PRACTICE 3 METHODS OF CHARGING OBJECTS
advertisement
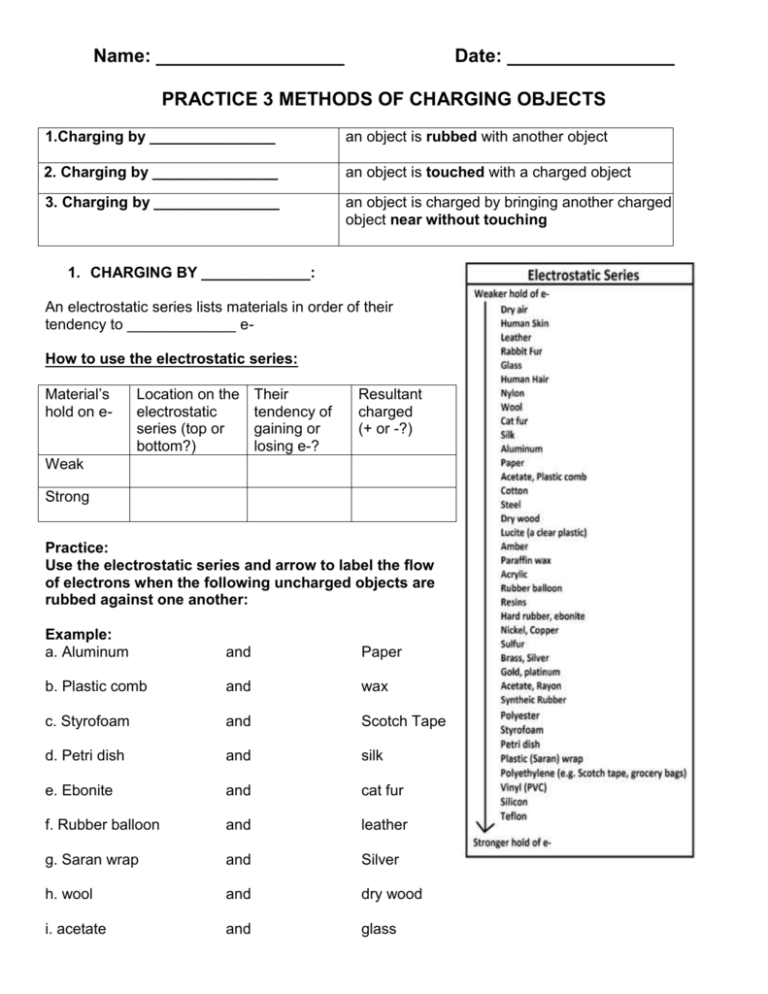
Name: __________________ Date: ________________ PRACTICE 3 METHODS OF CHARGING OBJECTS 1.Charging by _______________ 2. 2. Charging by _______________ 3. Charging by _______________ an object is rubbed with another object an object is touched with a charged object an object is charged by bringing another charged object near without touching 1. CHARGING BY _____________: An electrostatic series lists materials in order of their tendency to _____________ eHow to use the electrostatic series: Material’s hold on e- Location on the electrostatic series (top or bottom?) Their tendency of gaining or losing e-? Resultant charged (+ or -?) Weak Strong Practice: Use the electrostatic series and arrow to label the flow of electrons when the following uncharged objects are rubbed against one another: Example: a. Aluminum and Paper b. Plastic comb and wax c. Styrofoam and Scotch Tape d. Petri dish and silk e. Ebonite and cat fur f. Rubber balloon and leather g. Saran wrap and Silver h. wool and dry wood i. acetate and glass 2. CHARGING BY CONTACT (I.E. CONDUCTION) Two scenarios Before touching Upon touching After touching When a negativelycharged touches a neutral object Both objects are _________ _____________ after touching When a positivelycharged touches a neutral object Both objects are _________ _____________ after touching Conclusion: The neutral object always ends up having the _______ type of charge as the charging object 3. CHARGING BY INDUCTION Describing what happens here as a negatively charge balloon is brought near but not touching the neutral pop can: How to permanent charge a neutral object by induction? In 4 steps: Step 1: Bring the charged object near, but not _______________ the neutral object Step 2: Ground the neutral object Step 3: Remove the ground connection Step 4: Withdraw the charging object To charge an object permanently by induction, it needs to be _______________. Grounding is a process of _______________ charges from an object by contact with large, neutral object (such as the Earth) Notice: The initially neutral sphere now carries ________________________________________to that of the charging object Try it on your own: Now you can draw diagram show how to permanently charge an object by induction with a positively-charged rod. Ms. Pham’s initial HERE ________________ Conclusion: The general rule is that the initially neutral sphere now carries ________________________________________________to that of the charging object when charged by induction APPLICATIONS OF STATIC ELECTRICITY 1. LIGHTNING: Method of charging: _______________ - swirling winds in a storm cloud cause water and ice particles to become charged - Positive charges move to the top of the cloud - Negative charges move to the bottom of the cloud - The ground below is induced by the cloud to develop a positive charge. - When the difference in charge between the cloud and Earth becomes great enough, a path forms and a surge of electrons travel along this path producing a giant flash called lightning. Lightning rod: - a pointed metal rod attached to the roof of a building. See picture beside. - is used to carry the harmful electrical current away from buildings and safely to the ground when lightning strikes. - A person is likely to be struck by lightning in an open field, under a tree Safe places to hide from lightning: House Car (rubber tires) Unsafe places to hide from lightning: Open field Under a tree On a boat Videos: Airplane struck by lightning: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hZCzintiS4c Safety first at gas station: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tuZxFL9cGkI 2. Static-cling decals: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hKP3pwNLcb8 3. Static spray: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nQWYP9ucyqk 4. Photocopier https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MJ5ghlTdF9k 5. Anti-static sheets Clothes are made of different materials like cotton, wool and nylon. When the clothes are put in a dryer, the materials tumble around and rub against each other. When the clothes are removed, they often stick to each other. This is known as static cling. To prevent static cling, an anti-static sheet (e.g. Bounce or Downy) is placed in the dryer with the clothes. The sheet contains a waxy compound that vaporizes when the dryers heats up with hot air. The waxy compound then coats all the clothing. 1. Explain why static cling happens by referring to the electrostatic series and electrons. 2. Explain how the anti-static sheet is able to prevent static cling. How does the waxy coating affect the materials on the electrostatic series? More Practice Charging by Contact:




