Catalyst
advertisement

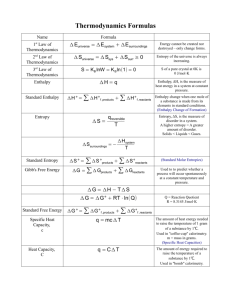
Catalyst 1. Define endothermic. Give an example. 2. Define exothermic. Give an example 3. I cool a glass of water, is this an endothermic process or an exothermic process? End Lecture 7.2 – Heating Curves and Phase Diagrams Today’s Learning Targets • 7.3 – I can draw a phase diagram to describe how pressure and temperature are related and discuss what a triple point is. • 7.4 – I can analyze and draw a heating curve to describe how energy is lost or gained while a substance changes phases. I can identify on the graph the Hfusion and the Hvaporization. • 7.5 – I can describe a reaction using the ideas of enthalpy and entropy. Today’s Focus Question • How much energy is required to turn my Flamin’ Hot Cheetos into a liquid? What are enthalpy and entropy? I. Enthalpy (ΔH) • Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy that a system has. • Amount of energy released or absorbed during a process/reaction. • Measured in kilojoules (kJ) II. Entropy (ΔS) • The universe tends towards disorder. • Entropy is the measurement of the randomness or disorder of a system. • More energy = more disorder • Measure in J/K How are enthalpy and phase changes related? I. ΔHfusion and ΔHvaporization • Large amount of energy that is required to change phases • ΔHfusion = Energy to change solid to a liquid. • ΔHvaporization = Energy to change liquid to a gas. • ΔHfreezing = Energy to change liquid to a solid • ΔHcondensation = Energy to change gas to a liquid II. Heating Curves • Heating curves are graphs of the relationship between temperature and time. • Allow us to identify important values ΔH of vaporization/condensat ion ΔH of fusion/freezing Summarize Justify – TPS • Why was the water able to boil at room temperature when we dropped the pressure? How are pressure temperature and phase related? I. Pressure and Temperature • The state of matter of a substance depends on both the temperature and pressure • A phase diagram is a graph temperature, pressure, and phase for a substance • II. Important Points on a Phase Diagram Triple Point – The temperature and pressure conditions at which the solid, liquid, and gas phases of a substance coexist • Critical Point – The temperature and pressure at which the gas and liquid state become identical and form one phase. Melting/Fusion Freezing Vaporization Condensation Sublimation Deposition Class Example • You have a solid at a pressure of 30 atm and -15 oC, if you decrease the pressure at constant temperature, what phases will the substance go through? Table Talk Stop and Jot • Atmospheric pressure on Mt. Everest is 0.29 atm. What is the boiling point of water there using the phase diagram below. Summarize Vocab Direct Instruction Assignment • With our group, let’s do some vocab definitions! • Make a power point defining each of these • terms: • • Enthalpy • • Entropy • • Δhfusion • • Δhvaporization • ΔHfreezing for each vocab word with a picture, title, and a definition! Δhcondensation Heating curves phase diagram Critical Point Triple Point Collaborative - Let’s Heat Some Water! • With the table complete the heating curve lab activity. • Heat the ice until it reaches a rolling boil • Show Mr. Astor when you are done Independent Work Time Complete the phase diagram homework you picked up when you came in. Learning Log Assessment Rate yourself 1 – 4 on LTs 7.3, 7.4, and 7.5 Exit Slip 1. What is entropy? 2. Draw a basic heating curve. Have temperature on the y-axis and heat added on the x-axis. Label solid, liquid, gas, boiling, and freezing. 3. What is the triple point on the graph below? Learning Log Assessment Rate yourself 1 – 4 on LTs 7.3, 7.4, and 7.5 Closing Time • Homework 7.2 due Monday/Tuesday • Rough Draft Due Monday/Tuesday • Quiz on Cheetos lab Monday/Tuesday