Sex Cells - Manhasset Public Schools
advertisement

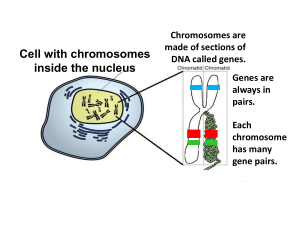
Aim #51: How do organisms create offspring through sexual reproduction? What is Sexual Reproduction? It involves the joining of two cells to begin the development of a new individual. These special cells are called: Sex Cells (Gametes) What are the names of these sex cells? Egg cell (Female) Sperm Cell (Male) The joining of a sperm cell with an egg cell is called fertilization. 1) How many chromosomes do we have in our cells? We have 46 chromosomes in each our body cells. We can also say that we have 23 pairs of chromosomes Karyotype 2) Why do we have 2 of each chromosome? We get one chromosome from each parent 3) Each pair of chromosomes are called: Homologous Chromosomes 4) Homologous Chromosomes: Mom Eye Color B Dad G Hair Color B R Gene Part of a chromosome that codes for a trait Have genes that code for the same trait, but may have different versions of that trait 5) How are chromatids different than homologous chromosomes? Chromatids are exact duplicates of each other Homologous chromosomes have genes that code for the same trait, but they may code for different versions of that trait 6) How many chromosomes do the offspring have after mitosis? 46X Mitosis 46X 46X 7) Do our sex cells have 46 chromosomes? NO!!! 8) What would happen if our sex cells did have 46 chromosomes? 46 + 46 Egg 92 Offspring Sperm The offspring would have 92 chromosomes 9) Sexual Reproduction: 23 + 23 Egg Sperm 46 Offspring A fertilized egg cell is called a Zygote 10) Characteristics of Sexual Reproduction: 1) Is the creation of a new individual from 2 parents. 2) Offspring are not genetically identical to the parents. Date: February 3, 2016 Aim #51: How do organisms create offspring through sexual reproduction? Do Now: Warm-Up Notebook Date Title of Activity 2/3 Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction Page # 89 HW: 1) Read Chapter 11-4 (Meiosis) pages 275-278 and complete Cornell Notes Outline due Friday – Consider Section Assessment Questions (p. 278) in your summary 2) Yarn Lab due Friday! 11) Sex Cells (Gametes) • Sex Cells: SPERM and EGG • Sex cells should have 1/2 the normal number of chromosomes 12) Chromosome Number • Diploid cells: (2n) normal number of chromosomes (Body Cells) • Haploid cells: (n) ½ the normal number of chromosomes (Sex Cells) Diploid vs Haploid Diploid Cells Haploid Cells and Fertilization 13) Meiosis •The process by which haploid (sex) cells are produced with half the number of chromosomes. 14) What is the end result of meiosis? 46X Meiosis 23X 23X 23X 23X 15) Where does meiosis occur? Gonads – Ovaries and Testis 16) Why is meiosis important? • Maintains the number of chromosomes from generation to generation • Provides genetic variation • Only during fertilization (union of sperm and egg) is the full (diploid) set of chromosomes restored. Practice Problems: