Chapter 1 - Maria Regina
advertisement

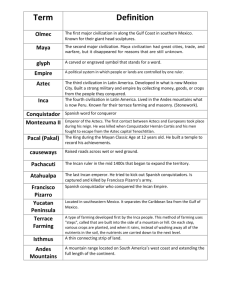
Chapter 1 Section 1 The First People Land Bridge Theory • Between 10,000 and 100,000 yrs ago, much of the world was covered with glaciers (thick sheets of ice) • b/c H2O levels dropped, land was exposed, incl. area btwn Alaska & Siberia • Land bridge (Beringia) is now covered by Bering Strait • 1st people probably came btwn 20,000 and 30,000 yrs ago, hunting prehistoric animals like the wooly mammoth Coastal Route Theory • idea that 1st people crossed arctic waters by boat and traveled S along Pacific coast Native American groups have their own theories Development of Farming • 1st people got food and other things by hunting game and gathering nuts, berries, etc. • Eventually, prehistoric animals disappeared • Changed way of life for early people • Began farming—lima beans, squash, maize • Farming meant people didn’t have to wander in search of food • Raised cattle, pigs, and llamas—domestication (training animals to meet human needs) • Those living in dry areas used irrigation (method of watering crops by channeling H2O from rivers or streams) • People could now settle in one area, population increased, and a surplus (extra) of crops led to trade and the development of cities • Civilization: advanced culture in which people have developed cities, science, and industries • Culture: way of life of a group of people (including language, religion, government, traditions, education, etc) Three Early Civilizations • Maya (250-900 AD) • Aztec (1100-1500s AD) • Inca Mayan Civilization • built cities in Mexico and Central America • Cities had large public plazas with pyramids, temples, ball courts, palaces • Developed arts, government, written language (glyphs) observed stars, created a calendar • Abandoned cities ©900 AD, reason unknown Aztec Civilization • Capital: Tenochtitlan (located where present-day Mexico City is) • City had population of 200,000 people • Built on a series of islands in a large lake • Connected to mainland by stone roadways • Raised crops on floating platforms • Religion dominated Aztec life • Conquered tribes sent treasure, food, and prisoners to Aztec capital and paid taxes Inca Civilization • 1400s—largest empire in the world at the time • stretched across South America • capital—Cuzco • linked to other towns by network of roads • messengers delivered news to all parts of empire • buildings made of stone • used terrace farming to grow crops in Andes Mountains • built canals and bridges • had a system of medicine • fine weavings, metalwork (jewelry) Section 2 • Cultures: ways of life First Cultures • 3000 yrs ago, grps emerged in area btwn Appalachian Mts. & Mississippi Valley Mound builders: constructed piles of earth • Burial places • Foundations for buildings • Mississippians: built 1st cities in North America – Cahokia (in present-day IL) was largest city Anasazi • S. Utah, CO, N. AZ, NM • Large cliff dwellings (for defense) • Made baskets, pottery, jewelry • Traded • Abandoned cliff dwellings c. 1300 Hohokam • • • • 300 BC-1400 AD AZ Dug irrigation canals Traded for seashells (jewelry, religious objects) Culture area: region in which grps of ppl have a similar way of life Meeting Basic Needs • women collected roots, wild seeds, nuts, acorns, berries • men hunted game & fished • grew and stored food suited to climates they lived in • sticks used for digging • bones & shells used as hoes • used fertilizer (Ie. dead fish) to make soil richer • traded-used beads or shells as currency • traded shells, flint (used to make fires), copper, salt Shared Beliefs • felt close relationship to natural world • believed spirits dwelled in nature and were a part of daily lives • Nat. Am. in SE—Green Corn Ceremony (late summer) • Pueblos—Kachinas (benevolent spirits)— carved dolls to teach children • Used oral tradition to pass on history Far North • Arctic-land vast and harsh • Parts covered w/ ice all yr • Ate fish, shellfish, birds • Hunted whales, seals, walruses, caribou • Kayaks-sm. boats made from animal skins • Subarctic-dense forests • Hunted caribou, moose, bear, sm. animals • Gathered plants Northwest – S. Alaska to N. California – Deer, bears, roots, berries (forests) – Salmon – Abundance of food— allowed for permanent settlement even though most weren’t farmers – Potlatch-ceremony @ which hosts showered guests w/ gifts (woven cloth, baskets, canoes, furs) – Status judged by how much wealth you gave away Far West • • • • • • Winters cold in N. forests and grasslands California-warm summers, mild winters Food abundant-small game, fish, berries Pit houses-dug in ground Cone-shaped houses covered w/ bark N-houses made of wood planks Southwest • • • • AZ, NM, S. UT, S. CO Dry most of yr Some farming, hunted Collected and stored rain from summer thunderstorms for dry times • Pueblos such as Hopi & Zuni—had stable towns that lasted hundreds of yrs • Built apt. houses made of adobe (sun-dried brick) for defense Great Plains • Mississippi River to Rocky Mts. • E. Plains good for farming • Women collected corn, beans, squash (3 Sisters) • Earth lodges—log frames covered w/ soil • West too dry for farming • Lived in teepees or dug round pits for shelter • Buffalo—ate meat, used hides for teepees, robes, & shields, bones used for tools Eastern Woodlands • • • • Forests of maples, birches, pines, beeches Hunted, fished, foraged for nuts & berries Farmed Algonquian—S. Can., Great Lakes, along Atlantic coast to VA • Iroquois—five nations – – – – – Clans-grps of families related to one another Matrilineal—membership passed through mother Women had great influence in Iroquois society Chose sachem (tribal chief) 1500s—formed League of Iroquois—est. council to make laws to keep peace Southeast • climate was mild but summers were hot & humid • farmed • Cherokees & Creek built houses of wood frames covered w/ steel mats plastered w/ mud clay to keep interiors cool & dry Section 3 Muslim Link in Trade • Merchants dev. trade routes linking Eur., Asia, & Afr. • Linked ppl living far away from each other • Passed through Arabian Peninsula Rise of Islam • Spread through conquest & trade • Conquered Spain, N. Afr, Persia, India • Achievements in math, medicine, astronomy, ships w/ sails African Link in Trade • Egyptians traded for cedar logs, silver, horses, ivory, spices, copper, cattle East African Trade Centers • 1000 AD trade centers dev. • Zimbabwe most powerful – Btwn E. coast of Afr & interior • Kilwa—chief trading center – Exchanged cloth, pottery, & manufactured goods for gold, ivory, furs – Slave trade dev. West African Trade Centers • Linked Middle East & Africa • Ghana—btwn salt of desert & gold further S. – Ppl exchanged salt for gold – Made kingdom rich • Absorbed by Mali Empire – Led by Mansa Musa – Timbuktu—center of learning – Traded for kola nuts, food, gold • Absorbed by Songhai Empire – Center of Islamic learning – Traded salt, gold, slaves East Asian Link in Trade • China linked by highways, canals, & postal system • Traded w/ India, Korea, Japan, Middle East, & Asia • Chinese invented movable type, magnetic compass • Traded silks & pottery for spices, gems, medicinal herbs, ivory • Silk Road: series of routes that stretched 5,000 mi. from China to Persia Section 4 Judeo-Christian Tradition • Judaism, Christianity Greek & Roman Tradition • Direct democracy • Republic • Code of laws Middle Ages • Feudalism • Importance of Catholic Church (faith, education) Crusades • Wars fought to win back Holy Land • 9 total • Put Europe in closer contact w/ Muslim civilization (which was much more advanced than European civ @ the time) • Eur. attracted to new foods, spices, navigation tech., & other rich goods (oranges, pepper, ginger) Renaissance & Reformation Renaissance • Rebirth in learning • Printing press—spread knowledge, more books available • Emergence of nation states (Spain, Portugal, England, France) • Italian city-states controlled Mediterranean route to the East Protestant Reformation • Led by Martin Luther (German monk) • Challenged many Catholic ideas • Led to split from Catholic Church Beginning of the Age of Exploration • • • • Prince Henry the Navigator (Portugal) Wanted to expand Portuguese pwr & Christianity Sagres—center for exploration Taught crews about navigation & map-making – How to use astrolabe, magnetic compass • Vasco de Gama—explored around coast of Africa to India • Helped boost Port. wealth & pwr • Traded w/ East Indies for spices Henry the Navigator astrolabe