Histology of Bone
advertisement

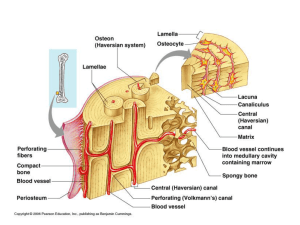
Osseous Tissue (Histology) Review: • Bone is a type of connective tissue 2 Parts: 1. Cells (living) 2. Matrix (nonliving substance released by cells) A. Fiber B. Ground Substance 1. Cells • • • Osteocytes— mature bone cells Osteoblasts— bone-forming cells (germ cells or “bud” cells) Osteoclasts —bone-destroying cells (“breakers”) 2. Matrix A. primarily collagen fibers flexibility tensile strength (the strength to endure stretching forces) B. calcium salts (hardness) contain calcium and phosphorus great compressional strength (the strength to endure squeezing forces) Classification of Bone by Tissue Type • Two basic types of Tissue 1. Compact bone • Homogeneous • Looks “smooth” 2. Spongy bone • Small needle-like pieces of bone • Many open spaces (like sponge) • Keep bones light Figure 5.2b Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Figure 5.3a http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4qTiw8lyYbs&NR=1 Microscopic Anatomy of Bone • Osteon (Haversian system) – A unit of bone containing central canal and matrix rings • Central (Haversian) canal – Opening in the center of an osteon – Carries blood vessels and nerves • Perforating (Volkman’s) canal – Canal perpendicular to the central canal – Carries blood vessels and nerves Microscopic Anatomy of Bone • Lacunae – Cavities containing bone cells (osteocytes) – Arranged in concentric rings • Lamellae – Rings around the central canal – Sites of lacunae Microscopic Anatomy of Bone • Canaliculi – Tiny canals – Radiate from the central canal to lacunae – Form a transport system connecting all bone cells to a nutrient supply Microscopic Anatomy of Bone Figure 5.3b–c