Genetics
advertisement

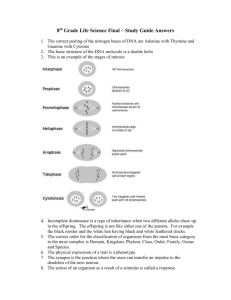
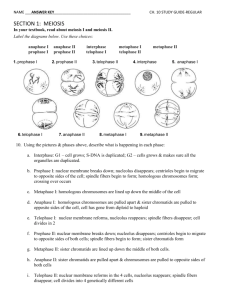
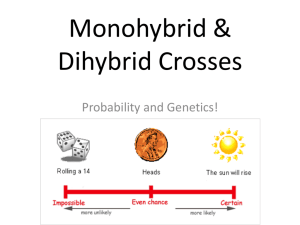
GENETICS Ch. 11 Gregor Mendel Genetics is the study of heredity. Gregor Mendel (1860’s) discovered the fundamental principles of genetics by breeding garden peas. 2. Mendel crosspollinated pea plants He cut away the male parts of one flower, then dusted it with pollen from another 3. What did Mendel conclude? He concluded that factors are passed from one generation to the next. eye color locus b = blue eyes eye color locus B = brown eyes 4. The Principle of Dominance The Principle of Dominance – some alleles are dominant and other are recessive. Paternal Maternal Alleles 1. Alternative forms of genes. 2. Units that determine heritable traits. 5. Dominant and Recessive alleles Dominant alleles – upper-case a. homozygous dominant (BB – Brown eyes) Recessive alleles – lower case a. homozygous recessive (bb – blue eyes) b. Heterozygous (Bb – Brown eyes) Phenotype vs. Genotype Outward appearance Physical characteristics Examples: 1.Brown eyes 2.blue eyes Arrangement of genes that produces the phenotype Example: 1. TT, Tt 2. tt 6. Segregation Alleles separate during meiosis 7. Recessive traits show th up about 1/4 of the time. Because there is only a 25% chance that two recessive alleles will be paired together. 9. Punnett square A Punnett square is used to show the possible combinations of gametes. Monohybrid Cross Monohybrid Cross Example: Cross between two heterozygotes for brown eyes (Bb) BB = brown eyes Bb = brown eyes bb = blue eyes B b B Bb x Bb b female gametes male gametes Monohybrid Cross B b B BB Bb b Bb bb Bb x Bb 1/4 = BB - brown eyed 1/2 = Bb - brown eyed 1/4 = bb - blue eyed 1:2:1 genotype 3:1 phenotype Dihybrid Cross Dihybrid Cross RY RY Ry rY ry Ry rY ry Dihybrid Cross RY RY RRYY Ry RRYy Ry RRYy RRyy rY RrYY RrYy ry RrYy Round/Yellow: 9 Round/green: 3 Rryy wrinkled/Yellow: 3 rY RrYY RrYy rrYY rrYy wrinkled/green: ry Rryy rrYy rryy 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio RrYy 1 Dihybrid Cross Example: R r Y y = round = wrinkled = yellow = green cross between round and yellow heterozygous pea seeds. RrYy x RrYy RY Ry rY ry x RY Ry rY ry possible gametes produced 10. Independent Assortment Chromosomes separate independently of eachother Bb B Ff This means all gametes will be different! B B F b f sperm B Bb Bb Ff B Bb diploid (2n) f b b Ff B b meiosis I meiosis II F haploid (n) Independent Assortment Genes for different traits can segretate independently during the formation of gametes without influencing eachother Question: How many gametes will be produced for the following allele arrangements? Remember: 1. 2. 3. 2n (n = # of heterozygotes) RrYy AaBbCCDd MmNnOoPPQQRrssTtQq Answer: 1. RrYy: 2n = 22 = 4 gametes RY Ry rY ry 2. AaBbCCDd: 2n = 23 = 8 gametes ABCD ABCd AbCD AbCd aBCD aBCd abCD abCD 3. MmNnOoPPQQRrssTtQq: 2n = 26 = 64 gametes 11. Incomplete Dominance One allele is not completely dominant over another R R r Rr Rr produces the F1 generation r Rr Rr All Rr = pink (heterozygous pink) 11. Codominance Both alleles are expressed Example: blood 1. type A 2. type B 3. 4. type AB type O Black cow + white cow = spotted cow = IAIA or IAi = IBIB or IBi = IAIB = ii 12. Which shows more genetic variation. (more combos?) Male CC with female Cc C Male cc with female Cc C c C C c c c Genetic Engineering Gene Therapy Is cloning a possibility? Is it right to use cloning to create an entirely new human being? Is it ethical to create an embryonic copy of John Doe to supply cells to keep John alive? Does a multicellular ball of tissue -- an embryo -- have the same rights and status as a human being? How does Mendel’s principles apply to organisms The basic principals can be applied to humans as well as any other living organism. And now it’s time for…. Spongebob Genetics!!!!!