Unit Factors in Pairs
advertisement

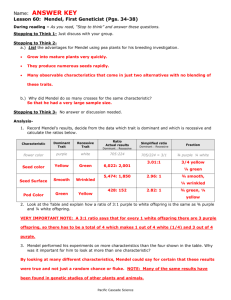
Mendel’s Contribution(s)? Mendel’s First Postulate Unit Factors in Pairs Genetic characteristics are controlled by unit factors that exist in pairs in individual organisms, each individual receives one unit factor from each parent, in a monohybrid cross, three combinations of unit factors are possible, Mendel’s Second Postulate Dominant/Recessive When two unlike unit factors are present in a single individual, one unit factor is dominant to the other, which is said to be recessive. Mendel’s Third Postulate Segregation During the processes of heredity, the paired unit factors separate so that the offspring receives one unit factor from each parent, The unit factors segregate to offspring randomly. Mendel’s Forth Postulate Independent Assortment How do two traits segregate in the offspring of an individual that is heterozygous for both traits? Forked-Line Method Haplo/Diplo and complementation 1. Both recessive: aaDD x Ad female: AaDd, male aD 2. Both Dominant: aaDD x Ad female: AaDd, male aD 3. One dominant*: aadd x AD female: AaDd, male ad or… AADD x ad female: AaDd, male AD dominant! * need to define which is Forked-Line Method Haplo/Diplo AaDd 1/2 A 1/2 a ½D 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 AD ½d 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 Ad 1/2 D 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 aD ½d 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 ad Forked-Line Method Haplo/Diplo AaDd x AD* (*male genotype could be ad, aD, Ad) 1/2 A 1/2 a ½D 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 AD 1 AD = ¼ ADAD ½d 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 Ad 1 AD = ¼ AdAD 1/2 D 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 aD 1 AD = ¼ aDAD ½d 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 ad 1 AD = ¼ adAD Lab Life Cycles Wasp Development Timelines o o 18 , 28 C C. elegans Nomenclature Tower of Babel
![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)








