Respiratory System
advertisement

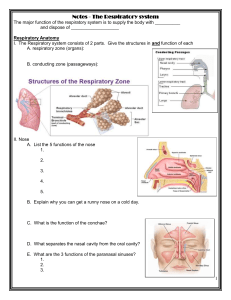
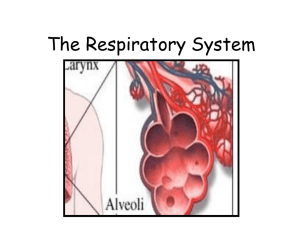
FUNCTION OF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM • The respiratory system’s primary function is to supply oxygen to all parts of “your” body • This system includes your airways, your lungs, and the blood vessels and muscles attached to them STRUCTURE OF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM • The respiratory system is divided into the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract • Included in the upper respiratory tract are the nose, mouth, and the beginning of the trachea • The lower tract consists of the trachea, bronchi, broncheoli, alveoli, and lungs UPPER MAJOR ORGANS AND FUNCTIONS • Nasal cavity/Oral cavity- primary upper reparatory organ in which air enters into and exits from the body. Cilia and mucus line the nasal cavity and traps bacteria and foreign particles that enter in through the nose • Pharynx- The pharynx is a tubular structure, positioned behind the oral and nasal cavities, that allows air to pass from the mouth to the lungs. The pharynx contains three parts • Larynx- part of the upper respiratory tract that has two main functions: a passageway for air to enter into lungs, and a source of vocalization. The larynx is made up of the hyoid bone and cartilage, which helps regulate the flow of air. The epiglottis is a flap-like cartilage structure contained in larynx that protects the trachea against food aspiration LOWER MAJOR ORGANS AND FUNCTIONS • Lungs- spongy, air-filled organs located on both sides of the chest cavity. The left lung is divided into a superior and inferior lobe, and the right lung is subdivided into a superior, middle, and inferior lobe. Pleura, a thin layer of tissue, line the lungs to allow the lungs to expand and contract with ease. Respiration is the primary function of lungs, which includes the transfer of oxygen found in the atmosphere into the blood stream and release of carbon dioxide into the air. • Diaphragm- a muscular structure located between the thoracic and abdominal cavity. Contraction of the diaphragm causes the chest or thorax cavity to expand, which occurs during inhalation. During exhalation, the release of the diaphragm causes the chest or thorax cavity to contract. LOWER MAJOR ORGANS AND FUNCTIONS • Bronchi- branches from the trachea into the right bronchi (tube leading to the right lung) and the left bronchi (tube leading to the left lung) these bronchi divide smaller and smaller and they ultimately branch into tiny tubes whose walls contain only smooth muscle • Bronchioles- the small passageways formed by the decreased bronchi. The bronchioles subdivide into microscopic tubes called alveolar ducts. • Alveoli- tiny grape-like sacs at the end of the bronchioles that resemble grapes. The exchange of oxygen and carbon gases occur at the alveolar level. Effort is required to inflate them, and minimal effort is needed to deflate the alveoli RESPIRATORY SYSTEM WITH OTHER SYSTEMS • It interacts closely with the circulatory system because blood picks up oxygen in the lungs and then transports it around the body including your respiring tissues as muscles • It works with the immune system because its lined with mucous membranes which contain mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue, this tissue is an essential part immune system because it produces immune cells. Lymphocytes just defend the body against infections and viruses. Also, the bronchus in the lungs are lined with cilia that move debris up and out of the airways. Scattered throughout the cilia are goblet cells that secrete mucus which helps protect the lining of the bronchus and trap microorganisms IMPROVING THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM • Don’t smoke – smoking causes lung cancer it may cause lung diseases. • Exercise – When you exercise, your respiratory system gets a workout. As your breathing rate and depth increases, your lungs absorb more oxygen, which means more oxygen-rich blood is sent to your muscles • Keeping your lungs clean and well-exercised ensures proper functioning and overall good respiratory health DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) - is the intersection of three related conditions – chronic bronchitis (long time cough with mucus), chronic asthma, and emphysema (involved the destruction of the lungs over time). COPD is most commonly caused by smoking but pollution and genetics also play a role. This obstructive lung disease is characterized by chronically poor air flow, shortness of breath, and cough. Lung Cancer - often associated with smoking, but the disease can affect non-smokers as well. Every year, about 16,000 to 24,000 Americans die of lung cancer, even though they have never smoke, according to the American Cancer Society. Like all cancers, lung cancer is cause by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells. If lung cancer is left untreated, the uncontrolled growth can spread into nearby tissue and other parts of the body. 1) WHAT IS THE MAIN FUNCTION OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM? A) To break down food for energy B) To supply the blood with oxygen C) To circulate blood through the body Answer: B 2) WHICH PART OF THE BODY IS NOT INCLUDED IN THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM? A) Mouth B) Diaphragm C) Small intestine Answer: C 3) WHAT ARE LOCATED AT THE END OF THE BRONCHI? A) Alveoli B)Diaphragms C)Cells ANSWER: A 4) WHAT WOULD HAPPEN IF YOUR RESPIRATORY SYSTEM WERE TO STOP FUNCTIONING? A) Nothing B) Breathing would be difficult C) YOU WOULD DIE ANSWER: C 5) HOW MANY MILES OF AIRWAYS DO YOUR LUNGS CONTAIN? A) 10 miles B) 1500 miles C) 500 miles ANSWER: B BIBLIOGRAPHY Zimmermann, Kim Ann. “Respiratory System: Facts, Function and Diseases.” LiveScience.TechMedia Network, 01 Oct. 2014. Web. 13 Oct. 2014 “Year of the Lung – Fact Sheets.” Year of the Lung – Fact Sheets. N.p., n.d. web. 15 Oct. 2014.