Ch 27: Female Reproductive System
advertisement
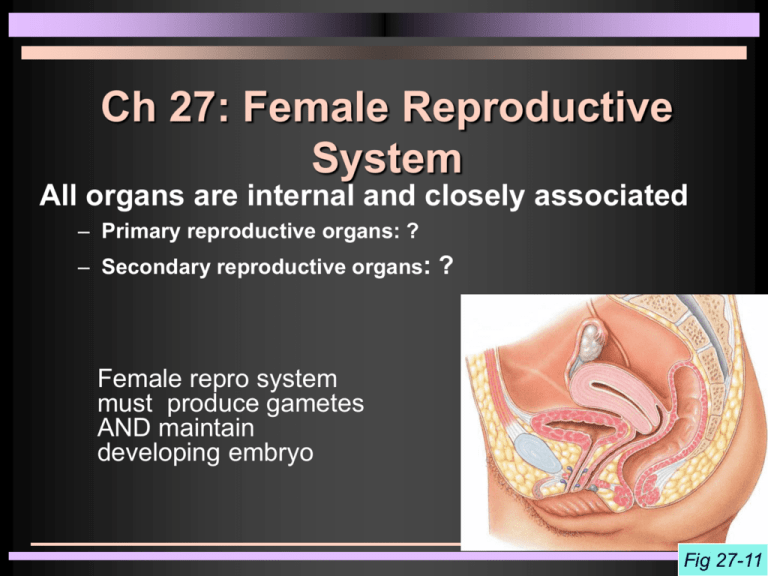
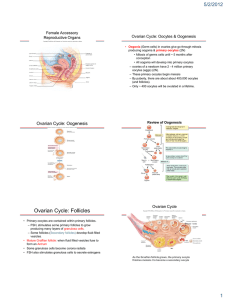
Ch 27: Female Reproductive System All organs are internal and closely associated – Primary reproductive organs: ? – Secondary reproductive organs: ? Female repro system must produce gametes AND maintain developing embryo Fig 27-11 Ovaries Suspended by ovarian ligament & suspensory ligament Functions: 1. Ova production 2. Hormone production Oogenesis (= ovum production) takes place inside ovarian follicles in ovaries as part of ovarian cycle Oogonia (= stem cells) complete mitotic divisions before birth At birth: ~ 2 mio primary oocytes At puberty: ~ 400,000 primary oocytes 40 years later: 0 (even though only ~ 500 used) Atresia Oogensis Ovarian cycles start at puberty under influence of ___ Primordial follicle Each month some proceed Primary follicle Few proceed Secondary follicle Few proceed Tertiary (Graafian follicle) Fig 27-12 Primordial Follicle or Egg Nests Present at birth (simple squamous layer) in cortex Primary Follicle Follicle cells Oocytes Follicles enlarge in response to FSH and produce estrogens Secondary Follicle Few relative to number of primary follicles Produce follicular fluid Rapid enlargement = Clear glycoprotein layer Tertiary or Graafian Follicle Spans entire width of cortex First meiotic division being completed: 1oocyte divides into one 2 oocyte and one polar body Oogenesis Suspended in prophase I Happens in tertiary follicle Ovulation Stops in Metaphase II Ovulation Oocyte and follicular cells shed into abdominal cavity then 1. Empty follicle forms corpus luteum which produces progesterone 2. Corpus luteum degenerates and becomes corpus albicans 3. GnRH increases under low estrogen and progesterone levels Uterine Tube = Fallopian tube = oviduct = salpinx Two muscular tubes – – – – infundibulum with fimbriae Ampulla (place of fertilization) Isthmus intramural portion Tubal ligation Fig 27-14 Uterine Tube Histology Ciliated and nonciliated simple columnar epithelium Ciliary movement and periodic peristaltic contractions move ova Secretion of nutrient substances The Uterus Uterine wall ~ 1.5 cm made up of 1. Endometrium, 2. Myometrium, 3. Incomplete perimetrium Fig 27-16 Blood supply – – Uterine arteries from internal iliac Ovarian arteries from abdominal aorta (inferior to renal arteries) Histology of Endometrium Functional zone – deciduum, sheds during menses – menstruation - flow sheds functionalis layer of endometrium – proliferative phase - under influence of estrogen basal cells proliferate – secretory phase - progesterone maintains functionalis Basilar zone – permanent layer, deep to functionalis Fig 27-16 Functions of Uterus Protection of embryo/fetus Nutritional support Waste removal Ejection of fetus at birth Cervix and Vagina Cervix attaches to vagina at ~ 90° angle Fornix – pocket surrounding uterine cervix (surgical access to pelvic cavity; location of birth control device) Vagina – fibro-muscular organ serving as – receptacle for intercourse – passageway for menstrual products – birth canal Fig 27-20b The Mammary Gland Modified sweat gland Overlaying the ____________ muscle 15-20 separate lobes separated by suspensory ligaments; each lobe contains several secretory lobules Lactiferous ducts leaving lobules; converge into 15-20 lactiferous sinuses Milk stored in lactiferous sinus until released at tip of nipple Fig 27-21 Lymphatic Drainage of Mammary Glands . . . . . . is of considerable clinical importance, why ??