Chapter 26
advertisement
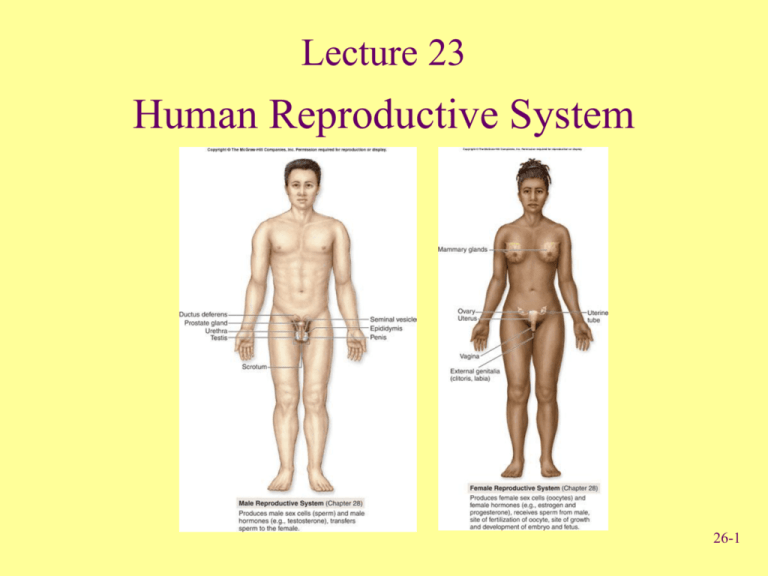
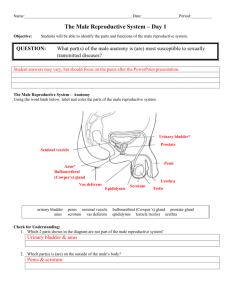
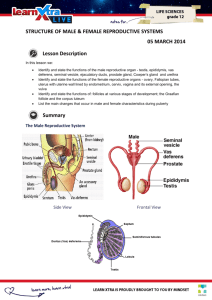
Lecture 23 Human Reproductive System 26-1 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System • Testes – Produce spermatozoa Urinary bladder (gametes) – Produce androgens Ductus (hormones) deferens • Series of ducts • Accessory glands (3) – Secretions added to sperm to form semen – Seminal vesicle, prostate gland, and bulbourethral gland Ureters Seminal vesicle Ejaculatory duct Prostate gland Bulbourethral gland Anus Urethra Penis Epididymis Glans Prepuce Testis Scrotum Fig. 28.11 26-2 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System • Supporting structures – Scrotum • 2 chambered sac that contains testes • Muscles help regulate temperature – Penis • Important sexual organ and part of the urinary system Ureter Penis Urinary bladder Ductus deferens Spermatic cord Epididymis Cremaster muscle Testis Dartos muscle Scrotum Fig. 28.12 26-3 Descent of Testes • Descent – Pass from abdominal cavity through inguinal canal to scrotum 26-4 Testes • Compartments divided by septa – Seminiferous tubules • Empty into efferent ductules • Efferent ductules empty into epididymis – Epididymis • Site of sperm cell maturation • 12-16 days Fig. 28.13 26-5 Male Reproductive Structures Ducts Urinary bladder • Ductus deferens or vas deferens – Passes from epididymis into abdominal cavity • Ejaculatory duct – Joining of ductus deferens and seminal vesicle Ureter Seminal vesicle Ejaculatory duct Prostate gland Bulbourethral gland Ductus deferens Urethra Epididymis Testis Fig. 28.15 26-6 Male Reproductive Structures Urethra Urinary bladder • Urethra – Extends from urinary bladder to distal end of penis – Passageway for urine and male reproductive fluids Ureter Seminal vesicle Ejaculatory duct Prostate gland Bulbourethral gland Ductus deferens Urethra Epididymis Testis Fig. 28.15 26-7 • Male Reproductive Structures Penis Three columns of Urinary bladder erectile tissue that engorge with blood Ureter – Corpora cavernosa (2) – Corpus spongiosum (1) • Glans penis – Prepuce or foreskin covers Corpus cavernosum • Circumcision: Surgical removal Urethra Testis Penis Corpus spongiosum Glans Fig. 28.15 Clinical View, pg. 866 26-8 Anatomy of Female Reproductive System • Female reproductive organs – – – – – Ureter Uterine tube Ovary Fimbriae of uterine tube Uterus Ovaries Urinary bladder Uterine tubes Uterus Urethra Clitoris Vagina External urethral orifice External genital Vaginal orifice organs – Mammary glands Cervix of uterus Rectum Vagina Anus Fig. 28.2 26-9 Uterine Tubes • Uterine or fallopian tubes or oviducts – Open directly into peritoneal cavity to receive oocyte from ovary – Transport oocyte or zygote from ovary to uterus Uterine tube Infundibulum Uterus Fimbriae Broad ligament Cervix Vagina (a) Posterior view Ovary Ureter Fig. 28.3 26-10 Uterus & Vagina • Uterus Fig. 28.7 – Parts: fundus, body, cervix – Composed of 3 layers • Perimetrium: Serous membrane • Myometrium: Smooth muscle • Endometrium: Mucous membrane 26-11 Female External Genitalia • Vulva external female genitalia – Vestibule: Space • Labia minora: Form borders on sides • Clitoris: Erectile structure – Corpora cavernosa – Corpora spongiosa Fig. 28.9 26-12 Review Question The structure of the female reproductive system that is homologous to the penis of the male system is the (a) Vagina (b) Labia minora (c) Uterus (d) Fallopian tubes (e) Clitoris 26-13 Points to Remember • Male and female reproductive systems share similarities as evidence of homology • Important functions of: – Production of gametes and sex hormones – Production of sperm (temperature-sensitive) – Receiving sperm (semen is mixture of sperm and secretions of three accessory glands) – Providing site for development of fetus and birth – Breast milk secretions provide nourishment 26-14 Questions? 26-15