Cultural Processes
advertisement

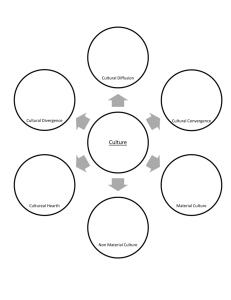
CULTURE PATTERNS AND PROCESSES Chapter 5 Culture Culture is a complex concept Def #1 A particular way of life, such as a set of skilled activities, values, & meanings surrounding a particular type of practice Def#2 A shared set of meanings that is lived through the material & symbolic practices of everyday life Could be values, beliefs, ideas, and practices Concepts of Culture Cultural geography Definition: Study of people’s lifestyles, their creations, and their relationships to the Earth Non-material components of culture Thoughts/ ideas Religion, laws “built landscape” Physical imprint a culture makes on the environment Looks at why and how culture is expressed in different ways and different places Involves: Material components of culture Tangible artifacts Clothing, architecture Cultural Landscape Carl Sauer 20th century geographer Culture leaves “imprint” Cultural Ecology Buildings, artwork, music Study of human-environment interaction and its results Sequent Occupancy Theory that a place can be occupied by different groups of people, and each group leaves its imprint on the place from which the next group learns Ex. England Cultural Ecology England Called Historical Geography France Defined as “geography in the past” Called “genre de vie” H.C. Darby Implemented his historical approach to cultural geo and landscape by developing a geography based on the Domesday Book. Used data to reconstruct the political, social, and economic forces that shaped past landscapes Def: a functionally organized way of life that is seen to be characteristic of a particular cultural group Centered on livelihood practices of groups that were seen to shape physical, social, and psychological bonds. Vidal de la Blanche Emphasized need to study small, homogeneous areas to uncover relationship between people and their surroundings Natural vs. Cultural landscape Human-Environment Interaction Environmental Determinism Theory that human behavior is controlled (or determined) by physical environment Counterargument to environment determinism Argues the natural environment places limits on the set of choices available to a people Theory that the environment places no restrictions on humans whatsoever Only restrictions are the ones humans create themselves Egypt vs. Siberia Possibilism Cultural Determinism Ex: ideal climates cause more productive citizens People, not the environment, propel human development Political Ecology Attempts to answer why human cultures interact with environments the way they do Government of a region affects the environment in that region which affects choices available to people Ex: zoning laws Layers of a Culture Culture Traits Def: A single attribute of a culture Ex: bowing to show respect Not always unique to one group Def: Combination of all culture traits creates a unique set of traits No two cultures in the world have the same culture complexes Culture Systems Def: Culture Complex Culture Regions Def: Ex: Germany Ex: The South Culture Realms Def: When many culture complexes share particular traits, those traits can merge into culture systems Region that includes places and peoples with similarities in their culture systems People in culture region often share a sense of common culture and regional identity Boundaries defined by perceptions and opinions Formed through the fusing together of culture regions that share enough in common to be merged together ex: Anglo-American realm Latin American realm Sino- Japanese realm Culture regions: Religion Cultural Diffusion Cultural/Spatial Diffusion People’s material and nonmaterial creations spread across time and space, moving to new places and being carries through generations. Cultural diffusion: Spread of people’s cultural across space Spatial diffusion: Spread of any phenomenon (such as a disease) across space Two categories of diffusion: Expansion relocation Cultural Diffusion Expansion Diffusion Def: Relocation Diffusion Cultural component spreads outward to new places while remaining strong in the hearth Forms of Expansion Diffusion Idea diffuses from hearth but original idea is changed Iced tea vs Sweet tea Idea spreads from a place or person of power Hip-hop moving from large cities to other larger cities to smaller cities to suburbs/ rural areas Contagious Numerous places or people near the point of origin become adopters Ex: Tuberculosis Involves actual movement of the original adapters from their hearth to a new place People do the “moving” not the innovation Migrant diffusion Hierarchical Stimulus Def: Innovation spreads and lasts only a brief time in the newly adopted place Ex: Band Concert Mix of Patterns Many diffusing phenomenon spread through mix of patterns Ex: HIV/ AIDS Culture Hearths Definition: Areas where innovations in culture began, such as where agriculture, government, and urbanization originated Direction of Diffusion of Civilization from Ancient Hearth Andean America Eastward t/out S. America Mesoamerica Eastern/Western N. America West Africa T/out Africa Sources of human civilization Nile River Valley Ancient Hearth Ancient culture hearths believed to have developed in places with the capacity for innovation Near sources of water/ arable land Not all innovations required interaction Independent innovation T/out Africa and S.W. Asia Mesopotamia T/out S.W. Asia, Europe, Central and East Asia, W. Africa Indus River Valley T/out S.W., Central, East Asia Ganges River Valley T/out South, SE, and SW Asia Huang River Valley T/out East and SE Asia Torsten Hagerstrand Theorized that innovations of all kinds tend to diffuse from their hearths in stages 1st stage: Gain acceptance in place of origin 2nd stage Begin to spread rapidly outward from region Early adopters “innovators” Majority adopters 3rd stage Slowing and reaching maximum dispersal and saturation Late adopters “Laggards” Research led to seeing that diffusion followed an S-curve pattern Example: Cell phone diffusion Cultural Convergence and Divergence Cultural Convergence Definition: Definition: Acculturation Occurs when two cultures adopt each other’s traits and become more alike Cultural Divergence Assimilation Occurs when two cultures become increasingly different Occurs when two cultures come into contact with one another and the “weaker” of the two adopts traits from the more dominant culture Sometimes acculturation leads to assimilation Often one group moves away from the territory of other When the original traits of the weaker culture are completely replaced by more dominant culture Transculturation When two cultures of just about equal power meet and exchange ideas Acculturation NH BMHAWK #3 BMHAWK #4 Assimilation