Lesson #1: Reform in Industry - North Clackamas School District
advertisement

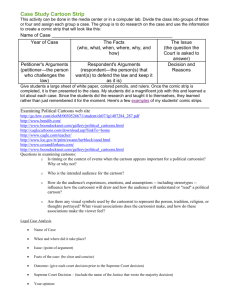
Unit Three: Lesson One- An Age of Reform In Industry Kirby World History CHS UNIT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: North Clackamas School District Social Studies Priority Standards: HK 2. Analyze the complexity and investigate causes and effects of significant events in World History. LESSON ONE : DAILY LEARNING TARGET I Can….Create a Political Cartoon Commenting on Aspects of the Industrial Revolution. REVIEW OF ECONOMIC PHILOSOPHERS WITH A PARTNER HI-LITE SECTIONS I. AND II. Hi-lite keys words in section A-D Create a memory device/picture for Capitalists Socialists Communists USE THE UNIT THREE PACKET TO HI-LITE AND TAKE YOUR NOTES TODAY! Relax and enjoy the ride In History Class! Group Brainstorm: As a small group, brainstorm a review list of the “Negative effects of the Industrial Revolution.” Do this at the bottom of page One Possible Answers: Air pollution Tension between social classes Poor work conditions Crowding of cities Poverty Taking advantage of Children in factories Dangerous work conditions Other hazards (lack of fire escapes/exits) Define the word/term “Reform” in your small group: Write the definition beside: III. Reforms Reform: Make changes in something (a social, political, or economic institution or practice) in order to improve it. Example: Change “Child Labor Laws!” In the 19th Century Reforms: HI-LITE KEY WORDS Union Movement in the early 1800’s leads to calls for “collective bargaining” (for better pay and conditions). Management would have trouble replacing “skilled workers” Governments initially prohibited unions, workers joined anyway AFL formed in 1886 Laws: HI-LITE KEY WORDS Factory Act (1833) – Children under 9 could not work; children between 9-12 limited to 8 hours. Mines Act (1842) – Prevents women and children from working underground. Ten Hours Act (1847) – Limits work day for women and children in factories. National Child Labor Committee (1904) – Set up to abolish child labor. Abolition of Slavery in Britain (1833.) INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION POLITICAL CARTOON- ASSIGNMENT Task: You are a cartoonist for a London newspaper during the Industrial Revolution and feel troubled by the different problems that are happening as a result of this “revolution.” Your newspaper editor has asked you to create two political cartoons (cartoons that convey a message in humorous and/or thought-provoking ways) that highlights a condition or problem associated with the Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. POLITICAL CARTOON - ASSIGNMENT Some problems you may choose to illustrate are: the pollution of the air the hierarchy of social classes the dangerous conditions in the factories the crowded living conditions Reforms/Laws/Unions (see “An Age of Reform” outline. Remember: Cartoons should combine both drawings and text POLITICAL CARTOONS Introduction to Political Cartoons: Decoding Political Cartoons 1. Acquire Knowledge 2. Identify the Issue 4. Identify Bias of the Cartoonist 3. Analyze Devices 5. Interpreting the Cartoon Bias: The opinion of the artist Just remember - K.I.D.B.I. Identifying Bias of Cartoonist National or Regional Economic Political Gender Religious Historical Influences Racial or Ethnic Personal Values Vocational Marital Status Essential Devices Caricature- Words- Purpose: to identify the Purpose- commentary, people, place, or event Device: simplify, distort, or exaggerate explanation, revelation, Devices: titles, captions, name tags, dialogue, balloons Analogy Purpose: creation of settings, situations, for comparison Device: historical, literary, cultural Signs and related devices Purpose: quick communication Devices: signs, symbols, stereotypes, size, shading Caricature Caricature is a form of visual satire and is nearly always negative. Focus on a an individual’s unique physical characteristics and exaggerate or distort them! Analogy Analogy draws on a rich pool of historical, literary, and cultural references to create a fantasy setting or situation which relates in some way to reality. The similarity forces the viewer to think about the situation in a new way. Words Cartoons usually have titles or captions, and sometimes they have name tags, balloon comments or dialogue. Road signs, warning signs, Signs informational signs. Abstract + = ÷×≠®™ Facial expressions, gestures, attitude and position of body, also used to convey messages. They all emphasize ideas and convey emotions. Canada: Maple Leaf Beaver Jean Baptiste USA: Uncle Sam Stars and Stripes Eagle Britain: Union Jack The Lion Symbols Stereotypes A stereotype is an oversimplified mental picture of characteristics supposedly shared by many people in a group. Stereotypes may be unfair and insulting to the group they represent! Size Size is frequently used by cartoonists to draw attention to a particular figure in the cartoon or to emphasize status or power. Shading Another visual device used by cartoonists is shading. The dark figures represent the ‘bad’ guys, and the light figures the ‘good’ guys. How is shading used here? RUBRIC FOR “INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION” POLITICAL CARTOON EXCEEDING 5 PROFICIENT 4 Creative, thought Very Creative, provoking political thought cartoon. Quality provoking colored shaded political cartoon. drawing with Detailed, quality, humorous writing colored &shaded or caption. Shows drawing with “Point of View” humorous writing Writing. Contain 3 or caption. Shows of the essential “Point of view” devices. Writing. Contains all 4 of the essential devices. PROGRESSING 3.5 Political cartoon drawn to complete the assignment Colored and shaded drawing with writing or caption. Shows some understanding of “Point of View” writing. Contains 2 of the essential devices. . EMERGING 3 Political cartoon drawn and colored hastily. May look like a rough draft. Has writing. Lack of understanding of “point of view” writing. Contains only one of the essential devices.