METHODS OF RESEARCH
advertisement

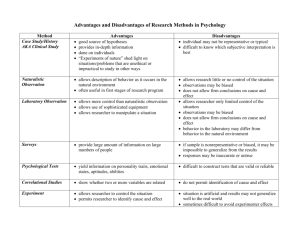
METHODS OF RESEARCH HOW PSYCHOLOGISTS ANSWER THE “WHY” OF ANIMAL AND HUMAN BEHAVIOR NATURALISTIC OBSERVATION DEFINITION: secret observation of the subjects-animal or human-in daily activity, recording their behavior. ADVANTAGES and DISADVANTAGES ADVANTAGE Creatures will behave normally because they don’t know anyone is watching them. DISADVANTAGES Since researchers can’t talk to subject they may misinterpret behavior. EXAMPLE OF NATURALISTIC OBSERVATION Jane Goodall’s research with the Gorillas. Charles Darwin-sea journey INTERVIEWS Definition: Research method for studying people face to face and asking questions. Advantages: Researcher can obtain personal, detailed information. Disadvantages Researcher biases can influence behavior.— how? All of us have our own prejudices against certain types of people, certain age groups, etc. These factors could influence our questions as well as our interpretations of the answers Subject’s responses may not be completely honest. CASE STUDY METHOD Definition: Research that collects lengthy, detailed information about a person’s background, usually for psychological treatment. CASE STUDY METHOD **The goal is to find out as much as possible about how the individual’s personality has evolved from early years in order to shed light on their present-day problems. (This is an advantage to this method) Disadvantage: Subject may not be honest. Researcher bias can influence behavior **Caution: You can’t generalize from your findings—it may not be true of others. PSYCHOLOGICAL TESTS: . Definition: objective methods for observation and measurement of subjects in various areas, such as IQ or personality PSYCHOLOGICAL TESTS Advantages: Accurate, objective information-little chance of distorting the results. Disadvantages: Tests are limited in the amount of info. they can obtain. Definition: a method of research that studies the same group of people over an extended period of time. ( years) Advantages: good for certain types of research like studies on development Disadvantages: expensive and timeconsuming (representative sample) Definition: method of research that looks at different age groups at the same time in order to understand changes that occur during lifetime. CROSS-SECTIONAL METHOD Example: Does intelligence notably decline with age? Researchers took samples from each age group and compared them. Advantages: Samples used are usually representative of population as a whole. Less expensive and time- consuming than longitudinal Disadvantages: Not appropriate for some types of research.