Chap 19 powerpoint
advertisement

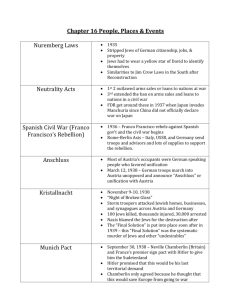
Unit 6: Global Struggles 1931-1960 Chapter 19 Adolf Hitler A World in Flames Francisco Franco Pearl Harbor Emperor Hirohito Benito Mussolini I. America and the World A. Between the Wars - US determined not to be drawn into another foreign war - worked for int’l agreements & arms control 1. 1919: US refuses to ratify Treaty of Versailles. Why? 2. Problems in Europe a. Communism in Russia b. Unrest in Germany c. widespread economic distress 3. Actions taken by US to prevent further overseas involvement a. Ended draft b. 1921: Washington Conference – 1st successful disarmament conference in US History c. 5/4/9 Power Treaty – 1920s treaties aimed at maintaining peace - 5/4 power treaty – to prevent hostile actions - 9 power treaty – to keep China independent and open to foreign trade d. 1928: Kellogg Briand Pact – pledged to renounce war as an instrument of national policy. But no way to enforce it and it didn’t rule out defensive wars 4. War Debts & Reparations – Europe couldn’t pay war debts. a. b. c. d. France & GB owed US Germany owed France & GB Germany could not pay France & GB So France & GB could not pay US 5. 1924: Dawes Plan – US plan to improve German economy so it could pay – failed B. The Rise of Dictators - after WWI, US hoped to aid in the establishment of democracy throughout the world. Instead, in the 1920s-30s, totalitarian gov’ts appeared in Italy, Germany, and the USSR – ALL used terror and force to suppress the opposition 1. Mussolini - Italy (Il Duce) a. Problems in Italy 1) Scorn for Versailles Treaty – didn’t get Austrian territory 2) Economy failing, political and class tensions 3) unemployment, inflation led to strikes, fear of Communism b. Mussolini blamed problems on Communists, corrupt biz leaders & weak politicians – promised to restore to Italy the honor, glory & prosperity of ancient Roman Empire c. founded Fascist party in 1919 1) Fascism stresses nationalism and the supreme authority of the leader 2) believed nations made great by expanding territory and building up military 3) nation more important than Believe, Obey, Fight individual. Individualism = “The function of a citizen and a soldier weakness are inseparable” 4) anti-communist: stood for protection of pvt property & middle class; full employment for industrial workers; social security; national prestige 5) organized blackshirts – militia used gang tactics to suppress strikes & attack leftist trade unions Mussolini with Blackshirts 1922 Benito Mussolini Il Duce 2. Stalin Takes Over the USSR (1926) a. Bolshevik Revolution 1917 (Lenin) b. Instituted one-party rule, suppressed individual liberties, punished opponents c. Stalin takes over 1926 - advocated rapid industrialization, state control of farms – his methods caused famine and starvation. Kept control through series of purges - killing or imprisoning political enemies and possible opposition Josef stalin 3. Hitler & Nazism a. political & economic chaos in post-WWI Germany - economic burden of reparations and rebuilding + skyrocketing inflation - Weimar Republic: A Democracy, but little experience; weak & ineffective. Weimar Republic’s Paul - workers begin to support Von Hindenburg Communists; upper class wants return to monarchy b. humiliated by terms of WWI surrender Terms of Treaty of Versailles c. Adolf Hitler blamed Germany’s problems on - Communists - foreign powers who stripped Germany of its land & military abilities at Versailles - Jews who controlled world finances d. Mein Kampf: Hitler outlines his Mein Kampf plan for Germany (from jail 1923) became a bestseller in Germany - Germans are a superior race w/ right to conquer & rule other peoples (especially Slavs/Jews) - Germany needed lebensraum (living space) – should expand east e. Rose to power through Nazi Party (National Socialist German Workers Party) Nazism = fanatical ideas of nationalism, German racial superiority, and supremacy of the “fuhrer” f. 1932: Both Communists & Nazis gain seats in German parliament g. Hitler became President in 1934. Called himself der fuhrer. Vowed to: 1) rebuild German economy 2) restore lands lost after WWI 3) to rearm Germany (in defiance of Treaty of Versailles) Adolf Hitler 4. Francisco Franco - Spain a. Spanish Civil War 1936 – republican govt vs fascists b. Germany & Italy helped arm Franco’s fascist forces (German arms, weapons, new tactics are battle tested) c. USSR helped loyalists. GB, France, US did nothing d. Democracy lost Francisco Franco "Our regime is based on bayonets and blood, not on hypocritical elections.“ Francisco Franco Ernest Hemingway was moved to write the following words after witnessing the treachery and wastage of the ignominious Spanish Civil War: "They wrote in the old days that it is sweet and fitting to die for one's country. But in modern war there is nothing sweet or fitting in your dying. You will die like a dog for no good reason." Ernest Hemingway Notes for the Next War 5. Militarists Gain Control of Japan a. background. 1920s: Japan had close ties with West, was developing democratic system b. But economy suffering – trade deficit, unemployment etc. c. Nationalists/Military leaders, some biz leaders urged return to glory of Japan’s past with absolute rule by emperor - Japan destined to dominate East Asia - Preached virtues of territory expansion d. Why Expand? 1) expanding population 2) economic expansion (defense contracts) 3) lack of natural resources e. Sept 1931: military (w/o support of gov’t) invaded Manchuria, a resource-rich province of China f. Japanese civilian gov’t tried to intervene. Prime Minister and many other supporters of democracy assassinated g. Series of military officers now serving as Prime Minister h. League of Nations complained – Japan simply withdrew from L of N C. America Turns to Neutrality - America supports Isolationism – the belief that the US should avoid int’l commitments that might drag US into another foreign war 1. Isolationism a. Isolationism grew in popularity. Why? 1) war debt – Europeans weren’t paying loans 2) belief that US arms manufacturers influenced WWI Nye Committee Findings b. Nye Committee – confirmed that arms manufacturers made huge profits – believed these companies influenced US decision to enter war 2. Legislating Neutrality – supporting Isolationism a. Neutrality Act (1935) – barred sale of munitions to all belligerents (nations at war) b. 1936: another Neutrality Act passed to ban sale of arms to either side in a civil war - reaction to Spanish Civil war (1936) c. Neutrality Act of 1937 – continued ban on arms sales to belligerents but allowed sale of nonmilitary supplies - on “cash and carry” basis & on their own ships - reaction to Rome-Berlin Axis and Anti-Comintern Act (Japan & Germany agree to exchange info about commies) thus, Germany, Japan, Italy = Axis Powers For or Against neutrality?? 3. Roosevelt & Internationalism a. FDR an internationalist (not an isolationist) – believes trade btwn nations creates prosperity & helps prevent war b. Japan attacks China again in July 1937 A survivor after intense bombing during the Japanese attack on Shanghai's South Station. August 1937. - FDR ok’s sale of weapons to China - this he says, does not violate Neutrality Act , as neither side declared war Rape of Nanking • Btwn Dec.1937 and March 1938 Japanese troops captured Nanking (then the Capital of China) and embarked on a campaign of murder, rape and looting. • An estimated 250,000 and 300,000 (out of 600,000 total) killed, many of them women and children. • # women raped is estimated at 20,000+ w/ many accts of civilians being hacked to death. • Like other genocides, some refute this atrocity • (acct by BBC http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/39166.stm) Rape of Nanking Japanese soldiers carrying rifles on their shoulders walk across a bridge, through a pillared gate, into the walled city of Nanking, China. Chinese men rounded up by the Japanese, in “Nanking.” Japanese Troops raising rifles in victory – somewhere near Nanking II. World War II Begins A. Pre-War German Aggression 1. 1935: Germany rearms (violating Treaty of Versailles) a. Nat’l pride soars b. German economy improves – unemployment fell, new opportunities grew c. Result? Devotion to Hitler grew d. No reaction from France/Britain 2. 1936: Germany sent military into Rhineland (demilitarized region along border w/ France) – again, in violation of the T of V - no reaction from France whose army could easily have overpowered German forces at this time 3. March 1938: Austrian Anschluss – the annexation of Austria (again, a violation of the T of V) a. part of Hitler’s goal to unite German-speaking people b. Germany stood to gain territory, food, soldiers, defensible frontier c. Austrians divided over the issue, but little int’l opposition to the takeover • 4. Sept. 1938: Munich Conference a. Hitler lays claim to the Sudetenland = German speaking region in Czechoslovakia b. Unlike Austrians, Czechs wanted to resist. + very diff. scenario ** Czech. = democracy ** Czech. in defense alliance w/ USSR & France ** multilingual (not just German) c. Munich Conference : Britain, France, Germany & Italy agree to allow Germans to occupy Sudetenland (APPEASEMENT!!) - Brit PM Neville Chamberlain declares that there would be “peace in our time.” d. March 1939: Hitler seizes the rest of Czechoslovakia - Britain & France realize that appeasement had failed 5. Oct 1938: Hitler demands return of Danzig (Baltic Sea Port) from Poland + hwy & RR across Polish corridor - March 1939: Brits & French announce plan to defend Poland - Poland refuses Hitler’s demands knowing Brits & French will come to her aid 6. Aug 1939: Brits & French asked for USSR support for Poland, but instead, Stalin informed them of one of the century’s biggest diplomatic surprises The Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression Pact - Germany free to attack Poland and elsewhere w/o USSR opposition - Stalin agreed to this pact believing that the USSR would be protected by turning the capitalists against e/o (Germany vs. GB/France) - contained secret deal to divide Poland btwn Germany/USSR Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact German Aggression Prior to Outbreak of WWII The Big Question Why did European leaders do nothing to stop the Nazis in Germany in the early1930s when they had the chance? Answer/Explanation? a. Memory of WWI – horrors of war b. Fear of Soviet communism - strong Germany = good balance against Soviets c. Objections to the Treaty of Versailles d. Hope for compromise w/ Germany - thought some of his demands were reasonable - believed appeasement would work (appeasement = accepting demands in hope of avoiding conflict) B. The War Begins 1. Sept 1, 1939: Germany invades Poland (from west; USSR from east) a. Blitzkrieg “lightning war” b. Sept 3, 1939: GB and France declare war on Germany, but Poland can’t be saved (divided btwn Germany/USSR) c. USSR takes over Baltics, invades Finland Nov. 1939 d. US response? Neutral but… Neutrality Act of 1939: allowed sale of arms to belligerents, but no US ships in war zone 2. Germany targets France a. Last months of 1939: Sitzkrieg; Phony War; Bore War – not much action b. French & British troops in France on the defensive. - Maginot Line: a line of concrete bunkers & fortifications along German border Maginot line Anti-Tank Defenses on the Maginot Line c. April 1940: German unleashes “blitzkrieg” into neutral Denmark, then Norway d. To get to France, Hitler went around the Maginot Line, invading Netherlands, Belgium, & Luxembourg “The thing about the Maginot Line was that it pointed to exactly the spot where the French Army could be found; therefore, the Germans avoided it.” 3. May 1940: Miracle at Dunkirk a. Brit and French Armies trapped in Belgium b. Germans captured all ports except Dunkirk - (in France on Belgian border) c. Brits sent over 850 ships (warships, sailboats, fishing boats etc) across English Channel to Dunkirk - rescued 338,000 Brit & French troops!!!! But almost all of Brit’s army equipment was left behind d. Americans inspired! Miracle at Dunkirk Rescue at Dunkirk 4. June 1940: The Fall of France a. June 5: Germany invades France b. France surrenders June 22, 1940 c. West & North of France under Nazi Rule - rest of France governed by neutral but German friendly regime = Vichy Fall of France German soldiers marching past the Arc de Triomphe after the surrender of Paris, 14 June 1940 Fall of France d. Only Britain left to fight against Hitler and Nazi Germany C. The British 1. Winston Churchill = new Prime Minister of Britain a. Germany expects Brits to negotiate peace b. Churchill’s response? “We shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall never surrender!” 2. July-Oct 1940: Battle of Britain a. Air war b. German Luftwaffe (LW) vs. British Royal Air Force (RAF) RAF Spitfire c. Germany’s plan? - to disrupt wartime production & break British civilian morale d. Germany’s mistake? LW Heinkel HE 111 - Luftwaffe bombs London accidentally, RAF responds by bombing Berlin. Hitler furious – orders LW to stop bombing military targets to focus on bombing London * duh… what about that wartime production! 3. Oct 1940: Hitler gives up on invasion of England. What happened? a. RADAR: Brits able to detect incoming LW aircraft and intercept them b. LW: poor leadership etc. See attached article:How the Luftwaffe lost the Battle of Britain Notice that Luftwaffe greatly outnumbered RAF Churchill to the RAF Fighter Pilots The gratitude of every home in our Island, in our Empire, and indeed throughout the world, except in the abodes of the guilty, goes out to the British airmen who, undaunted by odds, unwearied in their constant challenge and mortal danger, are turning the tide of the world war by their prowess and by their devotion. Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few. III. The Holocaust A. Nazi Persecution of Jews 1. Nazi Ideology: aim of Hitler’s regime to create a European world dominated and populated by the “Aryan” race as outlined in Mein Kampf - plan to eradicate undesirables (based on who you were – genetic, cultural, health or what you did ) 2. Jews: (Undesirable based on who you were) - already centuries of antiSemitism in Europe a. Nuremberg Laws 1) stripped of German citizenship 2) banned intermarriage 3) disenfranchised & loss of most political rights 4) defined Jew as anyone w/ 3 or 4 Jewish gdparents (nothing to do w/ religious beliefs) b. Nov 1938: Kristallnacht Cities where synagogues - Nazis burned synagogues, & were destroyed vandalized Jewish biz - Gestapo (German secret police): arrested 20,000+ Released if they agreed to emigrate & surrender all their possessions 3. Other undesirables b/c of who you are a. Poles & other Slavs – considered untermenschen (subhuman); an obstacle to gaining lebensraum for German race b. Roma (gypsies) – considered asocial & racially inferior c. Physically or mentally disabled – Gypsy Patch threatened the Nazi plan for “human perfection” – faced sterilization or euthanasia 4. Undesirable based on what you did a. Political dissidents & dissenting Clergy b. Homosexuals – considered an obstacle to keeping Aryan birthrate Dietrich Bonhoeffer: high German Lutheran Pastor & Anti-Hitler c. Jehovah’s Witnesses – for refusal resistance fighter – executed April, 1945 to salute flags, “Heil Hitler” or to serve in German army Jehovah’s Witness inmates were identified by purple triangles on their uniforms. “Undesirables” Prisoners standing during a roll call. Each wears a striped hat and uniform bearing colored, triangular badges and identification numbers. 1. German political prisoner. 2. Criminal prisoner - German or other nationality. 3. Political prisoners of other nations, e.g. 'P' Polish; 'L' Luxembourg, etc. 4. Homosexual, 'gay' 5. Antisocial called 'Arbeitsscheue' (to shy to work)- mostly German prostitutes, pimps, etc. 6. 'Bibelforscher' (Jehovah's Witnesses) 7. Jew, political or racial. 8. 'Emigranten' (Migrants) - Members of International Brigade of Spanish War. 9. Jews, criminals, mostly because of financial 'offences' e.g. transactions or non-disclosure of foreign currencies. B. Jewish Emigration 1. 1933-1939: 350,000 German Jews emigrate (exit) ex. Einstein & other Jewish Scientists to US; Anne Frank family to Holland a. What prohibited more Jewish immigration into the US? Albert Einstein 1) Jews prohibited from taking more than $4 from Germany 2) 1920s immigration quotas in US 3) high unemployment in 1930s US restricted immigration further 2. German transatlantic liner St. Louis ( May 1939) a. 930 Jewish refugees arrive in Havana, Cuba hoping to get to US b. Cuban gov’t refused to allow refugees ashore c. Denied permission to land in US d. Back to Europe June, appx 250 died in Holocaust C. The Final Solution 1. Berlin 1942: Wannsee Conference a. Nazi leaders met to determine “Final Solution” to the Jewish question b. Previous methods too slow & inefficient c. Plan to send Jews and other undesirables to -concentration camps -extermination camps 2. Concentration Camps a. Detention centers for healthy individuals b. Work as slave laborers until they died of exhaustion, disease or malnutrition Bergen Belsen Concentration Camp 3. Extermination Camps a. Detention centers for the elderly, the sick, and young children b. Execution in massive gas chambers c. Auschwitz – could kill 2000 at a time/12,000 per day - appx 1.6 million killed there Auschwitz-Birkenau D. How could this happen? Theories… 1. Germany’s sense of injury after WWI 2. Severe Economic problems 3. Hitler’s grip on the nation 4. lack of a strong tradition of representative gov’t in Germany 5. fear of Gestapo 6. Long history of anti-Semitism in Europe The Holocaust IV. America Enters the War A. America Supports England 1. Neutrality Act of 1939 a. US officially neutral: BUT – found a way to help Britain & France b. Revise neutrality laws: allow warring countries to buy arms from US as long as “cash & carry” 2. Sept 1940: Destroyers for Bases Deal a. Churchill asks FDR for destroyers to protect Brit cargo ships from U-boats & to block German attempts to invade Britain b. FDR gave Brits 50 aging destroyers in exchange for free 99 yr lease of British Naval Bases in Canada & Caribbean c. Since deal wasn’t a sale, Neutrality Act didn’t apply B. The Isolationist Debate in US 1. Support for Brits increases (thanks to Dunkirk & Invasion of France) 2. America First Committee a. Favored continued isolation b. Opposed to ANY US intervention or aid to Allies c. Famous members: Charles Lindbergh, Senator Nye C. Election of 1940 1. FDR reelected for unprecedented 3rd term - breaks precedent b/c he believed a change in leaders would not be in the best interest of the country at that time 2. FDR promises to keep US boys out of war 1940 Election D. FDR aids our Allies as US edges closer to WAR 1. Jan 1941: In 4-Freedoms Speech, FDR claims US has a duty to assist democracies at war to protect: The Four Freedoms: 1) Freedom of Speech 2) Freedom of Worship 3) Freedom from Want 4) Freedom from Fear The Four Freedoms Freedom from Fear Freedom of Worship Freedom of Speech Freedom from Want A Series by American Artist, Norman Rockwell 2. March 1941: Lend-Lease Act a. Problem: Brits out of $$$. FDR must come up w/ way to remove cash requirement from neutrality act b. Solution: LEND-LEASE Act 1) allowed US to sell, lend, or lease war materials to any nation whose defense was vital to US security 2) US could send weapons to Brits if they promised to return or pay rent for them after the war c. FDR argued that US should be the “arsenal of democracy” b/c if Britain fell, Axis would conquer the world & Americans would be living at the point of a gun Arsenal: an establishment for the manufacture or storage of arms and military equipment US = Arsenal of Democracy 3. June 1941: Germany invades USSR!! Operation Barbarossa a. Violation of the Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression Pact b. US begins to send aid to USSR: “the enemy of my enemy is my friend” Operation Barbarossa • Stalin Betrayed! • US aid follows (Lend-Lease) 4. Hemispheric Defense Zone a. FDR declares entire western ½ of Atlantic as part of Western Hemisphere (OUR hemisphere!!) b. Neutral territory c. US Navy ordered to patrol it to reveal location of German UBoats to the Brits who could sink them 5. Aug 1941: Atlantic Charter a. FDR & Churchill plan for the post -war era and commit to : 1) democracy 2) nonaggression 3) free trade 4) economic advancement 5) freedom of the seas b. Sept. 1941: USS Greer Incident 1) U-boat fires on the Greer, a US destroyer that was radioing U-Boat’s position to the Brits 2) FDR orders US ships to follow a “shoot on sight” policy toward German Uboats c. Oct 1941: USS Reuben James torpedoed, 115 US sailors dead d. Late 1941, US & Germany in tense standoff in North Atlantic D. Japan Attacks US 1. FDR’s pre-war objective? To help Brits defeat Germany a. Brits Navy can’t protect its Asian colonies b. FDR institutes policies to discourage Japan from attacking Brit’s Asian empire 2. The policies: a. Export Control Act: restricted sale of strategic materials to Japan b. Sent Lend-Lease aid to China c. Froze Japanese assets in US d. Cut off oil exports to Japan 3. Japanese Reaction? Believed that only the US stood in its way to unite all East Asia under Japanese control - Japan made plans to: 1) attack British & Dutch colonies in SE Asia 2) seize the Philippines 3) attack US Naval fleet at Pearl Harbor Japanese Plans 4. Dec 7, 1941: Japan attacks Pearl Harbor Pearl Harbor Timeline “A date which will live in infamy” USS Arizona burning after forward magazine explodes killing 1177 US sailors 5. The Result? a. 21 ships sunk or damaged; 188 airplanes destroyed; 2403 Americans killed b. What did they miss? - The aircraft carriers!!! (they were at sea) 6. Dec 8, 1941: US declares war on Japan President Roosevelt Asks Congress for a Declaration of War on Japan 7. Dec 11, 1941: Germany and Italy Declare War on US Li’l Hitler 8. Neutral no more! America is at war