ppt of lymph system - faculty development
advertisement

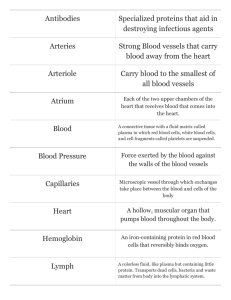
The Lymph System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Overview • • • • lymphatic vessels lymph lyphoid cells and tissues lymphoid organs lymph nodes o spleen o thymus o tonsils o other lymphoid tissue o • • • lymphatic vessels collects excess interstitial fluid returns fluid to blood one way system o flows toward the heart lymphatic vessels lymphatic capillaries - cells overlap - collagen filaments anchor ends lymphatic vessels lacteals - specialized lymph capillaries in lining of small intestine - absorb fats - chyle = fatty lymph that is milky white - moves into lymph vessels lymphatic vessels lymphatic collecting vessels - similar structure to veins - more valves - reconnect (anastamose) more often lymphatic vessels lymphatic trunks - formed by union of largest vessels lymphatic vessels lymphatic ducts - right - thoracic - cisterna chyli enlarged sac where lumbar trunks meet lymphatic vessels • lyphangitis o when lymph vessel is inflamed, blood vessels that feed them become congested with blood lymph - similar to blood plasma - white blood cells - debris/pathogens lymph transport • • • no pump skeletal muscles muscles used to breathe o • • • o diaphragm intercostal muscles smooth muscle in lymphatic trunks and thoracic duct valves prevent backflow arterial pumping lymph transport • lymphedema o • o flow is blocked lymph vessels removed lymph vessels can regrow! lymphoid cells • lymphocytes o • • • o T cells B cells macrophages dendritic cells reticular cells lymphoid tissue • • houses and provides a site for proliferation of lymphocytes surveillance point for lymphocytes and macrophages lymphoid tissue types diffuse • found in every body organ o scattered o • lymphoid follicles o o solid spherical bodies germinal center lymph nodes clusters - inguinal - axillary - cervical functions - filter lymph - help activate the immune system lymph nodes - average 1" bean shaped - capsule with trabeculae - cortex - medulla lymph nodes flow through node - afferent lymph vessels - efferent lymph vessels spleen • • • • size of fist largest lymphoid organ site of lymphocyte proliferation site of immune surveillance spleen • cleans the blood o o o stores and releases breakdown products of RBCs stores blood platelets site of RBC production in fetus spleen spleen thymus thymus • • many thymic lobules cortex o • rapidly dividing lymphocytes medulla o thymic corpuscles development of regulatory T cells • prevent autoimmune diseases tonsils • • • • palatine tonsils lingual tonsil pharyngeal tonsil tubal tonsils tonsils tonsillar crypt other lymphoid tissue Peyer's patches - aggregated follicles in the far end of the ileum and appendix - immune function of GI tract other lymphoid tissue MALT - mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue - Peyer's patches - appendix - tonsils - lymphoid follicles in bronchi - lymphoid follicles in genitourinary organs