Cell Cycle
advertisement

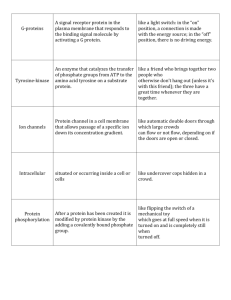
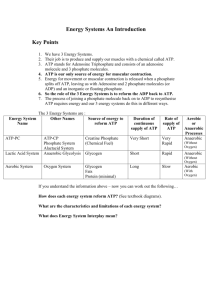
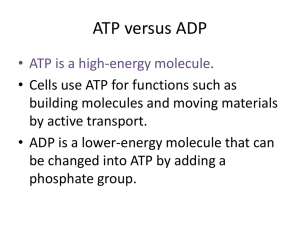
Biology Mr. Solis Energy is essential to life. Metabolism involves using energy to build or breakdown molecules. Some organisms trap sunlight for energy. (Autotrophs) Others eat to obtain energy. (Heterotrophs) The need for energy is important for cell movement, active transport, cell division and reproduction. ATP- adenosine triphosphate. 1adenosine molecule and 3 phosphate groups. Phosphate Groups have polarity which requires a lot of energy to add these groups to adenosine. When the ATP molecule only has one phosphate group, it is called AMP Adenosine monophosphate. Energy is required to add a second Phosphate group and the name becomes Adenosine diphosphate. When the third group is added then the name changes to adenosine triphosphate. The energy that becomes available for the cell is when the molecule is broken down back to ADP. Since it took a lot of energy to add the phosphate group. Then a lot of energy is released. Protein with in the cell attach themselves to ATP and as soon as the Phosphate group is uncoupled, the protein releases the ADP and a new ATP attaches itself to protein. Makes new molecules Maintain homeostasis Keeping needed substance in the blood stream. Cellular movement Trapping Energy from sunlight to create sugars which will later be used for energy. Photosynthesis happens in two phases. ▪ Light-dependent reactions ▪ Light-independent reactions Convert Light energy to chemical energy. This occurs when sunlight strikes the chlorophyll. Light is transferred to electrons, which then passes through an electron transport chain. An electron transport chain is a series of proteins embedded in the thylakoid membrane. These energized electrons provide energy to bond Phosphate groups to ADP and form ATP. Or it splits water to release oxygen to form NADPH. These two are used for light-independent reactions. The Third Stage is called Calvin Cycle. This is composed of series of enzyme reactions that use carbon dioxide to form sugars. (Carbon dioxide fixation) This takes place in the stroma. 1. 2. 3. 4. Each molecule of CO2 is added to a five carbon compound by an enzyme. The result is a 6 carbon compound. This compound splits into 2 three carbon compounds. One of the three is used to make organic compounds. Used for stored energy. The other three carbon sugar is used to regenerate the initial five carbon compound. Light intensity: as it increases photosynthesis increases. As all pigments are used, it reaches saturation point and photosynthesis level off. Temperature: Unfavorable temperatures may inactivate certain enzymes. The process by which mitochondria breaks down food molecules to form ATP is called respiration. Stages in Cellular Respiration Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle also called Krebs Cycle The electron transport chain Series of chemical reactions in the cytoplasm of a cell that breaks down glucose into two pyruvic acid and a three carbon compound. This is also called anaerobic respiration. No oxygen is required for this reaction to occur. Also known as the krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions similar to the Calvin cycle in that the molecule used in the first reaction is also one of the end products. Anaerobic process that follows glycolysis and provides a means to continue ATP until oxygen is available again. Lactic Acid Fermentation: is one of the process that supplies energy when oxygen is scarce. Alcoholic Fermentation: is used by yeast cells and some bacteria to produce CO2 and ethyl alcohol. Photo Food synthesized Energy from sun stored in glucose CO2 taken in O2 given off Produces sugars Requires sunlight Occurs only in the presence of chlorophyll Cellular Food broken down Energy of glucose released CO2 given off O2 taken in Produces H2O and CO2 Does not require light Occurs in all living cells.