Orbital Notation, Valence Electrons & Lewis Dot Structures

Orbital Notation, Valence Electrons
& Lewis Dot Structures
1.
Get out your notes
2.
Wait quietly
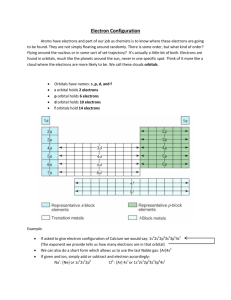
Electron Configuration Rules
1.
Aufbau Principle
Each electron MUST occupy the lowest energy orbital available first
2.
Pauli Exclusion Principle
A maximum of 2 electrons can occupy a single orbital, but only if the electrons have opposite spins
3.
Hund’s Rule
Single electrons with the same spin must occupy each equal energy orbital before additional electrons with opposite spins can occupy those same orbitals
Aufbau Principle
Each electron MUST occupy the lowest energy level and sublevel available first
Determine the order of energy levels, sub-levels, and the orbitals within the sub-levels
Energy levels are in the order of the periods down the periodic table
Order: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7
Sub-levels: are in the order of s, p, d, and f
Aufbau Principle:
Notice that d and f sub-levels are “behind” s and p sub-levels
Pauli Exclusion Principle
A maximum of 2 electrons can occupy a single orbital, but only if the electrons have opposite spins
Remember the amount of orbitals in each sub-level
S-sublevel = 1 orbital = 2 electrons
P-sublevel = 3 orbitals = 6 electrons
D-sublevel = 5 orbitals = 10 electrons
F=sublevel = 7 orbitals = 14 electrons
Each energy level holds a set amount of electrons:
1 st energy level = 1 sublevel and 1 orbital = max 2 electrons
2 nd & 7 th energy level = 2 sublevels and 4 orbitals = max 8 electrons
3 rd & 6 th energy level = 3 sublevels and 9 orbitals = max 18 electrons
4 th – 5 th energy levels = 4 sublevels and 16 orbitals = max 32 electrons
Remember that d and f sublevels are behind s and p
Hund’s Rule
Single electrons with the same spin must occupy each equal energy orbital before additional electrons with opposite spins can occupy those same orbitals
Orbital Notation:
Shows the electrons in an orbital and their spin
S- 1 orbital, p- 3 orbitals, d – 5orbitals, and f – 7 orbitals
Lines/boxes represent the orbitals
The number of the energy level and its sublevel are written below the line
Uses up and down arrows to represent the electrons and their spins
Example: Lithium – 1s 2 2s 1
_________ _________
1s 2s
Hund’s Rule
Orbital Notation
Let’s Try Nitrogen:
1s 2 2s 2 2p 3
___________
1s
_____________
2s
__________ ___________ ___________
2p
*This is called an orbital diagram/notation
A little more of a challenge: Sulfur
What is Sulfur’s electron configuration?
________________________________________________________
What is Sulfur’s orbital notation?
*Remember:
S- 1 orbital, p- 3 orbitals, d – 5orbitals, and f – 7 orbitals
Your Turn:
Complete these in your notes
Write the orbital diagrams for the following elements:
Manganese
Potassium
Gallium
Valence Electrons
The electrons that determine the chemical properties of an element
The electrons in the highest (outermost) energy level
How do we know what is the highest/outermost energy level?
The electron configuration for Chlorine is:
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 5
• The outermost energy level is the 3 rd energy level
• Chlorine has 7 valence electrons (2 + 5 = 7)
Valence Electrons
How many valence electrons are found in the following atoms?
Element Electron Configuration # of Valence Electrons
Sodium
Carbon
Gallium
Oxygen
Fluorine
Valence Electrons
THERE IS AN EASIER WAY!!!!
Lewis Dot Structure
A model that uses electron-dot structures to show how electrons are arranged in molecules.
Shows the valence electrons around the element symbol
What is an element symbol?
Aluminum =
Aluminum has _____ valence electrons
Imagine aluminum symbol with a box around it
Al
*Each side of the box can only hold 2 electrons
*Put 1 dot (to represent 1 electron) on each side before adding a second dot to that side of the box – Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
So the final product looks like this: Al
Give Sulfur a try:
How many valence electrons does Sulfur have? ______
S
Your turn:
Complete these in your notes
Draw the Lewis Dot Structure for the following elements:
Element Symbol and number of valence electrons
Lewis Dot Structure
Lithium
Nitrogen
Calcium
Bromine
Carbon
Selenium
Until the Bell Rings:
Work on your homework: Page 7 in packet and prelab
REMEMBER:
LAB TOMORROW YOU MUST BE DRESSED IN LAB
ATTIRE
Closed shoes
Long pants (no skin, not even ankles)
NO baggie sleeves
Hair pulled back