Personal Freedoms - Marmaton Valley Schools
advertisement

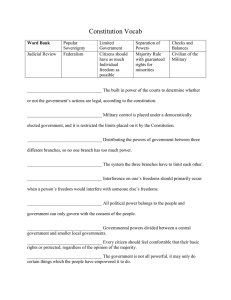
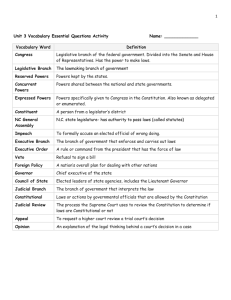
1. Organization of the constitution A. Based upon popular sovereignty B. preamble 1. 6 goals of the constitution C. 7 Articles 1. Legislative congress upper house-senate-statehood lower-house of rep-population make laws 2. Executive-president enforces laws 3. Judicial-courts interpit laws-final say on constitution 4. Relations among the states 5. Amendments 6. National supremacy 7. Ratification D. amendments 1. 27 2. 1st 10 the bill of rights-deal with personal freedoms 3. Added to deal with a changing nation 4. Proposed and ratified E. 6 principals of American Gov. 1. Popular sovereignty 2. federalism 3. Separation of powers 4. Checks and balances 5. Judicial review-elevated the courts to equal power with the other 2 6. Limited government F. Powers listed 1. Expressed-protects liberty and checks power 2. Delegated 3. Implied a. elastic clause or necessary and properarticle 1 section 8 4. Inherent powers 5. Reserved powers 6. Concurrent powers 2. Relations among the states A. full faith and credit B. extradition C. privileges and immunities Personal Freedoms • • • • • • • • • 1st-personal freedoms 2nd keep a gun 3rd no housing of soldiers 4th free from unreasonable search and seizures 5th protects the rights of the accused 7th protects the right to speedy trial by jury 8th prohibits excessive bail and cruel punishment 9th rights to the people 10th powers to the states 3. Growing National government A. War powers act B. Commerce power C. power to tax and spend 1. Alcohol and tobacco 2. Unemployment taxes 3. Dangerous products 4. Use them to force states to adopt certain kinds of programs D. courts 1. Judicial activism-courts are actively involved in seeking cases starts with Chief Justice Earl Warren 2. Their decisions can only be turned over by themselves or constitutional amendment