File
advertisement

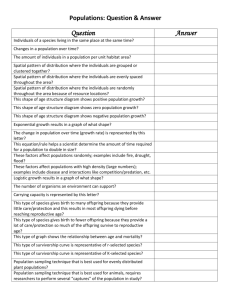
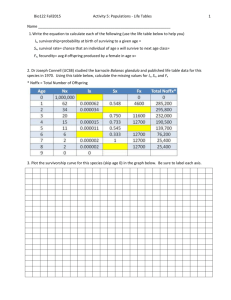
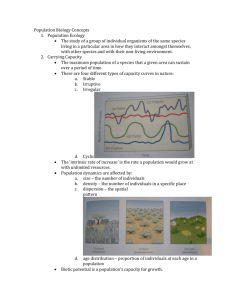
You graphed your population survivorship % over the weekend! Now we are going to use a different type of graph paper to make ANOTHER graph, for a different type of analysis Semi-log graph paper!!! Size Density Distribution Age structure Birth rate Death rate Population growth rate Reproductive strategy Describes the number of individuals per unit area Usually, larger organisms have lower population densities because they require more resources to survive Higher densities make it easier for organisms to find mates but leads to competition ◦ They may also be more vulnerable to predators and disease Describes the spatial distribution of organisms within an area Random distribution— individuals located haphazardly in space in no particular pattern Uniform distribution— individuals are evenly spaced Clumped distribution— organisms arranged according to the availability of resources needed to survive ◦ Most common in nature Describes the relative numbers of organisms of each age within a population A population made up mostly of individuals past reproductive age will decline over time A population with many individuals of reproductive age will increase over time Male Female Rapid Growth Guatemala Nigeria Saudi Arabia Ages 0-14 Slow Growth United States Australia Canada Ages 15-44 Zero Growth Spain Austria Greece Negative Growth Germany Bulgaria Sweden Ages 45-85+ Survivorship curves show the likelihood of death Type I survivorship curves have a high death Type II survivorship curves have equal rates Type III survivorship curves have highest rate at older ages of death at all ages death rates at young ages Populations grow when the birth rate is higher than the death rate When a population increases by a fixed amount each year Every population is eventually constrained by limiting factors These may include ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Habitat size Food Mates Other resources Rises sharply at first but then begins to level off as the effects of limiting factors become stronger 1. involves two parents 2. involves sex cells that contain half of the genetic information (sperm and egg) 3. offspring receive genes from both parents 1. involves only one parent 2. offspring are genetically identical to parent 3. ex) strawberries, bacteria, mushrooms 1. Males do not give birth • 2. 3. Females need to have twice as many young as an asexual organism to maintain the same number of young in the next generation Increased change of genetic errors and defects Courtship or mating rituals consume time and energy, can transmit disease, and can inflict injury on males of some species if they compete 1. Provides greater genetic diversity • 2. Greater chance of reproducing and evolving if environmental conditions change Males of some species can gather food for the female and young and protect them Over time, most populations exhibit an Sgrowth curve that levels off at a value K. This value is known as (A) equilibrium growth rate (B) exponential growth rate (C) carrying capacity (D) logistic growth rate (E) minimum population density R-selected species have a capacity for a high rate of population increase ◦ Have many small offspring ◦ Little to no parental care or protection ◦ Overcome the massive loss of offspring by producing so many that a few will survive ◦ Algae, bacteria, rodents, annual plants (dandelions), and most insects R-selected species are opportunists/generalists ◦ Reproduce and disperse rapidly when conditions are favorable or when a disturbance opens up a new habitat or niche for invasion ◦ Adapted to unstable climate and environmental conditions Most r-selected species go through (A) irregular or irruptive population changes (B) irruptive or stable population changes (C) stable or irregular population changes (D) stable or cyclic population changes (E) cyclic or irregular population changes K-selected species have a lower population growth rate ◦ Have fewer, larger offspring with long life spans ◦ Later reproductive age ◦ Offspring are born fairly large, mature slowly, and have high parental care ◦ Most large mammals, birds of prey, large and longlived plants K-selected species do well in competitive conditions when their population size is near the carrying capacity of their environment ◦ Specialists ◦ Competitors ◦ Adapted to stable climate and environmental conditions Which of the following types of species would be least susceptible to the fragmentation of its habitat due to human influences? (A) generalists (B) specialists (C) large predators (D) K-Selected species Opportunist species are most commonly (A) introduced exotics (B) competitors (C) K-strategists (D) r-strategists (E) none of the above A bottom-heavy age structure diagram is indicative of (A) a population at carrying capacity (B) slow growth (C) rapid growth (D) low mortality rate (E) low natality rate Age structure diagrams provide information about a country’s I. growth rate II. Generational composition III. Accumulated retirement funds (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) I and II only (E) I, II, and III The best measure of a society’s quality of life is its (A) Gross national product (B) Educational standards (C) Life expectancy (D) Infant mortality rate (E) Fertility rates