia nigra 9) Which association regarding the function and location of the cerebrum is most accurate? A) sensory-anterior B) motor-medial C) sensory-medial D) motor-anterior