Chapter 4 American Life in the 17th Century 1607-1692
advertisement

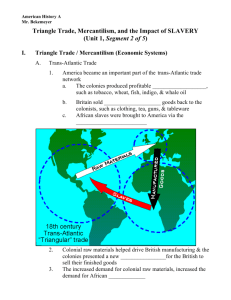
Colonial Society & Democratic Growth 1607-1692 The Unhealthy Chesapeake • Life expectancy cut by 10 years (few lived to be 40-50 yrs. Old); ½ died by 20 years old. • Grew slowly- mostly with new immigrants • 1600’s- ½ people born in Va. & Maryland lived to be 20. • 6 to 1 male to female ratio • 1/3 of brides were pregnant before wedding • Marriages ended by death (avg. 7 years) • Disease- malaria, dysentery, typhoid • Late 1600’s Chesapeake was growing through natural increase • Virginia became most populous colony (59,000 by late 1600’s) Population Comparisons: New England v. the Chesapeake Tobacco Economy & Geography Over Time– Tobacco became an important export crop for the Chesapeake & North Carolina. Role of Geography in Shaping Development of the Chesapeake & North Carolina •Longer growing season (due to shorter & less severe winters) •Soil conducive to growing—tobacco, cotton etc. •Hot, Humid climate= disease (malaria)= shorter life spans at first. Tobacco Economy •If prices fell…planters would just plant more & more…Tobacco outpaced food crops •1.5 million pounds exported in 1630’s; 40 million lbs. by 1700 (change over time!) •Rising prices= demand for more land= demand for more labor (indentured servants) •Most laborers'= indentured servants (3/4 of European immigrants in Chesapeake) What factors led to the introduction of African slavery replacing indentured servitude as the labor force in the American Colonies? Bacon’s Rebellion (1676 - 1677) Nathaniel Bacon represents former indentured servants. Governor William Berkeley of Jamestown •As early as the 1660’s, the English economy was improving. •Indentured servants harder to lure to British colonies. •African servants were NOT classified as “chattel” (permanently slave)…YET! •So large numbers of impoverished, discontented people existed in the colonies (little access to land, disenfranchised…) •Forced to live in the “backcountry” along side hostile Indians. Governor Berkeley faced a revolt of discontented backcountry farmers in Virginia. Nathaniel Bacon (29 yrs. old) – led a mixed race group of backcountry frontiersmen angry about a variety of issues including the Governor's cozy relationship with Indians (he was making big money in the fur trade with the Indians). •The rebels attacked Indians, ran Gov. Berkeley out of Jamestown (capital) & burned Jamestown (plundered stores) •Bacon dies of disease…his followers scatter, those captured by colonial militia are executed. Significance of Bacon’s Rebellion • Foreshadows future class revolts (Culpepper’s In NC, Paxton Boys Revolt in Penn., Regulators In NC, Leisler’s in NY). • The Planter class starts to divide poorer masses By RACE…by making laws that say that African slaves are slaves for life. • Planters create the “Herrenvolk” Democracylimited to the white nation only, elevating the yeoman farmers but still denying them the vote through property requirements. Slaves captured in Africa •Slavery has been practiced since the beginning of documented history. •Slavery introduced by the Spanish into the West Indies after Columbus’s discovery of America. •Spanish and Portuguese expanded African slavery into Central and South American after enslaved Indians began dying off. •In 1619, the first recorded introduction of African slaves or black indentures into what would become the United States was in the settlement of Jamestown……Only 20 slaves/indentured were purchased…. Slaves aboard ship—Middle Passage ** Every colony before the Revolution will have slavery present. Note the date Of this chart…1770! •Can you tell why Southern colonies were Called “Slave Societies”? •Can you tell why •Middle & New England colonies were known as “Societies With Slaves”?? Note the dates each colony legalizes slavery & the growth of slavery In each colony from 1680 to 1740. • Note that the growth of the overall population of the colonies grew exponentially after 1700. • The African population in the Colonies also grew but to a lesser degree compared to the overall population. This is called the Middle Passage Slavery in Colonial America • Slavery grew slowly in British North American Colonies (few whites could afford, white servants were cheaper) Reasons for Growth of African Slavery 1. Mid to late 1600’s, English economy improved= less people were coming as Indentures. 2. 1680’s- fewer indentured servants & fear of angry farmers (Bacon’s Rebellion)= more reliance on African slaves 3. 1698- Royal African Co.- lost monopoly = North American shippers (Rhode Islanders esp.) began trading in slaves= more slaves= part of Triangle Trade • 1600’s –10,000 Africans brought to British North America • 1700’s– 390,000 Africans brought to British North America • 1750- slaves count almost half of Va. Population • Slave Codes- define slaves as lifetime chattel, forbids teaching reading or writing to slaves African to African-American • Dragged from various parts of Africa, the first Africans in America struggled to preserve diverse heritages. • The American born children of African slaves blended a variety of African traditions into a distinctive AfricanAmerican culture. The First Africans in America 1600’s • Brought a variety of African traditions, languages, skills, music, and foods etc. Example: Africans with knowledge of rice growing introduced rice to European diets. • Mostly male who were slaves on small isolated farms • Some slaves were able to purchase their freedom from masters (Anthony Johnson-former slave who became a slaveholder). African Slaves in the 18th Century (1700’s) • • • • A settled slave society emerged in the southern colonies. Slave laws tightened Importations of slaves increased---large plantations formed. **A new generation of American-born slaves joined older generation in the fields. From African to African-American • American-born slaves had a hard time finding ways to resist slavery. • Men worked from sun up till sundown. Women worked in fields in the day…spun cloth at night. • Women lived in fear of sexual exploitation by masters. • A Vibrant Slave Culture Emerged 1700’s • A unique New World blend of African & western cultures. Example Religion: most slaves became Christian & fused elements of African & western traditions in worship. • • • Developed their own Biblical interpretations (whites emphasized Biblical teachings about humility & “staying in your place”---slaves emphasized liberation elements (Moses). Black Methodists incorporated the “Ring shout” (a dance in which the legs do not cross)---later the 1920’s dance craze the Charleston results. “ Negro Spirituals” – created songs that emphasized liberty, freedom The Stono County Rebellion, 1739 •September 9, 1739, twenty black Carolinians met near the Stono River, approximately twenty miles southwest of Charleston. They took guns and powder from a store and killed the two storekeepers they found there. •"With cries of 'Liberty' and beating of drums," "the rebels raised a standard and headed south toward Spanish St. Augustine. Burned houses, and killed white opponents. •Largest slave uprising in the 13 colonies prior to the American Revolution. •Slave-owners caught up with the band of 60 to 100 slaves. 20 white Carolinians and 40 black Carolinians were killed before the rebellion was suppressed. Slave Revolts would lead plantation owners to develop a series of slave laws/codes which restricted the movement of the slaves. •Slaves were not taught to read or write •Restricted to the plantation •Slaves could not congregate after dark •Slaves could not possess any type of firearm •A larger slave population than white in some states Slave owners wanted to keep their slaves ignorant of the outside world because learning about life beyond the plantation could lead to more slave revolts and wanting to escape. Slave Laws Southern Society • The Spread of slavery widened the social gap as the 17th century gave way to the 18th century. 1. The Planter Elites: All over the Chesapeake & South; owned huge tracts of land, ran & influenced the government, owned large numbers of slaves. (In Virginia--FF of V) • 1775- Planters elites in Virginia (FFV’s) make up 70% of the House of burgesses membership. 2. Small Farmers (Yeomen—”plain folk)- (largest group) owned small amounts of land (maybe 1-2 slaves) 3. Landless whites & Indentured Servants- barely made a living from the land 5. African slaves • • The Southern colonies had few cities of much size (Charleston was the largest & important seaport) Life revolved around plantations separated geographically New England Society The New England Family & life •Cooler climate & clean water= longer life expectancy (adds 10 years; avg. life expectancy= 70) •Migrated as an entire family units from England (intact families); more people came at once than southern colonies & Chesapeake. New England Families •Early marriage encouraged= booming birthrates •Large families encouraged (10 pregnancies – 8 surviving children)= tough on women=mortality •Children had stability, taught obedience=low premarital pregnancy rates •NE “invented grandparents” New England Marriage & Family • Southern society generally allowed married women to retain separate title to property & gave widows the right to inherit a deceased husband’s estate. Rights of Women in New England • • • • Gave up property rights at marriage Widow’s property rights protected Women could not vote Women considered “morally weaker” than men (The Scarlet Letter -1850 Nathaniel Hawthorne ) Laws Established to protect marriage in NE • Divorce was very rare—only granted in cases of adultery or abandonment; separated couples told to reunite • Divorce- granted for abandonment or adultery only (rare) • Adulterers whipped in public & forced to wear letter “A” • Abusive husbands punished The New England Town • Tightly knit communities (hemmed by Indians, French, Dutch) • Based on Small farms & villages • Puritanism= unity & purpose & concern for moral health of community • Towns grew in an orderly fashion (legally chartered by colonial authorities; distribution of land was entrusted to town fathers or proprietors) Development of a NE Town Upon receiving a tract of land from the colonial legislature, a proprietor would move his family there. • Planned out the town layout • A Meetinghouse –served as place of worship & town government (mix of church & state) surrounded by houses. • Village Green- place for militia to drill. • Each family got a woodlot, a pasture, land for crops. Land Division in Sudbury, MA: 1639-1656 Education in New England * Massachusetts School Law of 1647 – (“Old Deluder Law”)-required establishment of schools. Towns provided education • • • • 50 or more families= elementary school 100 or more = secondary school ½ of adults could read 1636- Harvard (8 years after founding colony) Democracy & Governemt in New England • **Town meetings- adult males met & voted (“the best school of political liberty the world ever saw.” Thomas Jefferson) • Elected schoolmasters, officials • Churches were tax supported (“Established”) Higher Education in the Colonies Harvard, 1636—First colonial college; trained candidates for ministry College of William and Mary, 1694 (Anglican) Yale, 1701 (Congregational--Puritan) Great Awakening influences creation of 5 new colleges in mid-1700s College of New Jersey (Princeton), 1746 (Presbyterian) King’s College (Columbia), 1754 (Anglican) Rhode Island College (Brown), 1764 (Baptist) Queens College (Rutgers), 1766 (Dutch Reformed) Dartmouth College, 1769, (Congregational) The decline of Puritanism Over time demographic changes led to declining Puritan fervor. Puritan populations moved out of town away from control of church. Puritan zeal began to diminish. There was a decline in conversions Mid 1600’s, a new form of sermon appeared =the “Jeremiad” The *Jeremiad, was used by preachers to scold parishioners into being more committed to their faith. *"Half-Way Covenant",1662: sought to attract more members by giving partial membership (baptism) but not full communion to children of existing church members (weakened line between the “elect” & others. Soon Puritan churches baptized anyone and the distinction between the "elect" and other members of society declined (*women became majority in churches now) The Salem Witch Trials took place in Salem, Massachusetts from March to September 1693, was one of the most notorious episodes in early American history. 19 hung, 1 pressed, two dogs hanged; 55 confessed as witches and 150 awaited trial Under British law and Puritan society those who were accused of consorting with the devil were considered felons, having committed treason and punished by death. Causes Girls caught dancing, began to throw fits and accuse people of bewitching (To put under one's power by magic or cast a spell on them). Originally based on the false accusations of two young girls, Elizabeth Parris and Abigail Williams Ended in 1693 when the Governor stopped the trials and pardoned those awaiting trial. The accused were mostly women from families associated with Salem’s market economy; their accusers were from subsistence families who lived outside the town Shows how unfounded rumors can cause hysteria even lead to illogical thinking …today we call such things “a witch hunt”. The New England Way “Yankee Way” Geography shaped them • back-breaking work & soil= industry, penny-pinching (frugal) • Less ethnically diverse than southern colonies • Diversified agriculture (slavery existed but was not profitable) & industry • Good harbors = shipbuilding & fishing • “Calvinism, soil, & climate”= energy, purposefulness, sternness, self-reliance • “Yankee ingenuity” Southern Colonies were more ethnically diverse compared to New England Generalities about all Settlers • Majority were farmers • Rose at dawn & went to bed at dusk (“worth the candle”) • Land was cheap (less available in the south; cheap in Northern & Middle) • European immigrants trying to recreate social structure in America were frustrated (Bacon’s Rebellion 1676, 1689-1691 Leisler’s Rebellion in NY) Trade Triangle Trade •Lumber •Tobacco •Rice •Indigo •Furs To England from Colonies The Triangle Trade •Furniture •Clothing •Colonials had not factories. From England to Colonies Religious diversity by 1775 Instructions: On your paper, write the correct colony with the number it matches…… 14 2 13 7 10 12 9 1 4 8 15. New England 5 16. Middle 17. Southern 6 3 11 List them in their regions. 18. Chesapeake