Introduction to Electricity

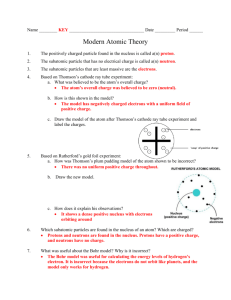
Introduction to Electricity
Energy is the ability to do work. One kind of energy is electrical energy. Electrical energy can be changed to heat, light or sound energy. There are two types of electrical energy- static and current.
1. Static Electricity – The electric charge stays in one place.
Usually found on insulators.
2. Current Electricity – The electrical charge moves.
Usually found of conductors and called electricity.
The Electrical Nature of Matter
All matter is made up of atoms. All atoms have a dense nucleus with positivity charged protons and neutral neutrons . A cloud of tiny negatively charged particles called electrons surround the nucleus. In each atom, the number of electrons surrounding the nucleus equals the number of protons in the nucleus. A single atom is always electrically neutral. When an atom becomes charged ONLY electrons move from atom to atom.
Three subatomic particles of an atom:
Subatomic
Particle
Electrical
Charge
Location in
Atom
Proton
Neutron
+
0
Size
In nucleus of an atom
Very small
In nucleus of an atom
Very small
Electron - Zoom around the nucleus
Very very very small
Three conclusions to remember
1. All matter is made of atoms, usually neutrally charged
2. All atoms have a dense nucleus with protons and neutrons and the very tiny electrons zoom around the nucleus
3. Only electrons can move from one atom to another atom
If you remove electrons from a neutral atom, the atom becomes positively charged.
If you add electrons to a neutral atom, the atom becomes negatively charged.
The Law of Electrical Charges
1. Like charges repel
2. Unlike charges attract
3. Neutral charges have no reaction to neutral charges.
Homework: Read p 393-397 Do p 398 #1-4
Introduction to Electricity
Energy is the _______________________________. One kind of energy is electrical energy.
Electrical energy can be changed to ______________________________ There are two types of electrical energy- ___________________________________.
1. Static Electricity – ___________________________________, usually found on insulators.
2. Current Electricity – _________________________________________________. Usually found of conductors and called electricity
The Electrical Nature of Matter
All matter is ____________________________________. All atoms have a dense nucleus with positivity charged protons and neutral neutrons. A cloud of tiny negatively charged particles called _____________________________________. In each atom, _______________
___________surrounding the nucleus_______________________________________ in the nucleus. A single atom is always electrically neutral. When an atom becomes charged ONLY
_________________________________________________
Three subatomic particles of an atom: (Review)
Subatomic
Particle
Electrical Charge Location in Atom
Proton
Neutron
Electron
Size
Three conclusions to remember
1. All matter is _______________________, usually neutrally charged.
2. All atoms have a dense nucleus with protons and neutrons and the very tiny electrons zoom
_______________________________________
3. Only electrons can move from one atom to another atom
If you __________________ electrons from a neutral atom, the atom becomes
__________________ charged.
If you ________________ electrons to a neutral atom, the atom becomes _______________ charged.
The Law of Electrical Charges
1. Like charges___________________
2. Unlike charges ___________________
3. Neutral charges have no reaction to neutral charges.
Homework: Read p 393-397 Do p 398 #1-4