Egypt Presentation 2015-2016
advertisement

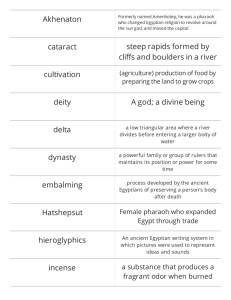
Overview • Ancient Egyptian civilization lasted from about 3100 B.C. to about 525 B.C. or just over 2500 years. • During that time, there were at least 20 different dynasties with many different rulers. • Historians divide the long history into 3 different periods. Periods of Ancient Egyptian History Pre-dynastic Egypt (4000 B.C. – 3100 B.C.) Old Kingdom (3100 B.C. – 2600 B.C.) First Intermediate Period (2600 B.C. – 2000 B.C.) Middle Kingdom (2000 B.C. – 1786 B.C.) Second Intermediate Period (1786 B.C. – 1539 B.C.) New Kingdom (1539 B.C. – 1085 B.C.) Third Intermediate Period (1085 B.C. – 525 B.C.) Persian Rule (525 B.C. – 332 B.C.) Greek Rule (332 B.C. – 50 B.C.) Roman Rule (50 B.C. to 700 A.D.) Islamic Rule (700 A.D. – 1500 A.D.) 3 Map Activity • Place this on page 57 of ISN. Label the following: – Lower Egypt – Upper Egypt – Western Sahara Desert – Eastern Sahara Desert – Nile Delta Ancient Egypt • Place on page 58 of ISN. • Follow the PowerPoint to add information under the tabs Geography of Egypt • Physical Features: – Settled along the fertile Nile River – Every year, the river flooded bringing up a mineral called silt that made the land fertile. – Around it was the Sahara Desert – This offered protection from invaders – To the north, the Nile River emptied into the Mediterranean Sea. Geography of Egypt • Water Features: – Nile River was lifeblood of ancient Egyptian life. – Irrigation for crops, silt for fertile land, water for cooking, bathing, transportation and trade . – It flows North to Mediterranean Sea How did geography affect the lives of Egyptians? • Glue on page 58 of ISN under the physical/water features. Follow the PowerPoint to add information under the tabs Floods & Farming Floods: • Egyptians discovered that the Nile River had predictable floods. • As the river flooded it covered the banks of the river with silt. • This made the land very fertile for crops. Farming: • They used their knowledge of floods to plan their planting and harvesting seasons. • They planted wheat and barley. • Irrigated crops using canals and used plows and rakes that they borrowed from Mesopotamians. Ancient Egypt’s Social Hierarchy Egypt’s Social Hierarchy Pharaoh • Political • Religious • Military leader • Seen as a god Egypt’s Social Hierarchy Priests & Nobles • Wealthy elite • Lived in estates near Nile • Wore clothes made out of white linen • Wore dark eye make-up Egypt’s Social Hierarchy Merchants, Artisans and Scribes • Owned businesses • Skilled workers • Middle class • Sold items in market • Educated scribes Egypt’s Social Hierarchy Farmers • Tend crops • Herd animals • Vital for Egyptians to survive Egypt’s Social Hierarchy Slaves &unskilled workers • Built homes • Built pyramids • Unloaded ships • Drove carts Overview • Ancient Egyptian civilization lasted from about 3100 B.C. to about 525 B.C. or just over 2500 years. • During that time, there were at least 20 different dynasties with many different rulers. • Historians divide the long history into 3 different periods. Old Kingdom Lower Egypt crown Upper Egypt crown Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt were once separate kingdoms and the kings or pharaohs wore two different crowns. 4 King Menes / Pharoah Narma • United Upper and Lower Egypt into ONE kingdom • Established the first capital of Egypt in Memphis. 5 Sobek - the Crocodile God Worshiped at the first capital of Egypt, named Memphis or sometimes called Crocodilopolis 6 Pharaoh Djoser • Pharaoh Djoser had his architect, Imhotep build a great burial tomb which started out as a mastaba, or tomb, but became the Step Pyramid. 8 Pharaoh Djoser 9 Imhotep - Pyramid Designer / Engineer 10 Mastabas 11 Step Pyramid of Djoser 12 Step Pyramid of Djoser 13 Pharaoh Sneferu Developed the building of Egyptian pyramids through practice. • Built the pyramid at Meidum • Built the Bent Pyramid • Built the Red Pyramid where he was buried. 14 Sneferu’s Pyramid at Meidum 15 Sneferu’s Bent Pyramid 16 Sneferu’s Red Pyramid 17 Pharaoh Khufu / Cheops • Son of Pharaoh Sneferu • Built the Great Pyramid on the Plateau of Giza. • Largest of the Pyramids of Ancient Egypt 18 Khufu’s Pyramid - The Great Pyramid 19 Look at the size of the pyramid blocks... 20 Khafre’s Pyramid 24 Khafre’s Pyramid 25 Khafre’s Sphinx 26 Khafre’s Sphinx 27 Khafre’s Sphinx 28 Pharaoh Menkaure • Son of Khafre • Built smallest pyramid on Plateau of Giza 29 Menkaure’s Pyramid 30 Menkaure’s Pyramid 31 END OF OLD KINGDOM Queen / Pharaoh Hatshepsut • Wife of Thutmose II • When Thutmose II died, his son Thutmose III was too young to rule, so Hatshepsut took the throne. • Hatshepsut transformed herself from a queen to a Pharaoh. 33 Queen Hatshepsut’s Mummy Queen Hatshepsut’s mummy was found buried in her temple in a tomb in the Valley of the Kings. 34 Queen Hatshepsut’s Temple Queen Hatshepsut had this temple built as a tomb for both her and her husband Thutmose II. It is located in an area called the Valley of the Kings where many other pharaohs are also buried. 35 Queen Nefertiti • Wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten • Considered the “ideal” beauty in Egyptian society. • May have been even more famous than her husband, the pharaoh. 37 Queen Nefertiti 38 Tutankhamen / King Tut • Known as the “boy king” because ruled and died at such a young age (maybe 18 or 19 years old). • His tomb was untouched when found by Egyptologists in 1922. • Famous for the amazing treasures found in his tomb. • “The Curse of King Tut” 40 King Tut Burial Mask Found in King Tut’s Tomb with his mummy 41 King Tut’s Sarcophagus A collection of the items found in King Tut’s tomb can be seen in a museum in Cairo, Egypt. 43 King Tut’s Sarcophagus 44 King Tut’s Mummy 44 END OF MIDDLE KINGDOM Pharaoh Ramses II • A strong military leader. • Participated in the first written treaty with the Hittites. • Had many wives and more than 100 children. • Ruled over Egypt for 67 years… Pharaoh for longest period. 49 Pharaoh Ramses II Temple/Tomb 50 Pharaoh Ramses II Statues 51 Pharaoh Ramses II mummy 53 Cleopatra • Seen as the last true Egyptian Queen before Egypt was taken over by foreign invaders. 55 Writing in Egypt Hieroglyphics Group Read Activity The Most Important Word Strategy Directions • Count off 1-7 • Buddy read with another person who is the same # as you the paragraph that was assigned to you. You can each read a sentence and switch, or take turns reading paragraphs. Paragraph assignments: look for your number and read those paragraphs ONLY • • • • Group 1: All Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphics Group 2: Papyrus or Paper Group 3: “Scribes were the few Egyptians…” Group 4: “ A scribe’s profession” to “ Schools were attached”. • Group 5: “While Hieroglyphic writing” to “But now” • Group 6: “People realized” to “Finally, in 1822” • Group 7: “Translating English” to the end of the article On your sticky note… • Cover your sticky note from your partner • Write ONE word on your sticky note taken from what you read…the word that is the MOST IMPORTANT to you! • Cover up your word so no one can see! Regrouping • On the count of 3, revel your word to your “buddy-read” partner and why you picked this word. orally share • Now, I’m going to have you pair up will all the students in the class that share your number. Go ahead and all sit in one table. Show your work • Display your sticky note “important” words on the table. • Use ALL the important words to write the MOST IMPORTANT SENTENCE to reflect a summary of your reading. (stick the post-its in the middle of the sentence, where they belong) Mrs. Rida’s class is full of funa activities and interactive times. Display your work for your classmates • Then, choose a spokesperson • Bring your sentence strip to the area in the classroom where the headings are located. • Tape your sentence strip under the correct heading your read. • Read aloud to the class Article Summary • As a class, we have now summarized the whole article. • We will compile all the sentences together order in , and we have ourselves the summary of the article. Now lets go to our ISN • Article goes on page 65 in your notebook • Under the article • Write down the summary from the strips Core 1 • Egyptian writing was simplified to Hieratic Script and it had pictures to represent ideas. • Scrolls and papyrus were made out of reed stems and used for Egyptian writing. • Scribes have a very important job in the government and work for the pharaoh. • Egyptians wrote on papyrus which was very expensive, and used a brush called a menhed. • The Rosetta Stone was found in 1799 and it was used to translate Greek to Egyptian writing. • A cartouche is an oval slab that had a kings name on it and placed in the tomb. • Letters and symbols are written in columns from left to right or vice versa. Core 2 1. Picture writing was very intricate so Egyptians made an easier system called Hieratic Script. 2. Egyptians made paper called papyrus from reed stems. 3. Scribes had jobs like collecting taxes and worked for the pharaoh. 4. A menhed is a writing tool used on papyrus, which was very expensive. 5. A soldier in 1799 discovered the Rosetta Stone and it had 3 languages in it. 6. Champollion figured out how to read the cartouche and was able to understand hieroglyphics. 7. Hieroglyphics is written in columns and many directions from left to right and vice versa. Formative Assessment 3 sentence summary • On the index card I give you, write your: – Name – Core – Date Summarize what you read in EXACTLY 3 sentences.