Naming Acids
advertisement

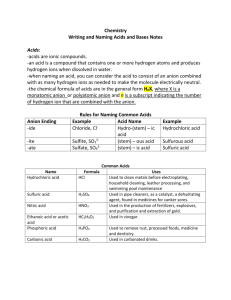
Name ___________________________________ Date ______________________ Class ______________________ Chapter 9 – Chemical Names and Formulas Acids and Bases An acid is a compound that produces H+ ions in an aqueous (water) solution. A base is a compound that produces OHions in an aqueous solution. Naming Acids Acids not containing a polyatomic ion (or oxygen) are named by using hydro- plus the root of the anion plus –ic plus acid. Acids containing oxygen are named by using the polyatomic root plus –ic if the original polyatomic name contained –ate or plus –ous if the original root was –ite. If there is sulfur in the polyatomic –ur is added before the –ic or –ous. If there is a phosphorus in the polyatomic –or is added before the –ic or –ous. These are summarized below. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. If no oxygen: hydro + anion root + ic + acid (example – HCl is hydrochloric acid). If oxygen present: polyatomic root + ic (replacing –ate ending) + acid (example HClO3 – chloric acid). If oxygen present: polyatomic root + ous (replacing –ite ending) + acid (example HClO2 – chlorous acid). If sulfur present: polyatomic root + ur + ic/ous + acid (example H2SO4 – sulfuric acid). If phosphorus present: polyatomic root +or + ic/ous + acid (example H3PO4 – phosphoric acid). **Work the following problems – name the following acids. Formula HBrO H2CO3 HCl H2S HNO3 H2SO4 HC2H3O2 H3PO3 HF HSCN Compound Name Writing Formulas for Acids To write the formula for an acid look at the name. Reverse the process and change the endings to find out which root anion or polyatomic ion you are dealing with. Next, balance the negative charges with hydrogen. Example 1: periodic acid…root polyatomic would be periodate or IO41- so balance that with hydrogen to get HIO4. Example 2: thiosulfuric acid…root polyatomic would bethiosulfate or S2O32- so balance that with hydrogen to get H2S2O3. **Work the following problems – write the formula for the following acids. Compound Name Formula Compound Name hydrosulfuric acid nitric acid bromous acid sulfuric acid thiosulfuric acid Formula chromic acid hydroiodic acid nitrous acid perchloric acid dichromic acid Naming Bases A base is composed of a metal and an OH- ion. You name the metal and then the OH- with hydroxide. Ammonia, NH3 is a base. When ammonia is put into water it forms ammonium, NH4 and gives off OH- ions. NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH-. Examples: NaOH is sodium hydroxide Fe(OH)3 is iron (III) hydroxide **Work the following problems – name the following bases. Formula KOH Fe(OH)2 Al(OH)3 Mg(OH)2 LiOH Compound Name Writing Formulas for Bases To write the formula for bases simply write the formula like you would for an ionic compound. Write the formula for the metal ion, using Roman numerals where needed, then the formula for hydroxide. Balance the formula and you’re done. **Work the following problems – write the formula for the following bases. Compound Name zinc hydroxide iron (III) hydroxide chromium (II) hydroxide beryllium hydroxide calcium hydroxide Formula Compound Name silver hydroxide nickel (II) hydroxide sodium hydroxide aluminum hydroxide copper (III) hydroxide Formula