File
advertisement

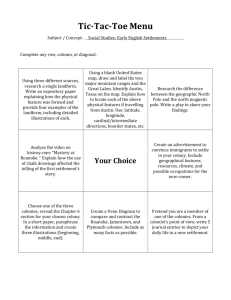
Good Morning! Please pick up a handout from the front desk. 1. List the Southern Colonies Chapters 2 & 3 The 3 G’s of Exploration: God – spread Christianity Gold – and other resources like silver & spices; also wealth & new markets for goods Glory – adventure, fame, and power Explorers & settlers from… ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ England Denmark The Netherlands France Portugal Russia Spain Think about it: Which groups settled in what is today the United States? What does that mean? ◦ charter – certificate of permission ◦ joint-stock company – business plan founded & run by a group of people who invest in the plan & share any money made (or lost) Delaware’s original royal charter Two Main Types of Colonies: ◦ Royal – under the direct control of the Crown (monarch of England) ◦ Proprietary – belonged to wealthy individuals or companies 1st English colony: Roanoke ◦ Sir Walter Raleigh ◦ island in Virginia (today NC coast) ◦ twice settled & failed ◦ Why? ships had trouble landing sandy, infertile soil http://www.history.com/news/askhistory/what-happened-to-the-lost-colonyof-roanoke Date founded: 1607 (1st proprietary, 1624 royal) Founder/Group: Virginia Company Reasons for Settlement: gain wealth for England and help with England’s population growth Significant Facts: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Jamestown (1607) Powhatan & Indian lands John Smith John Rolfe & Pocahontas tobacco cultivation House of Burgesses (1619) Bacon’s Rebellion (1676) John Smith took control, forced colonists to farm, & negotiated with nearby Powhatan Indians “He who will not work, will not eat” Read document and answer the questions included in the reading. Welcome! Please place your American Dream project in the blue chair in the front of the room. Please take out your Jamestown packet from yesterday and continue working on the assignment. What was life like in Jamestown. http://www.history.com/topics/jamestown Searching after the American Dream Disease Stake in the land Tobacco Cultivation Free Land especially Malaria from mosquitoes in swamps Hunger colonists too weakened by disease to farm War colonists owned and worked their own land led by John Rolfe, wealth for England with Indians under Powhatan’s leadership got 50 acres if your paid for your passage (or someone else’s) Reasons for Struggle Reasons for Success/Growth Think about it… What was the purpose of the House of Burgesses? representative body – people could make laws Who could participate in it? male landowners over 17 years What powers did it have? make laws and make taxes What legacy/trend did it start? colonists making decisions for themselves Social Hierarchy in the Chesapeake The owners of tobacco plantations Small farmers were the Tobacco was the basis largest class; Cameof as of wealth & cause indentured servants; social inequalities most were very poor Indentured servants were often mistreated African slaves Forced onto less fertile lands in interior b/c of population growth War w/ Indians Gov. William Berkeley taxed heavily & gave money to wealthy Causes Berkeley would not let settlers attack all Indians Settlers led by Nathaniel Bacon rebelled (1676) – burned Jamestown Bacon died & rebellion ended Events Significance: showed poorer farmers would not put up w/ a gov’t that only helped wealthy Date founded: 1632 (proprietary colony) Founder/Group: Lord Baltimore Reasons for Settlement: create a refuge (safe place) for Catholics who were discriminated against Significant Facts: ◦ More Protestants settled here Date founded: 1732 (proprietary colony) Founder/Group: James Oglethorpe Reasons for Settlement: create a buffer to protect S. Carolina against Spanish Florida Significant Facts: ◦ Last of the 13 colonies ◦ Set up as a haven for English debtors Because of Oglethorpe’s strict rules, it became royal colony in 1752 Colony Chart Activity (part 2): ◦ Read pages 50-52 ◦ Complete your chart for ONLY the following colonies: Massachusetts (2 settlements) Rhode Island New England Colonies 1. 2. 3. 4. New Hampshire Massachusetts Connecticut Rhode Island Massachusetts Date founded: 1620 Founder/Group: Pilgrims – William Bradford Reason for Settlement: religious freedom Significant Facts: ◦ Mayflower Compact 1620 – doc. that established self-government Plymouth Date founded: 1630 Founder/Group: Puritans – John Winthrop Reason for Settlement: religious freedom, create an ideal society Significant Facts: ◦ Elected own governor – only ones that did so Massachusetts Bay 67% 33% 100% 100% 67% 3 2 1 0 A* B* C Town D E Meetings Complete the reading Select one to two main points from the reading and share with a partner. As a group select the main point of the reading and share with the class. Created by 1662 by New England Puritans Form of partial church membership for children and grandchildren of full members Goal: keep current members & attract new ones Without looking at your notes or map, see if you can identify the following colonies. 4. 3. 2. 1. Date founded: 1636 Founder/Group: Roger Williams Reasons for Settlement: create a refuge for radical Puritans (religious dissenters) Significant Facts: ◦ Kicked out of Mass. Bay: Williams – pay Indians for land Anne Hutchinson – argued Mass. had not done enough to break from Anglican ways ◦ Separation of church & state Salem, Massachusetts major Indian rebellion 1692 1675 Authorities tried, convicted, & executed 19 suspected witches Ended when prominent citizens were accused Salem Witch Trials Indian chief Metacom (known as “King Phillip) blamed, but multiple tribes fought Indians defeated & lost most of remaining land King Phillip’s War Town Hall Meetings-conducted by local tax-paying citizens (males w/ property) to decide issues Massachusetts Legislature established by local towns to provide local leadership (not just the Crown) 1684 - Mass. lost its charter & a new legislature established Mass. became a royal colony in 1691 Colony Chart Activity (part 3): ◦ Read pages 55-59 ◦ Complete your chart for ONLY the following colonies: New York Pennsylvania ◦ Work on this part INDIVIDUALLY Middle Colonies 1. 2. 3. 4. New York Pennsylvania New Jersey Delaware Date founded: 1625, taken by English in 1664 Founder/Group: Dutch Reasons for Settlement: guard the mouth of the Hudson River to protect fur trade; English wanted it to control trade Significant Facts: ◦ Dutch settlement – New Amsterdam later became city of New York ◦ Tolerated other religious groups ◦ Drew diverse group of colonists Date founded: 1682 Founder/Group: William Penn Reasons for Settlement: debt paid to Penn by King Charles II of England; created to be a safe haven for Quakers Significant Facts: ◦ Quakers – followed “Inner Light” to understand Bible, men & women spiritually equal, pacifists, tolerated other faiths ◦ Peace w/ local Indians New England • small family farms (livestock & grew crops for own use, not trade) • exported lumber & fish • built ships • trade • manufacturing • major ports: Boston Middle Colonies Southern Colonies • small family farms • farming – most (exporting wheat profitable region, profitable) grew tobacco, • built ships rice, indigo • trade (cotton by 1790s) • manufacturing • major ports: (glass & iron) Charleston • major ports: Philadelphia New York New England Middle Colonies Southern Colonies • few African Americans • middle class families who could pay for trip • towns supported schools = more people literate • greater economic equality • a few colleges • few African Americans • came as families • mix of towns and small & large farms • most ethnically & culturally diverse • a few colleges • African American majority in areas • poor, young, single men – indentured servants • plantation economy, slavery • population spread far, few schools, higher illiteracy • econ. inequality Now that you have completed the colonial comparison chart, turn your sheet over and complete the Venn Diagram using the information from the chart. a. b. c. d. Why did the Puritans and Quakers create their own new settlements? Better soil for farming More space between neighboring colonists Religious freedom and tolerance Better opportunities for trade Furniture Weapons Exotic furs Tools Clothing Processed food Jewelry Books Paper Spices for cooking Tea Government: salutary neglect – allowed colonies local self-rule Economic: mercantilism – policy where a nation (mother country) gained wealth by exporting more manufactured goods than it imported; goal: get gold & silver through trade Good Morning. Please pick up a sheet of paper from the front desk. On the paper: ◦ Define mercantilism ◦ What impact did this have on the colonies? (without looking at your notes!!!) Three-part voyage called triangular trade Middle Passage – forced transport of enslaved Africans from W. Africa to Americas; cramped ships, suffered inhumane treatment = 10% died (pages 68-69) Cause: Southern Colonies needed plantation workers First used indentured servants European immigration declined by 1660s First treated like indentured servants – given freedom By mid-1600s laws to support permanent enslavement In North, worked in cities & could earn money to pay for freedom Many didn’t share a culture (language or religion) Blended African traditions to create new culture Most adopted Christianity blended w/ some African traditions What would happen if the colonies united? What would happen if England could produce natural resources? What would happen if England allowed the colonies to trade with other countries? What would happen if there were no Middle colonies? What would happen is the foundations of religion that were established in the New England colonies spread to the Southern Colonies? Enlightenment (1600s & 1700s) – thinkers believed that all problems could be solved using human reason; challenged old ways Significance for Colonies: Inspired Benjamin Franklin scientist (invented lightning rod & bifocal glasses), political statesmen, printer, and writer of American literature (Poor Richard’s Almanac) Represented social mobility & colonial spirit of individualism Great Awakening (mid 1700s) – religious movement that featured passionate preaching from evangelical leaders Preachers: Jonathan Edwards – “Sinners in the Hand of an Angry God” George Whitefield Significance: encouraged colonists to think for themselves on religious matters; extended to ideas about gov’t George Whitefield WHAT? Virginia’s development (Jamestown) House of Burgesses Bacon’s Rebellion half-way covenant French settlement of Quebec. SSUSH1 The student will describe European settlement in North America during the 17th century. a. Explain Virginia’s development; include the Virginia Company, tobacco cultivation, relationships with Native Americans such as Powhatan, development of the House of Burgesses, Bacon’s Rebellion, and the development of slavery. b. Describe the settlement of New England; include religious reasons, relations with Native Americans (e.g., King Phillip’s War), the establishment of town meetings and development of a legislature, religious tensions that led to the founding of Rhode Island, the half-way covenant, Salem Witch Trials, and the loss of the Massachusetts charter and the transition to a royal colony. c. Explain the development of the mid-Atlantic colonies; include the Dutch settlement of New Amsterdam and subsequent English takeover, and the settlement of Pennsylvania. d. Explain the reasons for French settlement of Quebec. e. Analyze the impact of location and place on colonial settlement, transportation, and economic development; include the southern, middle, and New England colonies.