Handy Web Addresses 10
advertisement

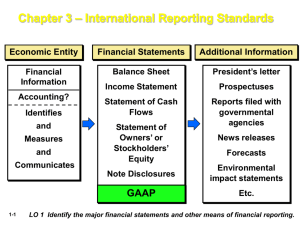
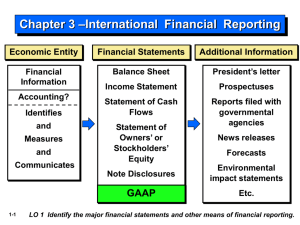
Corporate Finance Professor McCall Basic Information • Syllabus is online via my Faculty Profile • Read Syllabus and Attendance Policy • Required Book: William J. Carney, Corporate Finance Principles and Practice (Foundation Press) • A word on business and accounting background What is involved in the Study of Corporate Finance • Measurement, Calculation and Evaluation of Firms and their Output • The investment in and return from business ventures What do Corporate Finance Lawyers Do? • Represent Banks and Businesses in structuring and documenting secured and unsecured loans (Banking Law, Corporate Law, Contract Law, Uniform Commercial Code, Bankruptcy Law, State Debtor-Creditor Law, Tax Law) • Represent Investment Banks and Companies in accessing Public Finance Markets (Securities Laws, Contract Law, Corporate Law, Bankruptcy Law, Uniform Commercial Code, Tax Law) What do Corporate Finance Lawyers Do? • Represent Private Investors (Venture Capitalists, Business Angels, Private Equity Funds) and Companies in private investments in business ventures (Contract Law, Corporate Law, Securities Laws, Bankruptcy Law, Tax Law) • Represent Originators, underwriters and Services in Securitization (Securities Laws, Fraudulent Conveyance Laws, Corporate Law, Contract Law, Uniform Commercial Code, Bankruptcy Law, State Debtor-Creditor Law, Tax Law) Outline of Course • Accounting: Understanding and Using Financial Statements: Abbreviated Accounting for Lawyers • Understanding different metrics for valuing assets, liabilities, firms and investments • Overview of Capital Structure • Issues Connected with Common Stock • Corporate Debt with a focus on Corporate bonds • Issues connected to Preferred Stock • Options and Convertibles • Dividends and Distributions Accounting for Lawyers • • • • Why does it matter? I went to law school because I do not want to be an accountant Accounting – process of producing financial statements Auditing – Review of the methodology and processes for producing accounting statements • Public Company – A company with an obligation to file reports under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 usually as a result of conducting a public offering of securities • Private Company – A company which does nto have such an obligation Bodies of Accounting “Law” • US GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles in the United States) • Other country GAAP (UK GAAP, Mexican GAAP) • International Accounting Standards (IAS) also referred to as IFRS – transnational harmonization of accounting standards mandatory for European Public Companies and permitted in some US Public Company filings. Sources of Accounting “Law” • Financial Accounting Standards Board FASB – SFAS (Statements of Financial Accounting Standards) – (EITF) Early Issue Task Force Reports • US Securities and Exchange Commission – Regulation S-X – (SAB) Staff Accounting Bulletins – Office of the Chief Accountant and resolving Accounting Comments on Registration Statements • Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) • International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) Handy Web Addresses • Law.com’s daily corporate law news site: – http://www.law.com/jsp/pc/corplaw • The SEC’s EDGAR site for all corporate filings: – http://www.sec.gov/edgar/searchedgar/webusers.htm • The Corporate Library: – http://www.thecorporatelibrary.com • Financial Dictionary (your glossary for this course): – http://www.afponline.org/dictionary/bfglosa • Public Company Accounting Oversight Board – http://www.pcaobus.org/ 10 Handy Web Addresses • Financial Accounting Standards Board – http://www.fasb.org/ • Staff Accounting Bulletins – http://www.sec.gov/interps/account.shtml • International Accounting Standards Board – http://www.iasb.org/Home.htm 11