What is an Atom?
advertisement

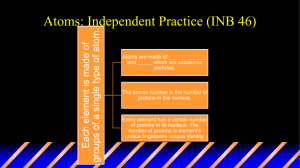
Lesson Objectives 1. Recap Atomic Structure 2. Isotopes Lesson Objectives 1. Recap Atomic Structure 2. Isotopes Recap on Atomic Structure A. Structure of atom B. Relative masses and charges of proton, neutron and electron C. Chemical symbols D. Electronic configuration Recap on Atomic Structure A. Structure of atom B. Relative masses and charges of proton, neutron and electron C. Chemical symbols D. Electronic configuration The Atomic Structure WHAT IS AN ATOM? Atoms are the smallest particle of an element. WHAT IS AN ELEMENT? pure substance that cannot be •An element is a ____ spilt _____up into 2 or more simpler substances by chemical processes. The Story of Atoms Atoms have positive charges concentrated in their small nucleus! There are neutrons! Democritus 460 BC Joseph John Thompson (1856-1940) PLUM PUDDING MODEL 1898 Ernest Rutherford (1871 -1937) Sir James Chadwick (1891 -1974) Niels Bohr (1885-1962) Bohr’s Atom electrons in orbits nucleus http://www.chem.iastate.edu/group/Greenbowe/sections/projectfolder/flashfiles/atom.swf Structure of Atom A positively charged nucleus, densely concentrated in the centre. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, which are tightly packed. An atom consists mostly of empty space. Negatively charged electrons move 10 around the nucleus in fixed orbits or paths. Recap on Atomic Structure A. Structure of atom B. Relative masses and charges of proton, neutron and electron C. Chemical symbols D. Electronic configuration Recap on Atomic Structure A. Structure of atom B. Relative masses and charges of proton, neutron and electron C. Chemical symbols D. Electronic configuration Relative Charges & Relative Masses Of Protons, Neutrons & Electrons Sub-atomic particles Symbol Relative mass Relative charge *Proton p 1 +1 *Neutron n 1 0 *Electron e 1/1840 -1 •When No. of proton = no. of electrons in an atom •It is electrically neutral •It has no net charge. Recap on Atomic Structure A. Structure of atom B. Relative masses and charges of proton, neutron and electron C. Chemical symbols D. Electronic configuration Recap on Atomic Structure A. Structure of atom B. Relative masses and charges of proton, neutron and electron C. Chemical symbols D. Electronic configuration Interpreting Chemical Symbol Mass=P+N mass number (nucleon number) mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Number of neutrons in the oxygen atom is: 16 – 8 = 8. proton number (atomic number) P=E No. of protons= no. of electrons 16 O chemical symbol 8 atomic number (proton number) is the number of protons in an atom. Each oxygen atom has 8 protons. As the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons in an atom, each oxygen atom contains 8 electrons. 16 Recap on Atomic Structure A. Structure of atom B. Relative masses and charges of proton, neutron and electron C. Chemical symbols D. Electronic configuration Recap on Atomic Structure A. Structure of atom B. Relative masses and charges of proton, neutron and electron C. Chemical symbols D. Electronic configuration The Electronic Configuration of Atoms 16 O 8 Atomic number (Proton) Mass number (Nucleon) O The Electronic Configuration of Atoms Mg Summary for Atomic Structure (I) • The structure of an atom • The relative charges & relative masses of proton, neutron & electron • Defined mass number & atomic number • Learnt how to interpret chemical symbols • The electronic configuration of atoms Lesson Objectives 1. Recap Atomic Structure 2. Isotopes Today… Isotopes Isotopes 1. Definition of Isotopes 2. Uses of Isotopes Isotopes 1. Definition of Isotopes 2. Uses of Isotopes Activity • Find your fellow group members! (1min) Definition of Isotopes Isotopes are atoms of the same element which contains the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Isotopes mass number proton number 16 17 18 8 8 8 O O O Oxygen-16 n = 8 Oxygen-17 n = 17 – 8 = 9 Oxygen-18 n = 18 – 8 = 10 Isotopes Isotopes have the same chemical properties but slightly different physical properties Q. DO ALL ISOTOPES OF THE SAME ELEMENT HAVE THE SAME MASS? Isotopes 1. Definition of Isotopes 2. Uses of Isotopes Pair Work Uses of Radioactive Isotopes • • • • Food irradiation Archaeological dating (carbon-dating) Smoke detectors Radioactive tracers Summary Recap on Atomic Structure 1. Definition of Isotopes 2. Uses of Isotopes Definition of Isotopes Isotopes are atoms of the same element which contains the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Quiz • http://chemistry.about.com/library/weekly/bli onquiz.htm