Cells
advertisement

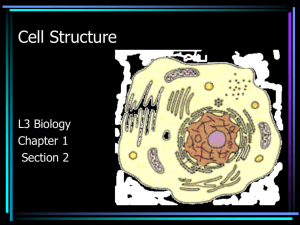
Cytology – the study of cells (pg. ??) Day 1 Cells Alive – www.cellsalive.com BrainPOP – www.brainpop.com username: edhpop password: edhpop1 Check out these videos: - Cells - Cell specialization Cell Theory The Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are composed of a cell or cells. 2. Cells are the basic (smallest) unit of life. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. 4. Cells contain hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division 5. All cells are basically the same in chemical composition 6. All energy flow of life occurs within cells Microscopes “Seeing is Believing” The light microscope or compound microscope allows us magnify objects up to 1000 times! Female egg cell is the largest cell in the body & can be seen without a microscope! A microscope can be used to view animal and plant cells. Do you see any visible organelles? Plant cells Magnification 10X 40 = 400X Animal cells Magnification 10X 40 = 400X Parts of a Microscope Match the names of microscope parts with the correct letter from the microscope diagram. _____1 Arm _____2 Body Tube _____3 Base _____4 Coarse Adjustment Knob _____5 Diaphragm _____6 Fine Adjustment Knob _____7 Light Source _____8 Objective (Lenses) _____9 Ocular Lens (Eyepiece) _____10 Revolving Nosepiece _____11 Stage _____12 Stage Clips Observation of Plant Cells Materials: Forceps, Microscope, Microscope Slide, Onion, Scalpel Onion Cells Procedure 1. Using a scalpel and forceps, remove a small piece of ONE LAYER of onion skin off of an onion and place it on a microscope slide. Avoid wrinkling the specimen. 2. View the onion cells on low power. Center the group of onion cells in field of vision. 3. View the onion cells on medium power. Only use the fine adjustment knob. If needed, center cells in field of view. 4. Use colored pencils to draw what you see. Label your drawing. Labels should include the name of the specimen, magnification level, and cell parts that can be seen. 5. Observe onion cells on high power. Only use the fine adjustment knob. As you focus through the group of cells you might see different layers of cells. Day 2 2 major types of cells Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell • Have nucleus • No nucleus • No membrane-bound • Membrane-bound organelles organelles • Evolved - like u & me • Circular • Linear chromosomes chromosome • Eubacteria Kingdom • Protista Kingdom • Fungus Kingdom • Archeabacteria • Plant Kingdom Kingdom • Animal Kingdom Organelles Very small size, can only be viewed with a microscope. Have specific functions. Found throughout cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells. Cell Structures and Functions Structure Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Golgi Bodies Lysosome Mitochondrion Nucleus Plasma Membrane Ribosome Vacuole Cilia Plant, Animal, Both Function City Comparison Organelles Found in Cells Endoplasmic reticulum (rough & smooth) – canals for movement Golgi Bodies – wrap & export proteins Nucleolus – makes ribosomes Lysosomes – digests & gets rid of wastes Ribosomes – makes proteins Golgi Bodies Stacks of flattened sacs Have a shipping side & a receiving side Receive & modify proteins made by ER Transport vesicles with modified proteins pinch off the ends Transport vesicle Lysosome Contain digestive enzymes Break down food and worn out cell parts for cells Programmed for cell death (lyse & release enzymes to break down & recycle cell parts) Nucleolus Cell may have 1 to 3 nucleoli Inside nucleus Disappears when cell divides Makes ribosomes that make proteins Smooth & Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth ER lacks ribosomes & makes proteins USED In the cell Rough ER has ribosomes on its surface & makes proteins to EXPORT Cell Powerhouse Mitochondrion ( mitochondria ) Site of Cellular respiration Active cells like muscles have more of these Burn sugars to produce energy ATP Surrounding the Cell Cell membrane Lies immediately against the cell wall in plant cells Made of protein and phospholipids Selectively permeable Cell or Plasma Membrane Cell membrane Living layer Controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell Selectively permeable Cytoplasm of a Cell Cytoplasm Jelly-like substance enclosed by cell membrane Provides a medium for chemical reactions to take place Nucleus/Inner membrane Nucleus Each cell has fixed number of chromosomes that carry genes Genes control cell characteristics Plant Cell Cell wall Made of cellulose which forms very thin fibers Strong and rigid Stations lab activity Station 1: Label Prokaryotic Cell - Bacteria All bacteria Ribosomes Label the 6 most important organelles! Station 2: Label Eukaryotic Cell - Plant Label the 13 most important organelles! Station 3: Label Eukaryotic cell - Animal Label the 13 most important organelles! Station 4: Create a Venn Diagram on LEFT PAGE to show organelles in common and organelles unique to each. Bacteria Cell Example Venn Diagram Animal Plant Unique Unique Organelles Organelles Shared organelles Bacteria Study your labeled cells – Quiz to follow! Quiz Quiz: 15.What kind of cell is cell A? 16.What kind of cell is cell B? 17.What type of cells are both A and B? Answers to quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Cell wall Cell membrane Mitochondrion Vacuole Golgi apparatus Cytoplasm Nuclear membrane Nucleolus Nucleus 10. Chromatin 11. Rough endoplasmic reticulum 12. Chloroplast 13. Centriole 14. Lysosome 15. Plant 16. Animal 17. Eukaryotic 9.