New England Colonies
advertisement

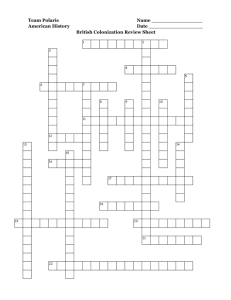
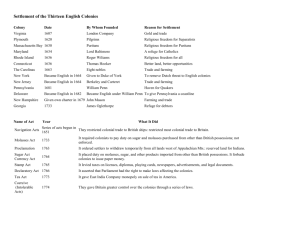
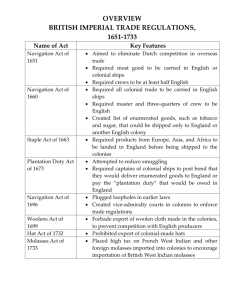
New England Colonies Colonies • • • • New Hampshire Massachusetts Rhode Island Connecticut Geography/Location • Thin, rocky layer of dirt • Forests and mountains • Climate went from warm to very cold • Farming was difficult Land Characteristics • Climate-Long harsh winters and short summers-short growing season • Mountainous • The soil was very rocky and thin (not deep), which was not good for farming • Direct access to waterways Resources • Wheat • Oats • Peas • Lumber • Fish – mainly Cod fish • Whales Industries • Fishing • Shipbuilding • Whaling • Exported lumber and fish to Europe These industries were possible due to the harbors and ports in the area. Triangular Trade Dropped off: molasses Picked up: rum New England The products of New England were often traded to other places. These are the shipping routes between North America, Europe, and Africa. West Indies Dropped off: slaves Picked up: molasses Africa Dropped off: rum Picked up: slaves People • Puritans /Pilgrims– English colonists who settled in the New England colonial region and wanted to form communities where they could follow the rules of the Bible and serve their God. • Sailors – hunted whales and fished • Shipbuilders – used wood provided from the thick forests to build ships What do you notice about the city and environment? Boston • Largest City for Trade • Boston Harbor for Shipping and Trading • Pivotal City in History We will learn later Education • Every town with more than 50 people had to have a school. • Had more schools than the other colonies would eventually have. • Harvard was the first university in the colonies. Roles • • • • Apprentice Artisan Industry workers Women Artisans • People who were skilled at making things by hand, like silver spoons or wooden chairs. • Liked the big cities as there were more customers in a city • Attracted by the free market economy-which means people could buy and sell what they wanted. Artisans worked as craftsmen in towns and on plantations. • They learned their craft by first working as apprentices. Women • Ran the store • Took care of the home • If the family was wealthy, they entertained and maintained the social status of the family. • Children were sent to school or private tutors if you were wealthy. Apprentice • Someone who studies with a master to learn a new skill or business • Boys learned shoemaking, printing or bookmaking • Girls learned how to spin thread and weave cloth.