PPOD Medications Supplement_(Master File)_ptr comments
advertisement

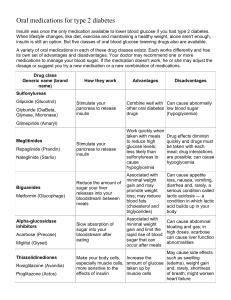
WORKING TOGETHER TO MANAGE DIABETES MEDICATIONS SUPPLEMENT SECTION A T AB L E 1 . O R AL AG E N T S T O T R E AT T Y P E 2 D I AB E T E S * DIABETES MEDICATIONS Agent Class Primary Action Typical Dosage Side Effects Precautions Critical Tests Comments Tolbutamide (Ornase TM ) Tolazamide (Tolinase TM ) Chlorpropamide (Diabenese TM ) Sulfonylureas (1st generation) Increases insulin production in the pancreas. Tolbutamide: 0.25–2.0 g/day in divided doses; maximum, 3 g/day Tolazamide: 100–1,000 mg/day in divided doses; maximum, 1 g/day Chlorpropamide: 100–500 mg/day twice a day; maximum, 750 mg/day Hypoglycemia, weight gain, hyperinsulinemia Disulfiram reaction with alcohol Chlorpropamide remains active for up to 60 hours. Use extreme caution with elderly patients or patients with hepatic dysfunction. All are metabolized in liver. Periodic evaluation of liver function is suggested. Use of these agents is not recommended unless the patient has a well-established history of taking them. Second-generation sulfonylureas provide more predictable results with fewer side effects and more convenient dosing. Glyburide (Micronase TM , Diabeta TM , Glynase TM ) Glipizide (Glucotrol, Glucotrol XL TM ) Glimepiride (Amaryl TM ) Sulfonylureas (2nd generation) Increases insulin production in the pancreas. Clearance may be diminished in patients with hepatic or renal impairment. Ineffective if c-peptide test is negative. (type 1 diabetes) Glipizide is preferred with renal impairment. Doses >15 mg should be divided. Glimepiride indicated for use with insulin. Shown to have some insulin-sensitizing effect. Repaglinide (Prandin TM ) Meglitinide Increases insulin release from pancreas. Glyburide: 1.25–5 mg/once or twice a day; Hypoglycemia, weight maximum, 20 mg/day gain, hyperinsulinemia Glynase: 0.75–12.0 mg/day; maximum 12 mg/day Glipizide: 2.5–20.0 mg/once or twice a day; maximum, 40 mg/day; or XL* 2.5–10.0 mg/once or twice a day; maximum, 20 mg/day Glimepiride: 1–8or mg/day; maximum, 8 mg/day Hypoglycemia, weight New diagnosis A1c <8%, 0.5 mg; A1c >8%, 1–2 mg, 15–30 min before gain, hyperinsulinemia each meal; increase weekly until results are obtained; maximum, 16 mg/day Use with caution on patient with hepatic or renal impairment. Ineffective if c-peptide test is negative. (type 1 diabetes) Patients should be instructed to take medication no more than 30 minutes prior to a meal. If meals are skipped or added, the medication should be skipped or added as well. Nateglinide (Starlix TM ) Phenylalanine derivative Increases insulin release from pancreas. 60–120 mg before each meal Minimal risk of hypoglycemia Currently no contraindications available. Use with caution with moderate to severe hepatic disease. Periodic evaluation of liver function tests. Approved as monotherapy or in combination with metformin or TZD. Has only a 2-hour duration of action. Metformin (Glucophage TM ) Biguanide Decreases insulin resistance, primarily decreasing hepatic glucose output; minor increase in muscle glucose uptake. 500 mg/day twice a day with meals, increase by 500 mg every 1–3 wk, twice or three times a day; usually most effective at 2,000 mg/day; maximum, 2,550 mg/day Nausea, diarrhea, metallic taste, possible lactic acidosis Due to increased risk of lactic acidosis, should not use if suspect frequent alcohol use, liver or kidney disease, or CHF. Contraindicated if serum creatinine is: >1.5 mg/dL in men or >1.4 mg/dL women. Do not use if creatinine clearance is abnormal. Monitor hematological and renal function annually. Especially beneficial in obese patients due to potential for weight loss, improved lipid profile, and lack of potential for hypoglycemia requiring supplemental carbohydrate intake. Discontinue for 48 hr after contrast dye procedures. Rosiglitazone (Avandia TM ) Thiazolidinedione Decreases insulin resistance, increasing glucose uptake, fat redistribution; minor decrease in hepatic glucose output; preserves ß-cell function; decreases vascular inflammation. Initially 4 mg/day in single or divided doses. Increase to 8 mg/day in 12 wk, if needed; maximum, 8 mg/day with or without food Minor weight increase of 3–6 lbs., edema Should not be used in patients with CHF or hepatic disease. Can cause mild-tomoderate edema. Avoid initiation if ALT >2.5X upper limit of normal. Measure ALT periodically. Discontinue if ALT >3X upper limit of normal. Approved for use as monotherapy and in combination with metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin. Less interactions associated with CYP-450 Pioglitazone (Actos TM ) Thiazolidinedione Decreases insulin resistance, increasing glucose uptake, fat redistribution; minor decrease in hepatic glucose output; preserves ß-cell function; decreases vascular inflammation. Initially 15 or 30 mg/day; maximum with or without food 45 mg for monotherapy, 30 mg for combination therapy Minor weight increase of 3–6 lbs., edema Should not be used in patients with CHF or hepatic disease. Can cause mild-tomoderate edema. Avoid initiation if ALT >2.5X upper limit of normal. Measure ALT periodically. Discontinue if ALT >3X upper limit of normal. Approved as monotherapy or for use with metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin. Metabolized via CYP-450. Patients taking other agents also using CYP-450 pathway should be evaluated for drug interactions and monitored more frequently for glycemic control. Acarbose (Precose TM ) Miglitol (Glyset TM ) Alpha-glucosidase inhibitor Slows absorption of complex carbohydrate from GI tract. 25 mg/day; increase by 25 mg/day every 4–6 wk; maximum, split dose before meals (with first bite of food) 300 mg/day (150 mg/day for weight <60 kg) Gas and bloating, sometimes diarrhea for both drugs Should not be used if GI disorders are concurrent. Avoid if serum creatinine is >2.0 mg/dL. Monitor serum transaminase every 3 months for 1st year of therapy. Approved for use as monotherapy and in combination with metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin. If used with hypoglycemic agents, such as sulfonylureas or insulin, must treat hypoglycemia with glucose. Glucovance TM (Glyburide and Metformin) Sulfonylureas and Biguanide Decreases hepatic glucose production and increases insulin secretion. Hypoglycemia, weight gain, lactic acidosis Should not be used if suspect frequent alcohol use, liver or kidney disease, or CHF. Contraindicated if serum creatinine is >1.5 mg/dL in men, or 1.4 mg/dL in women, or if creatinine clearance is abnormal. Monitor hematologic and renal function annually. Patients may frequently use 2 different dose tablets to attain desired daily dosage and results. Discontinue for 48 hr after procedure using contrast dye. Metaglip TM (Glipizide and Metformin) Sulfonylureas and Biguanide Decreases hepatic glucose production and increases insulin secretion. Ratios of glyburide and metformin (in mg): 1.25/250, 2.5/500, 5/500. Initial: 1.25/250 once or twice a day, increased every 2 weeks. 2nd line: 2.5–5/500 twice a day, increased every 1–2 weeks. Average dose 7.5/1,500. Maximum dose should not exceed 20 mg glyburide/2,000 mg metformin daily. Ratios of glipizide and metformin (in mg): 2.5/250, 2.5/500, 5/500. Initial: 2.5/ 250 once or twice a day, increased every 2 weeks. 2nd line: 2.5–5/500 twice a day, increased every 1–2 weeks. Maximum dose should not exceed 20 mg glipizide/ 2,000 mg metformin daily. Hypoglycemia, weight gain, lactic acidosis Should not be used if suspect frequent alcohol use, liver or kidney disease, or CHF. Contraindicated if serum creatinine is >1.5 mg/dL in men, or >1.4 mg/dL in women, or if creatinine clearance is abnormal. Monitor hematologic and renal function annually. Patients may frequently use 2 different dose tablets to attain desired daily dosage and results. Discontinue for 48 hr after procedure using contrast dye. Avandamet TM (Rosiglitazone and Metformin) Thiazolidinedione and Biguanide Decreases hepatic glucose production, increases glucose uptake, decreases insulin resistance, and preserves ß-cell function. Ratios of rosiglitazone and metformin: 1 mg/500 mg, 2 mg/ 500 mg, 4 mg/500 mg, 2 mg/ 1,000 mg, 4 mg/1,000 mg twice a day; dosage individualized based on current therapy. Maximum, 8 mg/2,000 mg per day Edema, possible lactic acidosis Should not be used if suspect frequent alcohol use, liver or kidney disease, or CHF. Contraindicated if serum creatinine is >1.5 mg/dL in men, or >1.4 mg/dL in women, or if creatinine clearance is abnormal. Monitor hematologic and renal function annually. Less expensive than using agents separately. Reported decrease in GI upset associated with metformin and weight increase associated with rosiglitazone. Discontinue for 48 hr after procedure using contrast dye. Combinations Adapted from © 2005 The Diabetes Center, Old Saybrook, CT. Used by permission. A1c = glycated hemoglobin ALT = alanine aminotransferase CHF = congestive heart failure FPG = fasting plasma glucose GI = gastrointestinal XL = extended release 1 WORKING TOGETHER TO MANAGE DIABETES *Agents in a class of medicines share mechanisms of action, require similar precautions, and generaly have similar side effects. For proper usage, please read label. Agents should not be used in patients with type 1 diabetes. DIABETES MEDICATIONS SUPPLEMENT 2 TABLE 2. IMPORTANT INSULIN INFORMATION* Insulin Onset Peak Effective Duration Maximal Duration TABLE 4. RECOMMENDED INSULIN STORAGE Comments Insulin Type Human Lispro (HumalogTM) Aspart (NovalogTM) Glulisine (ApidraTM) Regular NPH Lente Ultralente Novolin 70/30 Humulin 70/30 Humalog 75/25TM Novolog 70/30TM <15 min <15 min <15 min 0.5–1 hr 2–4 hr 3–4 hr 6–10 hr 0.5–1 hr 1–2 hr 1–3 hr 0.5–1 hr 2–4 hr 4–10 hr 4–12 hr Minimal 2–10 hr 2–4 hr 3–5 hr 3 hr 3–5 hr 10–16 hr 12–18 hr 18–20 hr 10–16 hr 3–5 hr 4–6 hr 3 hr 4–8 hr 14–18 hr 16–20 hr 20–30 hr 14–18 hr <15 min 1–2 hr 10–16 hr 14–18 hr Should be taken just prior to or just after eating. Insulin glargine (LantusTM) 4–6 hr None 24 hr 24 hr Cannot be mixed with any other insulin. Stress site rotation and not to use same syringe used with other insulins. Not recommended for pre-filling syringes. 0.5–2 hr 3–4 hr 4–6 hr 6–8 hr 4–6 hr 4–6 hr 8–14 hr 8–14 hr 16–20 hr 16–20 hr 20–24 hr 20–24 hr Conversion to human insulin recommended. Dose changes required (usually a 10% reduction in dose when switching to human). Animal Source Regular NPH Lente Should be taken just prior to or just after eating. Best if taken 30 min before a meal. Bedtime dosing minimizes nocturnal hypoglycemia. Frequently used in pediatric patients over NPH. Can convert to Humalog 75/25TM or Novolog 70/30TM dose per dose. Adapted from © 2005, The Diabetes Center, Old Saybrook, CT. Used by permission. *Site rotation for injections is necessary for a l types of insulin. Glucagon Exenatide (ByettaTM) Pramlintide (SymlinTM) Primary Action Converts liver glycogen to glucose Modulates gastric emptying, glucagon production. Increases satiety, leading to decreased caloric intake. For type 2 diaModulates betes gastric emptying, glucagon production. Increases satiety, leading to decreased caloric intake. How Supplied/Storage 1 mg vial with diluent; emergency kit, 1 mg vial with prefilled syringe of diluent. Before reconstitution, room temperature until expiration date. After reconstitution, may be stored for up to 48 hours under refrigeration. 5 mcg/ml prefilled pen 10 mcg/ml prefilled pen Typical Dosage 0.5–2 mg subcutaneous Duration Action 15 min, should be followed by carbohydrate snack. 5 mcg BID Approximately subcutaneous for 10 hours 1 month, then Not in use: refrigerate until 10 mcg BID, expiration date. In use: injected within room temperature, discard 60 minutes before after 30 days. morning and evening meal. 5 ml vials containing Type 1: Elimination t 0.6 mg/ml. Requires U-100 15–60 mcg of 48 minutes insulin syringe for injection starting; 15 mcg subcutaneous Not in use: refrigerate until before meals of expiration date. In use: 30 gm or more room temperature, discard carbohydrate. after 28 days. Type 2: 60–120 mcg starting; 60 mcg subcutaneous. Titrate as directed by prescriber. Adapted from © 2005, The Diabetes Center, Old Saybrook, CT. 2 1/2 Side Effects Precautions Comments Occasional nausea and vomiting Patient should be instructed to teach colleagues, family, etc. how to give injection. Only use if patient is unconscious or unable to eat or drink. Nausea and hypoglycemia most common; occasional vomiting, diarrhea, jitters, dizziness, headache. Must be reconstituted prior to injection. Should be followed by carbohydrate snack and blood glucose testing every 15 minutes until glucose level returns to acceptable levels. Consider lowering dose of sulfonylurea to avoid hypoglycemia when starting. May reduce the rate of absorption of oral medication. Medications requiring threshold concentrations should be taken 1 hour prior to injection. Nausea and Contraindicated with: Requires patient testing of hypoglycemia hypoglycemic unawareblood sugars before and most common. ness, gastroparesis. after meals, frequent Doses are Patient non-adherence. physician followup, and adjusted based thorough understanding of on presentation Should never be mixed how to adjust doses of with insulin. Insulin dose of these side insulin and Symlin. should be reduced by 50% May reduce the rate of effects. when starting. Occasional absorption of orally adminvomiting, istered medication. stomach pain, Medications requiring dizziness, threshold concentrations indigestion. should be taken 1 hour prior to injection. WORKING TOGETHER TO MANAGE DIABETES VIAL Opened HumalogTM, NovologTM, HumulinTM, NovolinTM, ApidraTM LantusTM (10 mL) Detemir (LevemirTM) release pending 28 days 28 days Unopened Until expiration date Until expiration date PENS/CARTRIDGES Room Temperature (59°F–86°F) Opened Unopened 28 days 28 days 28 days 28 days Not in use HumalogTM In use Humulin N Humulin 70/30TM Humalog Mix 75/25TM Until expiration date Until expiration date Until expiration date Until expiration date Until expiration date 28 days 28 days 14 days 10 days 10 days NovologTM Novolog Mix 70/30TM Novolin RTM (prefilled and 1.5-mL cartridge) Novolin RTM (3-mL cartridge) Novolin NTM (prefilled and 1.5-mL cartridge) Novolin NTM (3-mL cartridge) Novolin 70/30TM (prefilled and 1.5-mL cartridge) Novolin 70/30TM (3-mL cartridge) Detemir (LevemirTM) release pending ApidraTM LantusTM Self-filled syringes Until expiration date Until expiration date Until expiration date Until expiration date Until expiration date Until expiration date Until expiration date Until expiration date Until expiration date Until expiration date Until expiration date 14 days* 28 days 14 days 30 days 28 days 7 days 14 days 7 days 10 days Humulin RTM ( available in cartridge only) TM 28 days 28 days 7 days* Adapted from © 2005, The Diabetes Center, Old Saybrook, CT. Used with permission. *Suggested, not clinicaly established TABLE 5. GLUCOSE-LOWERING ACTIVITY—ORAL DIABETES AGENT “NEW TABLE 3.” GLUCAGON AND GLUCAGON-LIKE PEPTIDES (GLP-1 ) Agent Refrigerated (36°F–46°F) Not for use with type 1 diabetes, patients with severe renal disease or ESRD, or severe GI disease Medication Blood Glucose Most Affected SMBG* Testing to Recommend Greatest Risk for Hypoglycemia Sulfonylureas Fasting and postprandial Meglitinide phenylalanine derivative Biguanide Postprandial Fasting Alpha-glucosidase inhibitor Thiazolidinedione Postprandial Fasting and postprandial GlucovanceTM Fasting and postprandial MetaglipTM Fasting AvandametTM Fasting and postprandial 2–3 times per day, especially fasting 2 hr after meal Fasting 2 hr after meal 2–3 times per day, especially fasting 2–3 times per day, especially fasting 2–3 times per day especially fasting 2–3 times per day especially fasting Nocturnal, fasting, 4–6 hr after meals 2–3 hr after meals After exercise if prolonged and strenuous None None Nocturnal, fasting, 4–6 hr after meals Nocturnal, fasting 4–6 hr after meals None Adapted from © 2005, The Diabetes Center, Old Saybrook, CT. Used with permission. SMBG = self-monitoring of blood glucose “NEW TABLE 6.” RECOMMENDED CONTROL MEASURES Biochemical Index Goal Preprandial Peak postprandial ADA Alc AACE Alc Blood pressure LDL TG HDL 90–130 mg/dL <180 mg/dL <7% <6.5% <130/80 <100 <150 >40 Adapted from © 2005, The Diabetes Center, Old Saybrook, CT. Used with permission. LDL = low density lipoprotein TG = triclycerides HDL = high density lipoprotein DIABETES MEDICATIONS SUPPLEMENT 4 SECTION B M E D I C AT I O N S T O T R E AT HIGH BLOOD CHOLESTEROL Category Brand Name Generic Name Manufacturer Minimum Daily Maximum Daily Special Considerations* Dose Dose HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) Lipitor Lescol Lescol XL Mevacor Pfizer Novartis Novartis Merck generic† Aura Labs 10 mg 20 mg 80 mg 10 mg 10 mg 20 mg 80 mg 80 mg 80 mg 80 mg 80 mg 60 mg Pravachol atorvastatin fluvastatin fluvastatin lovastatin lovastatin lovastatin (extended-release) pravastatin 10 mg 80 mg Crestor Zocor Zetia rosuvastatin simvastatin ezetimibe Bristol-Myers Squibb Astra Zeneca Merck Merck Schering-Plough 5 mg 5 mg 10 mg 40 mg 80 mg 10 mg Niaspan nicotinic acid Kos (extended release) 300 mg 2,000 mg (starting dose) nicotinic acid generic† 300 mg Advicor lovastatinniacin Kos 20 mg/500 mg 40 mg/2,000 mg Vytorin Merck Schering Plough Pfizer generic† Abbott 10 mg/10 mg 40 mg/10 mg Tricor simvastatinezetimibe gemfibrozil gemfibrozil fenofibrate 1,200 mg 1,200 mg 54 mg 1,200 mg 1,200 mg 160 mg LoCHOLEST LoCHOLEST light Questran cholestyramine cholestyramine light cholestyramine Warner Chilcott Warner Chilcott 4g 4g 24 g 24 g Par Pharmaceuticals Par Pharmaceuticals Upsher Smith generic† generic† 4g 24 g 4g 24 g 4g 4g 4g 24 g 24 g 24 g Altocor Cholesterol absorption inhibitors Nicotinic acid (niacin) Lipid combinations Fibric acid derivatives Bile acid sequestrants Lopid Questran light cholestyramine light Prevalite cholestyramine cholestyramine cholestyramine light Welchol colesevelam 5 Sankyo 2,000 mg Main action: Lowers LDL (“bad”) cholesterol. Have blood tests for liver enzyme concentrations. Notify physician if severe muscle aches or pain develops. Use caution if combined with fibric acid derivatives due to the increased risk of rhabdomyolysis. Main action: Lowers LDL cholesterol; inhibits absorption of cholesterol. If used with a statin, take together. If used with bile acid sequestrant, ezetimibe should be taken 2 hr before or 4 hr after bile acid sequestrant. Main action: Lowers LDL cholesterol increases HDL (“good”) cholesterol, lowers triglycerides. Take with food. May cause flushing. May increase blood glucose levels. Have blood tests for liver enzyme concentrations. Long-acting forms may be more likely to cause liver malfunction. Main Action: Reduces LDL, TC, and TG increases HDLdue to the and individual Main Action: Reduces LDL actions of niacin and lovastatin. cholesterol. Main action: Lowers triglycerides, increases HDL cholesterol. Perform blood tests for liver enzyme concentrations. Notify physician of muscle pain immediately. Main action: Lowers LDL cholesterol. May cause constipation and stomach upset. May need to be taken at a different time than other medications to avoid drug interactions. May increase triglycerides blood concentrations. Welchol unit for dose? 1,875 (3 4,375 (7 tablets) tablets) HMG-Coa = LDL = low-density lipoprotein HDL = high-density lipoprotein TC = total cholesterol TG = plasma triglycerides †generic = generic drug manufacturers SECTION Category Brand Name Generic Name Manufacturer Angiotensinconverting Accupril Aceon quinapril perindopril Pfizer Solvay Altace enzyme (ACE) Capoten inhibitors Lotensin Mavik Monopril ramipril captopril captopril benazepril trandolapril fosinopril Monarch Apothecon generic† Novartis Abbot Bristol-Myers Squibb generic† Merck generic† Schwarz Merck generic† AstraZeneca AstraZeneca Bristol-Myers Squibb Sankyo Merck Novartis BoehringerIngelheim Biovail Bayer Searle Searle generic† Roche Roche Biovail Biovail generic† Searle Watson Reliant Reliant Abbott Abbott Pfizer AstraZeneca Pfizer Pfizer generic† AstraZeneca Andrx Pharm Forest Schwarz Schwarz Prinivil Univasc Vasotec Zestril Angiotensin II Atacand receptor Avapro blockers Benicar Cozaar Diovan Micardis Calcium channel blockers Teveten Adalat CC* Calan Calan SR Cardene* Cardene SR* Cardizem Cardizem CD Covera HS* Dilacor XR* DynaCirc* DynaCirc CR* Isoptin Isoptin SR* Norvasc Plendil* Procardia* Procardia XL* Sular* Taztia XT Tiazac Verelan Verelan PM fosinopril lisinopril lisinopril moexipril enalapril enalapril lisinopril candesartan irbesartan olmesartan losartan valsartan telmisartan eprosartan nifedipine verapamil verapamil verapamil nicardipine nicardipine diltiazem diltiazem diltiazem verapamil diltiazem isradipine isradipine verapamil verapamil amlodipine felodipine nifedipine nifedipine nifedipine nisoldipine dilaizem diltiazem verapamil verapamil Minimum Daily Maximum Daily Special Considerations Dose Dose 5 mg 4 mg 80 mg 16 mg 1.25 mg 25 mg 25 mg 5 mg 1 mg 10 mg 20 mg 450 mg 450 mg 20 mg 8 mg 80 mg 10 mg 2.5 mg 2.5 mg 7.5 mg 2.5 mg 1 mg 2.5 mg 15 mg 150 mg 80 mg 80 mg 80 mg 60 mg 40 mg 8 mg 80 mg 32 mg 300 mg 20 mg 25 mg 80 mg 20 mg 40 mg 100 mg 320 mg 80 mg 400 mg 30 mg 120 mg 120 mg 120 mg 60 mg 60 mg 120 mg 120 mg 120 mg 180 mg 180 mg 2.5 mg 2.5 mg 120 mg 120 mg 2.5 mg 2.5 mg 30 mg 30 mg 30 mg 20 mg 120 mg 120 mg 120 mg 100 mg 800 mg 120 mg 480 mg 480 mg 480 mg 120 mg 120 mg 360 mg 360 mg 360 mg 480 mg 540 mg 20 mg 20 mg 480 mg 480 mg 10 mg 20 mg 120 mg 120 mg 120 mg 60 mg 480 mg 540 mg 480 mg 400 mg May cause cough. May increase potassium concentrations. Do not use potassium or salt substitutes without consulting physician. WORKING TOGETHER TO MANAGE DIABETES Brand Name Thiazides and related diuretics Diuril Minimum Daily Maximum Daily Special Considerations Dose Dose 2,000 mg 2,000 mg 10 mg 100 mg 100 mg 100 mg 100 mg 5 mg 5 mg 100 mg 1.0 mg 10 mg 20 mg 10 mg 10 mg 10 mg 20 mg 20 mg 200 mg 80 mg 80 mg May increase blood glucose concentrations. Take in morning to minimize diuretic effect at night. May cause low potassium. Potassiumsparing diuretics Aldactone Diamox 400 mg 400 mg 300 mg 20 mg 20 mg 1,000 mg 1,000 mg Do not use potassium or salt Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 50 mg 50 mg 50 mg 5 mg 5 mg 250 mg 250 mg â-blockers Blocadren May cause dizziness and upset stomach. Do not use potassium or salt substitutes without consulting physician. May cause constipation, dizziness, upset stomach, and flushing. Call physician for shortness of breath, unusual heartbeat, or swelling of feet or hands. Manufacturer 500 mg 500 mg 2.5 mg 12.5 mg 12.5 mg 12.5 mg 12.5 mg 1.25 mg 1.25 mg 12.5 mg 0.25 mg 2.5 mg 2.5 mg 2.5 mg 0.5 mg 0.5 mg 5 mg 5 mg 25 mg 80 mg 80 mg Loop diuretics Do not use if pregnant or if trying to conceive. Caution if creatinine >1.5. Generic Name chlorothiazide Merck chlorothiazide generic† Enduron methyclothiazide Abbott HydroDIURIL hydrochlorothiazid Merck ehydrochlorothiazid generic† e Hygroton chlorthalidone Norvartis chlorthalidone generic† Lozol indapamide Aventis indapamide generic† Microzide hydrochlorothiazid Watson e Mykrox metolazone Celltech metolazone generic† Naturetin bedroflumethia Princeton zide Zaroxolyn metolazone Celltech Bumex bumetanide Roche bumetanide generic† Demadex torsemide Roche torsemide generic† Edecrin ethacrynic acid Merck Lasix furosemide Aventis furosemide generic† Do not use if pregnant or if trying to conceive. Caution if creatinine >1.5. *Agents in a class of medicines share mechanisms of action, require similar precautions and generaly have similar side effects. CC = extended release XL = extended release SR = sustained release CR = controled release CD = extended release XR = extended release PM = extended release, controled onset HS = extended release, controled onset †generic = generic drug manufacturers 7 Category Dyrenium Midamor spironolactone spironolactone triamterene amiloride amiloride acetazolamide acetazolamide Searle generic† GlaxoSmithKline Merck generic† Wyeth-Ayerst generic† Need blood test to monitor level. May cause low potassium. Need blood test to monitor level. May cause photosensitivity: sunscreen recommended. substitutes without consulting physician. May take with food if medicine upsets stomach. May cause hand/foot tingling that can be confused with neuropathy. Cartol Corgard Inderal Inderal LA* Kerlone Levatol Lopressor Tenormin Toprol XL* Visken Zebeta timolol Merck 2.5 mg 10 mg timolol carteolol nadolol generic† 2.5 mg 2.5 mg 40 mg 10 mg 10 mg 320 mg 40 mg 40 mg 40 mg 40 mg 5 mg 5 mg 10 mg 25 mg 25 mg 25 mg 25 mg 50 mg 2.5 mg 2.5 mg 2.5 mg 2.5 mg 320 mg 640 mg 640 mg 640 mg 40 mg 40 mg 40 mg 450 mg 450 mg 100 mg 100 mg 400 mg 10 mg 10 mg 20 mg 20 mg nadolol propranolol propranolol propranolol betaxolol betaxolol penbutolol metoprolol metoprolol atenolol atenolol metoprolol pindolol pindolol bisoprolol bisoprolol Abbott Bristol-Myers Squibb generic† Wyeth-Ayerst Wyeth-Ayerst generic† Searle generic† Schwarz Novartis generic† AstraZeneca generic† AstraZeneca Novartis generic† Lederle generic† May mask signs of low blood glucose levels. May alter blood glucose. Call physician for slow heart rate (<60), confusion, or swelling of feet or legs. Can cause claudication. XL = extended release LA = long acting †generic = generic drug manufacturers DIABETES MEDICATIONS SUPPLEMENT 8 C BLO O D PRES SURE * M ED I C AT I O N S T O L O W E R H I G H BL O O D P R E S S U R E ( c o n t i n u e d ) M EDIC AT IO NS T O LOW ER HIG H MEDICATIONS TO LOWER HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE ( c o n t i n u e d ) Category Brand Name Generic Name á-blockers Cardura doxazosin doxazosin terazosin terazosin prazosin prazosin carvedilol labetalol labetalol labetalol hydralazine hydralazine midoxidil methyldopa methyldopa clonidine Manufacturer Minimum Daily Maximum Daily Special Considerations Dose Dose Pfizer 1 mg 16 mg To prevent dizziness, avoid standing generic† 1 mg 16 mg up suddenly, especially with the first Hytrin Abbott 1 mg 40 mg few doses. generic† 1 mg 40 mg Minipress Pfizer 1 mg 20 mg generic† 2 mg 40 mg Combined áCoreg GlaxoSmithKline 6.25 mg 50 mg May mask signs of low blood glucose and â-blockers Normodyne Key 100 mg 2,400 mg levels. Trandate Faro 100 mg 2,400 mg Take with food to avoid stomach upset. generic† 100 mg 2,400 mg Direct Apresoline Novartis 40 mg 300 mg May cause headaches, fluid retention, vasodilators generic† 40 mg 300 mg or fast heart rate. generic† 2.5 mg 100 mg Central Aldomet Merck 250 mg 3,000 mg Do not discontinue drug suddenly † á-agonists generic 250 mg 3,000 mg without consulting physician. Catapres Boehringer0.1 mg 2.4 mg Ingelheim Catapres TTS* clonidine Boehringer0.1 mg 0.6 mg (patch) Ingelheim clonidine generic† 0.1 mg 2.4 mg Peripheral Hylorel guanadrel Fisons 10 mg 75 mg May cause dizziness, nasal AntiIsmelin guanethidine Novartis 10 mg 50 mg congestion, and depression. adrenergics resperine generic† 0.1 mg 1.0 mg *Agents in a class of medicines share mechanisms of action, require similar precautions, and generaly have similar side effects. TTS = transdermal therapeutic system †generic = generic drug manufacturers For all anti-hypertensives: Ask pharmacist before using OTC products. Monitor blood pressure regularly. To prevent dizziness, advise patient to stand up slowly. If dizziness persists, refer to health care provider. Information about high blood pressure can be found at the following Web sites: Health care professionals: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/prof/heart/index.htm Information for people with diabetes: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/hbp Drugs used to treat high blood pressure: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/hypertension/express.pdf Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Working Together to Manage Diabetes: Diabetes Medications Supplement. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, 2004. NDEP-54-S 9 WORKING TOGETHER TO MANAGE DIABETES