Sexual reproduction
advertisement

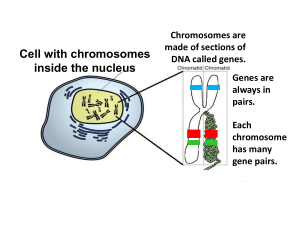
Chapter 4 Introduction Lesson 1 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Digital Vision Ltd./SuperStock What is sexual reproduction? • Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which the genetic materials from two different cells combine, producing an offspring. • The female sex cell is called an egg • The male sex cell is called sperm What is sexual reproduction? (cont.) During a process called fertilization, an egg cell and a sperm cell join together to create a zygote. Diploid Cells • Organisms that reproduce sexually form body cells and sex cells. • Diploid cells are body cells that have pairs of chromosomes. Diploid Cells (cont.) Different organisms have different numbers of chromosomes. Diploid Cells (cont.) Pairs of chromosomes that have genes for the same traits arranged in the same order are called homologous chromosomes. Because one chromosome is inherited from each parent, the chromosomes are not identical. MOM DAD 46 sperm Egg 92 46 chromosomes! chromo somes Zygote • Both sperm and eggs have only ½ the normal number of chromosomes • Human sperm and eggs have 23 chromosomes • No matching pairs!!! Haploid Cells Haploid cells are cells that have only one chromosome from each pair of chromosomes. haploid from Greek haploeides, means “single” Haploid Cells In meiosis, one diploid cell divides and makes four haploid sex cells. • Meiosis occurs during the formation of sex cells only. • Sex cells (sperm & egg cells) – Different from ordinary body cells – Each have 1 chromosome from each homologous pair • Only 23 chromosomes in human sex cells 23 sperm Egg 46 23 chromosomes! chromos omes Zygote Why is meiosis important? • Meiosis forms sex cells with the correct haploid number of chromosomes. • When haploid sex cells join together during fertilization, they make a diploid zygote, or fertilized egg. • Meiosis also creates genetic variation by producing haploid cells. Why is meiosis important? (cont.) The fertilized egg, formed when sex cells join together, divides by mitosis to create a diploid organism. How do mitosis and meiosis differ? • During mitosis and cell division, a body cell and its nucleus divide once and produce 2 identical cells. • The two daughter cells produced by mitosis and cell division have the same genetic information. How do mitosis and meiosis differ? (cont.) • During meiosis, a reproductive cell and its nucleus divide twice and produce 4 cells—each with half the # of chromosomes as the parent cell. • Meiosis forms sex cells used for sexual reproduction. Mitosis: The nucleus splits once resulting in 2 new cells Meiosis: The nucleus splits twice resulting in 4 new cells • Sex chromosomes carry genes that determine whether the offspring is male or female • Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) • Pair number 23 determines your sex • XX= female • XY= male Advantages of Sexual Reproduction • Sexual reproduction produces offspring that have a new combination of DNA. • Genetic variation occurs in all organisms that reproduce sexually. • Due to genetic variation, individuals within a population have slight differences that might be an advantage if the environment changes. Advantages of Sexual Reproduction (cont.) Ingram Publishing/ SuperStock Wally Eberhart/Visuals Unlimited/Getty Images Medioimages/PunchStock image100/SuperStock Stockbyte/Getty Images Selective breeding has been used to develop many types of plants and animals with desirable traits. Disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction • Organisms have to grow and develop until they are mature enough to produce sex cells. • Searching for a mate takes time and energy and might expose individuals to predators, disease, or harsh environmental conditions. • Fertilization occurs when an egg cell and a sperm cell join together. • Organisms produce sex cells through meiosis. • Sexual reproduction results in genetic variation among individuals. Digital Vision Ltd./SuperStock