Population Explosion
advertisement

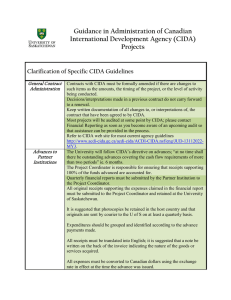
Population Explosion http://www.ted.com/talks/catherine_mohr_builds_green.html Questions to Think About… How fast has the human population grown in the past? What is the world population likely to be in the future? What factors are responsible for the world’s human population? Human Numbers Through Time: 2000 years ago At the dawn of the first millennium the world’s population was around 200 million people 1000 years later The population had risen by as little as 400 million. And well into the second millennium, it grew less than 0.1 percent each year. The numbers in Europe even fell in the 1300’s because of the Black Plague. But Beginning in the late 18th Century... The Industrial Revolution saw major changes occur within agriculture, manufacturing, and transportation industries, and they had a profound effect on society. Living standards were raised which in turn spurred growth. In the year 1800 The population climbed to 1 billion people, with 65% of the total population living in Asia. In the year 1927 One hundred and twenty seven years later the population reached approximately 2 billion people. In the Middle of the Century The discovery of antibiotics played an enormous role: Many bacterial infections in humans could be treated Cattle and farm animals could also be treated for disease, leading to their farming in larger groups Life expectancies began to increase leading to multiple generations of families living at the same time By the year 1960 Advances in medicine, agriculture and sanitation had spread to the developing world, increasing the population to 3 billion people. Medical Advances 1930 - 1940 Drug discoveries including antibiotics and anti-malarial medication First kidney dialysis machine Medical Advances 1940 - 1960 Heart-Lung Pump for open heart surgery developed (1953) Jonas Salk discovered the polio vaccine (1955) DNA structure was defined by Watson and Crick Medical Advances 1960 - 1980 First open heart transplant performed by Dr. Christian Barnard (1967) First CAT scanner developed First test tube baby born (1978) Medical Advances Since 1980 Fertility treatments Complex surgeries involving organ transplants Genetically modified organisms Edible vaccines Cloning The GREEN Revolution Between the 1940’s and 1960’s, a worldwide transformation of agriculture led to significant increases in food production. This transformation occurred as the result of programs of agricultural research, extension, and infrastructural development. Food Production The Green revolution resulted in increased food production to meet the demands of a growing population. Food Production Irrigation systems that allow for successful growth of crops Large scale machinery and silos for harvesting and storing grains Computerized milking machines to maximize milk collection Factory farming of pigs, cows and chickens Assembly line production and packaging facilities for virtually all types of foods How Factory Farming Started… Factory farming began with chickens in the United States about the 1930's Artificial incubators hatched the eggs that were taken from the breeding hens to replenish the broilers and egg-layers The enormous amount of excrement produced simply fell through the wire mesh floors of the cages the chickens were kept in – they ate, slept and defecated in the same small space, 24 hours a day Farmers gave the chickens sulphur drugs to prevent contagious diseases and fed them vitamin D to compensate for loss of sunshine Finally, to keep labour costs down, farmers automated lighting, watering and feeding Elsewhere in the World… India is the world's second largest producer of food next to China, and has the potential of being the biggest with the food and agricultural sector. The population of India has grown tremendously, in part due to their increased food production. This was accomplished by: Expanding farmland Planting more than one crop in a season Using genetically superior (or modified) seeds Factory farming methods 14 Years Later… New reproductive technologies had helped curb the growth rate. But with so many people already on the planet, a population "explosion" was under way, with most growth happening in the developing world. The four-billionth baby was born in 1974. 13 Years Later… In 1987 the five-billionth baby was born 12 Years Later… In 1999, the six-billionth baby arrived. Asia is home to the majority of Earth's inhabitants— roughly 61 percent, or more than 3.5 billion people. The World’s Current Population Estimated at 7 billion people and rising Over the next half century, our numbers will increase to approximately nine billion people Nearly all of this growth will take place in developing countries Population Growth in the Developing World Canada is a front-runner in assisting developing countries in the areas of agriculture, medicine and infrastructure CIDA (Canadian International Development Agency) is Canada’s lead agency for developmental assistance CIDA CIDA’s mandate is to support sustainable development in order to reduce poverty, and contribute to a more secure, equitable and prosperous world CIDA : Regions and Countries CIDA funds projects and programs around the world, including UN agencies CIDA also directly supports the governments of developing countries Global Population in 2050… “As you improve health in a society, population growth goes down. …before I learned about it, I thought it was paradoxical.” – Bill Gates, Microsoft Corp. http://www.gatesfoundation.org/Pages/home.aspx Human Population and Growth Is population growth really a problem? It has resulted in technological innovations, improved sanitation, better medical care, increased agricultural output, a decline in death rates and a drop in infant mortality. http://www.prb.org/pdf11/2011population-data-sheet_eng.pdf Demographic Transition Demographic transition is a theoretical model of economic and cultural change that explains the trend of declining death rates and birth rates that occurs when nations become industrialized. Demographic Transition Pre industrial: characterized by condition in which both death rates and birth rates are high Transitional stage: death rates decline and birth rates remain high. Industrial stage: creates employment opportunities, particularly for women causing birth rate to fall Post-industrial stage: both birth rates and death rates remain low and populations stabilize or decline slightly. 4 stages of demographic transition FIGURE 6.14 Population growth is seen as a temporary phenomenon Future of Humans ? Many people believe that humans will overshoot the Earth’s carrying capacity thereby degrading the earth and, in the long run, the carrying capacity will decrease overall. What do we know?? We do know that the population explosion has negatively affected both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, resulting in severe consequences for the future of mankind. Human impact: Habitat destruction – more land used for crops Global warming – (weather extremes and melting) Water pollution (oil spills) The challenge is to find balance and sustainable solutions. The challenge is up to you!!! Managing growth and resources In your text pages 557-568 Summarize the sections: • Food requirements • Waste disposal • Preserving Biodiversity References www.classbrain.com www.leeds.ac.uk www.enviroblog.org www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/worldbalance/ www.conservationtech.com www.faqs.org animalscience.wordpress.com www.leyden.co.nz http://www.inthesetimes.com excusetoeatvancouver.blogspot.com http://www.acdi-cida.gc.ca/index-e.htm