Human Digestive System Review Name: FI Bio Niehoff 2014 What is
advertisement

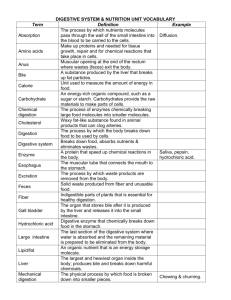
Human Digestive System Review FI Bio Niehoff 2014 Name: 1. What is the main goal of the digestive system? 2. Explain the phrase “you are what you eat.” 3. List the parts of the digestive tract in order, begin with the mouth and end with the anus. 4. What are the three main accessory organs that assist in digestion? 5. What is the role of the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder? 6. Where does digestion begin? 7. Explain the role of an enzyme. 8. What enzyme beaks down carbohydrates? Where does this digestion take place? 9. What enzyme breaks down protein? Where does this digestion take place? 10. What enzyme breaks down DNA? Where does this digestion take place? 11. What enzyme breaks down lipids? Where does this digestion take place? What product of the liver aids in fat digestion? 12. What is the difference between chemical and physical digestion? Give an example of both. 13. Where are the nutrients absorbed into the bloodstream? 14. What occurs in the large intestine? 15. What is the function of the rectum? 16. What is the benefit of the bacteria in our digestive tract? 17. What are some things you can do to maintain a healthy digestive system? 18. List the monomers and polymers for each of the macromolecules. 1. What is the main goal of the digestive system? The digestive system breaks down food for the body. It breaks the food down into useable parts for the body to use. 2. Explain the phrase “you are what you eat.” The food we eat is broken down into small pieces that are then used to produce the energy and structure of our body 3. List the parts of the digestive tract in order, begin with the mouth and end with the anus. Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus 4. What are the three main accessory organs that assist in digestion? Liver, pancreas, and gallbladder 5. What is the role of the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder? Liver- produces bile, gallbladder- stores bile, pancreas- produces hormones that control blood sugar levels 6. Where does digestion begin? In the mouth with teeth and saliva (amylase which begins carbohydrate digestion) 7. Explain the role of an enzyme. Enzymes are proteins that breakdown complex molecules into simpler, more useable, molecules 8. What enzyme beaks down carbohydrates? Where does this digestion take place? Amylase, mouth 9. What enzyme breaks down protein? Where does this digestion take place? Pepsin, stomach 10. What enzyme breaks down DNA? Where does this digestion take place? Nuclease, small intestine 11. What enzyme breaks down lipids? Where does this digestion take place? What product of the liver aids in fat digestion? Lipase, small intestine, bile 12. What is the difference between chemical and physical digestion? Give an example of both. Chemical digestion breaks bonds and chemically changes the molecular structure (an example is when amylase breaks down complex sugars into simple sugars) Physical digestion breaks down the food by physical means such as chewing 13. Where are the nutrients absorbed into the bloodstream? The nutrients are absorbed into the blood as the food travels through the small intestine 14. What occurs in the large intestine? Water from the food is absorbed into the bloodstream. The waste becomes solid 15. What is the function of the rectum? The rectum stores the waste 16. What is the benefit of the bacteria in our digestive tract? The good bacteria fight off bad bacteria to keep us healthy. Bacteria also break down foods that our body could not. 17. What are some things you can do to maintain a healthy digestive system? Eat fiber (fruits, veggies, whole grains), eat foods with good bacteria, do not overuse antibiotics 18. List the monomers and polymers for each of the macromolecules. Carbohydrates Polymer: Complex sugars Monomer: Simple sugars Protein Polymer: Protein Monomer: amino acid Lipid Polymer: lipids Monomer: fatty acids Nucleic Acids Polymer: DNA and RNA Monomer: nucleotides