Periodic Trends
advertisement

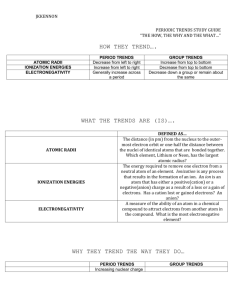
PERIODIC TRENDS!! VALENCE ELECTRONS Valence electrons: Electrons in the highest energy level These electrons are the ones that bond!! The group A # matches how many valence electrons VALENCE ELECTRONS Group # # of valence electrons 1 or 1A 1 2 or 2A 2 13 or 3A 3 14 or 4A 4 15 or 5A 5 16 or 6A 6 17 or 7A 7 18 or 8A 8 Group 13-18. # of valence electrons equal to group number - 10 YOU CAN PREDICT THE CHARGE OF THE IONS Octet rule: atoms will gain or lose electrons to have a full energy level (8 electrons) Period number responds to how many energy levels an atom has PREDICTING CHARGES OF IONS ION SIZE TRENDS ION: an atom that lost or gained electrons Cation: metal atom that loses e- (+) Anion: nonmetal atom that gain e- (-) ALL CATS HAVE PAWS (AND ARE MEAN) (cation is positive: metals) PERIODIC TRENDS There are 4 trends of the periodic table you will need to know Ionic Size Atomic Size Electronegativity Ionization Energy Need to know how AND why they trend the way they do. 1. IONIC SIZE TRENDS Cations are smaller than their neutral atoms Because they lost an electron and energy level Anions are larger than their neutral atoms Because another) they gain electrons (which repulse one IONIC SIZE EXAMPLE Ex 1: Which is larger? Mg or Mg2+ Ans: Ex Mg 2: Which is larger? S or S2- Ans: S2- 2. ATOMIC SIZE The size of the atom 2. ATOMIC SIZE Atomic size increases as you move: from right to left in a period from top to bottom in a group Francium has the largest size Fr ATOMIC SIZE REASON Going from Left to Right Gets smaller because you add more protons to nucleus and then pull in the electrons Going Down Gets larger because you add energies ATOMIC SIZE EXAMPLE Ex. 1: Arrange the following elements in order of their decreasing size. P(15), Ans: Mg(12), S(16) Mg,P, S 3. ELECTRONEGATIVITY TRENDS Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract electrons from another atom ELECTRONEGATIVITY TRENDS Electronegativity increases as you move: from left to right across a period from bottom to top in a group Fluorine (9) is the most electronegative element F ELECTRONEGATIVITY REASON Electronegativity is opposite of atomic size, because the smaller the atom…the more electrons are attracted to the nucleus TRENDS IN ELECTRONEGATIVITY Why are the noble gases not on here??! ELECTRONEGATIVITY EXAMPLE Arrange the following in order of their increasing electronegativity. Rb(37), I(53), Sn(50) Ans: Rb, Sn, I 4. IONIZATION ENERGY TRENDS The ionization energy is the energy needed to remove an electron from a gaseous atom. The higher ionization energy, the harder it is to pull off electrons IONIZATION ENERGY TRENDS Ionization energy increases as you move: from left to right across a period from bottom to top in a group Helium (2) has the highest ionization energy He IONIZATION ENERGY Reason: The smaller the atom, the closer electrons are to nucleus so higher the ionization energy IONIZATION ENERGY EXAMPLE Arrange the following in order of increasing ionization energy. He(2), Ans: Xe(54), Ar(18) Xe, Ar, He PERIODIC TRENDS SUMMARY METAL REACTIVITY TRENDS Metal reactivity increases as you move: right to left across a period top to bottom in a group Francium (87) is the most reactive metal Fr NON-METAL REACTIVITY TRENDS Non-metal reactivity increases as you move: left to right across a period bottom to top in a group Fluorine (9) is the most reactive non-metal F REACTIVITY EXAMPLES Ex. 1: Which is more reactive? Fe(26) Ans: Ex. or Co(27) Fe 2: Which is less reactive? Cl(17) Ans: or F(9) Cl