materials. - University of Toledo
advertisement

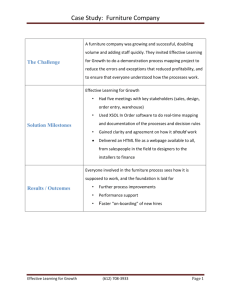
Inclusive Placement Opportunities for Preschoolers: A Systems Approach to Inclusion A project of the Virginia Department of Education and the Training and Technical Assistance Centers of Virginia Outcomes • Factors to consider when arranging the preschool environment • Understanding how environment impacts behavior • Resources Why use structure? Helps the person with autism . . . • Understand • Learn easier • Stay calm • Achieve independence • Learn appropriate behaviors Shopping Think about a store you dislike shopping in. Why? Think about a store you love to shop in. Why? Physical environment • Assess the need for physical structure o • Begin with more structure and fade as appropriate Establish clear physical and visual boundaries o Help the person with autism understand the function of different environments • Minimize potential visual and auditory distractions • Design specific areas o Design of classroom o Area specific Physical structure Clear physical and visual boundaries Established teaching areas Individual work area Individual work area • Schedule area Minimal visual and auditory distractions Large group Teacher’s Desk • 1:1 Break Area Computer • Coat area Physical structure Find the mistakes Independent Work area Circle Time Break area Door Teacher’s desk Computer Independent work area How might you change? • Think about what you just learned about structuring the environment for students with autism • Take graph paper out of your packet and sketch how you could change your classroom based on what you have just learned Factors affecting the classroom environment • Arrangement of the physical environment • Classroom schedule • Program staff • Children The physical environment Considerations • Natural flow of activities • Wheelchairs • Adaptive equipment • Number and characteristics of children Activity areas Considerations • Areas are clearly defined relative to activities • Wide paths exist for braces, wheelchairs, crutches, walkers, etc. • Areas invite the children to explore, discover and talk about their play Furniture and fixtures Considerations • Allows for active participation in activities with peers • Child-sized — there should be no dangling feet • Adaptations and modifications should be made to existing furniture, such as no tech/low tech, etc. Furniture and fixtures Considerations • Commercially made furniture, such as standing tables, special chairs, outdoor playground equipment, etc. • Bathroom adaptations may be needed, including adapted seats, potty chairs and a private diaper/catheterization changing area Materials Considerations – variety • Books should vary in length, complexity and genre • Puzzles should have different sizes and number of pieces • Have realistic and real play materials, such as pots, pans, clipboards, pens, flashlights, etc. • All materials should be developmentally, functionally and age-appropriate Materials Organization and storage • Easily accessible • Clearly visible • Clearly labeled • Tactile cues IPOP’s top 10 reasons for classroom schedules The daily classroom schedule provides a tangible sequence of activities over the course of the program and the amount of time spent in each activity The daily schedule Considerations • Keep waiting times to a minimum and plan for transitions and wait times • Provide adequate time for each activity • A labeled visual schedule promotes literacy and understanding of sequence Arrival and greeting Considerations • Warm, loving and enthusiastic greeting • Peer or adult assistance to help with the transition • Late arrivers • Extra support for extra special kids Circle Considerations • Duration • Set the tone for the day • Natural time to encourage and enhance language and social emotional skills • Developmentally appropriate for all children • Availability of technology Centers and free choice Considerations • Child vs. teacher directed • Duration • Purpose • Accessibility • Availability of technology Snack and lunch time Considerations • Embed language and daily living skills, objectives or benchmarks • Promote independence • Provide options for seating or positioning • Adapt utensils as necessary • Be aware of nutrition and oral sensory motor issues Outdoor play Considerations: • Gross motor development • Back-up plan in case of inclement weather • Accessibility and adaptation of activities • Child-to-child interaction versus adult interaction — level of support Story time Considerations • Short attention spans • Genre – ethnically diverse, children with disabilities • Child involvement vs. sitting and listening Closing Considerations • Method for dismissal • Plan for the various transitions, such as individual pick-up and different bus schedules Summarize with an acrostic Environment A transition is any shift in activity that requires students to change ________ or ___________. A transition is any shift in activity that requires students to change locations or materials. Project SLIDE, Juniper Gardens Children’s Project, (1998). “Effective instructional strategies to facilitate: Teacher’s guide for Project SLIDE.” Kansas City: The University of Kansas. Transitions Considerations • Plan for transitions! • Should be fun and short • Remember to plan for children who need extra assistance Behavior Considerations • Strategies for holding attention – novelty, seating options, high/low energy activities, etc. • Visuals to support children’s independence (behavior and communication) • Plan each transition as part of the lesson plan The program staff • Communication and collaboration • Team meetings • Staff support • Continued professional development The children Considerations • Number of children • Characteristics of the children • Needs of all children • Same-aged peers Resources • IPOP training guides • “Promoting the Social Emotional Competence of Young Children.” Center on the Social Emotional Foundations for Early Learning, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, (2003). • Your regional VDOE T/TAC o Region 1 and 8: www.vcu.edu/ttac/ o Region 2 and 3: www.ttac.odu.edu/ o Region 2 and 3: www.wm.edu/ttac/ o Region 4: www.kihd.gmu.edu/ttac/ o Region 5: ttac.cisat.jmu.edu/ o Region 6 and 7: www.ttac.vt.edu/