Chapter 11 Student Notes
advertisement

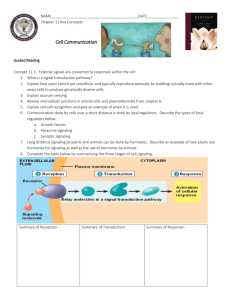
Chapter 11 Cell Communication Student Version - Cells can receive signals in several different ways o ______________________________________ – light o ______________________________________ – touch o _________________________________ – hormones **Most Common** - Cell Signaling Evolved Early in Life – YEAST! o There are 2 types of yeast, and they identify their mates using chemical signaling The chemicals they secrets causes ___________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ o Signal Transduction Pathway ___________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ This process evolved way before _____________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ - Communicating cells may be close together or far apart o _____________________________ Signaling (CLOSE) Transmitting cells secrete ______________________________________________, which influences cells in that vicinity Example of local regulators: GROWTH FACTORS ________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________; called paracrine signaling Animal Nervous system more specific; one nerve cells produces neurotransmitters and sends that signal to only ONE target cell; called __________ _____________________________________________ o Cells further away from each other: Hormones chemicals plants and animals use to signal at greater distances; utilizes the ________________________________ system and __________________________ system in animals; in plants hormones can travel in __________________________ but usually __________________________________________________________________ o Cells that are in direct contact can also communicate Animals = gap junctions (signals dissolved in cytosol can pass through using these) Plants = plasmodesmata In animals, signaling is important in _______________________________________ and in the _________________________________________ o When a cell receives a signal, it must be recognized by a specific receptor and then the information it carries must be changed into another form – this is called transduction; once this happens, then the cell can respond - Three Stages of Cell Signaling: Reception, Transduction, and Response o Earl W. Sutherland investigated how ______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ He came up with 3 specific steps in cell signaling: ________________________________ = ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ________________________________ = ________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________; may be a series of steps called a ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________ = cellular response that is triggered by the transduced signal SIGNAL RECEPTION AND THE INITIATION OF TRANSDUCTION - Signal receptors on the target cells are the key to signaling - Signal molecules binding to receptor proteins can cause the protein to change shape o The signal molecule is complementary in shape to the receptor and attaches like a lock and key o ________________________________ = small molecule that specifically binds to a larger one; the signal molecule behaves like a ligand in this case o Ligand binding usually causes ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ - Most signal molecules are too big to pass through, but the receptor proteins can be embedded in the plasma membrane, so it can transmit the signal to the inside of the cell by changing shape or opening/closing when the signal binds to it - 3 types of membrane receptors: o 1. G-protein linked receptors: Many different types but all have the same basic structure If _______________ is bound to the protein = ACTIVE If _______________ is bound to the protein = INACTIVE ** GTP is similar to ________, and GDP is similar to _________** See Figure 11.7 pg. 202 for mechanism of G-protein ______________________ converts the GTP back into GDP so the protein becomes inactive when the signal is no longer there o 2. Tyrosine-Kinase Receptors: A class of plasma membrane receptors characterized by enzymatic activity Receptors for Growth Factors Can trigger _______________________________________________________ _____________________________________ at once Membrane receptors that attach ___________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ See Figure 11.8 pg. 203 o 3. Ion-Channel Receptors Open or close in response to a __________________________________________, which allows _______________________________________________________________ _________________________________________(for example, Na+ or Ca2+) - Changes shape when molecules bind to create a channel Very important in the _____________________________ system Intracellular Receptors o Some signal receptors are proteins dissolved in the cytoplasm or nucleus of the cell o Signals need to be able to cross the ___________________________________________ in order to get into the cell (usually hydro___________!) Examples: steroid hormones,____________________________________, ____________ ______________________________ These receptors act as transcription factors – which activate transcription of the gene into _____________ SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS - Transduction stage is usually a multistep pathway o Benefit = a small number of extracellular signal molecules can produce a large cellular response; signal is amplified by one molecule in the chain transmitting the message to multiple molecules at the next step, and so on - Pathways relay signals from the receptors to the cellular response o The signal starts with the activation of the receptor protein, which then passes the signal to the next molecule, then to the next, etc. Usually the molecules in the pathways are proteins and the signals are brought on by conformational changes – usually caused by _________________________________ (protein kinases = _________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________) Many of the molecules in the signal transduction pathway are protein kinases that act on each other to create a “___________________________________________________” Protein kinases are EXTREMELY important in animals – involved in the regulation of most genes o To turn off the signal pathway when the initial signal is no longer present, _________________ _______________________________________ are used; these remove ___________________ groups from ____________________________ thus inactivating those proteins o THEREFORE…the activity in a cell depends on the balance between ________________________ _________________________ molecules and _________________________________________ molecules - Second messengers o Second messengers = _____________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ o Most important second messengers = __________________________ and ______________ o 1. Cyclic AMP (cAMP) Adenylyl cyclase = _________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Overview = the first messenger (the hormone) causes a membrane enzyme to make cAMP, which broadcasts the signal out to the cytoplasm o Phosphodiesterase = enzyme that converts cAMP into AMP (inactive), so once the hormone is gone, the signal stops o Many hormones can signal the formation of cAMP o cAMP usually works by activating _______________________________ ___________________________________________________________ (___________________/_____________________________ kinase) o See Figure 11.13 pg. 207 o 2. Calcium Ions More widely used as a second messenger than cAMP The concentration of Ca2+ is… Lower in _________________________________________________________ Higher in _________________________________________________________ Calcium is critical for both plants and animals Animals = _________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Plants = ____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Changes in the Ca2+ levels (usually by release of Ca2+ from the ER) initiates other second messengers _______________________________________ = Ca2+ binding protein found in eukaryotic cells; mediates many calcium-regulated processes by changing conformation and then binding to other proteins to activate or deactivate them CELLULAR RESPONSES TO SIGNALS - Signal transduction pathways lead to ____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ o Ex. The response of liver cells to signaling by the hormone ______________________________ helps regulate __________________________________________________________________ o Production of transcription factors (which can switch genes on and off) - Multi-step pathways have two important benefits: o 1. ________________________________________________ At each step in the process, the number of activated molecules is greater than the one before it o 2. ____________________________________________________________________ The same signal (ex. Hormone) can produce effects in one cell and not in another, OR it can activate both, but the cells can respond differently – it all depends on the _________________________________ that make up the cell How does a specific signal molecule find its substrate? Scaffolding proteins = ________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ See Figure 11.19 pg. 212