Chapter 11 – S'ENTRAINER A L'ENTRETIEN ORAL
advertisement
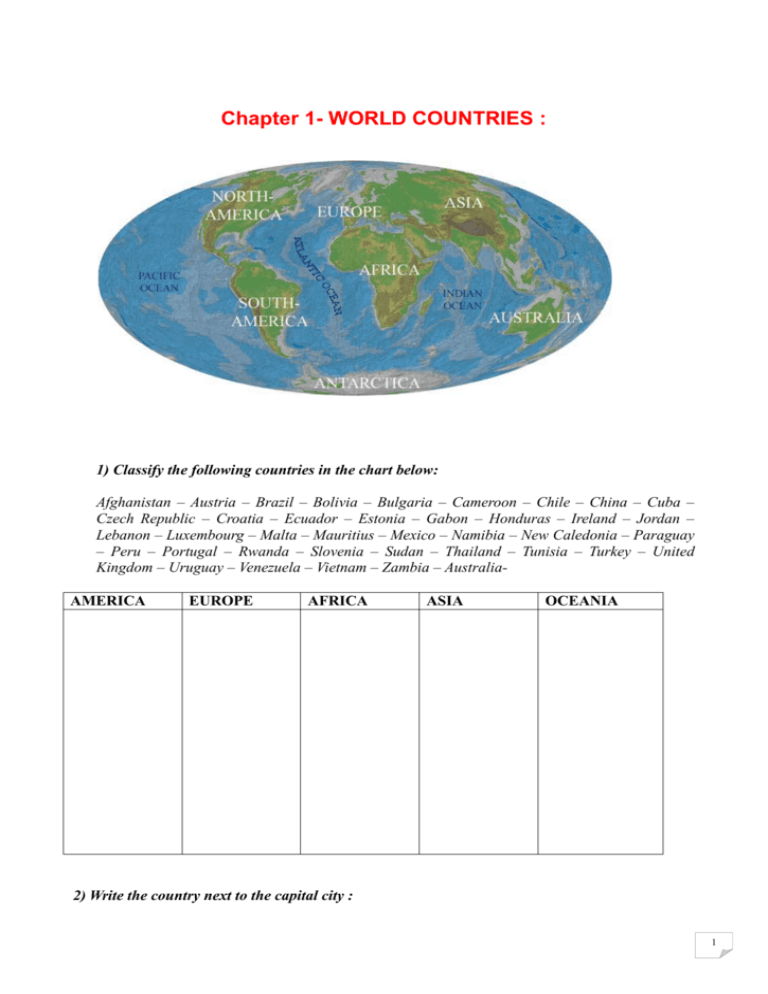
Chapter 1- WORLD COUNTRIES : 1) Classify the following countries in the chart below: Afghanistan – Austria – Brazil – Bolivia – Bulgaria – Cameroon – Chile – China – Cuba – Czech Republic – Croatia – Ecuador – Estonia – Gabon – Honduras – Ireland – Jordan – Lebanon – Luxembourg – Malta – Mauritius – Mexico – Namibia – New Caledonia – Paraguay – Peru – Portugal – Rwanda – Slovenia – Sudan – Thailand – Tunisia – Turkey – United Kingdom – Uruguay – Venezuela – Vietnam – Zambia – AustraliaAMERICA EUROPE AFRICA ASIA OCEANIA 2) Write the country next to the capital city : 1 COUNTRY A A A A B B B B C C C C C C C I C C C D CAPITAL CITY Algiers Buenos Aires Canberra Vienna Brussels La Paz Brazilia Sofia Yaounde Ottawa N’djamena Santiago Beijing Bogota San Jose Yamoussoukro Zagreb Havana Prague Copenhagen COUNTRY CAPITAL CITY E Quito E Cairo E Addis Ababa F Helsinki H Tegucigalpa H Budapest I Reykjavik I New Delhi I Tehran I Baghdad I Rome J Tokyo K Nairobi L Beirut Kuala Lumpur M M Bamako M Mexico M Rabat The N Amsterdam N Wellington COUNTRY P P P P R R S S S S S S S S S S T T U V CAPITAL CITY Asuncion Lima Warsaw Lisbon Bucarest Kigali Dakar Bratislava Ljubjlana Mogadishu Pretoria Madrid Colombo Mbabane Stockholm Berne Bangkok Ankara WashingtonDC Hanoi 3) Geography quizzes : a) Where can you find these mountain ranges or peaks : - Appalachians - Kilimandjaro - Urals - Aneto - Vesuvio b) What is the common religion to the following countries : - Spain, Portugal, Italy, Poland : _____________________________________ - Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Saoudi Arabia : ___________________________ - Germany, The Netherlands, Denmark : _______________________________ - Brazil, Argentina, Mexico : __________________________________________ - Thailand, Nepal, Vietnam : ___________________________________________ c) In which of the following countries do you not pay in euros? Austria, Switzerland, Germany, Luxembourg - d) In which of the following countries do you not pay in pounds ? England, Wales, Ireland, Scotland e) Where is the biggest forest and what is it called? _________________________ f) What is the longest river ? ___________________________ g)What is the biggest country in the world ? ________________________ h)What is the smallest country in the world? __________________________ i) What is the longest mountain range ? ___________________________ j)In which ocean is the Reunion Island located? ______________________ k)In which ocean is Cuba located? _____________________________ b) Where can you find these landmarks? 2 Write the names of the monuments below the photos and say where you can find them. Piazza San Marco – Acropolis - Loch Ness – Great Wall - Potala Palace - Saint Paul’s Cathedral – Angkor - Cappadocia – Fifth Avenue – Gyza Pyramid and the Great Sphinx – Stonehenge – Taj Mahal - 3 c) Which flags are these? South Africa – Canada – Lebanon – Japan - Argentina – Ireland - Hong Kong – Algeria – Paraguay – Israel – 4 Chapter 2- THE AIRPORT I- How much do you know about airports ? 1) What is the world's busiest airport : A- Heathrow airport, London, UK B- JFK Airport, New-York, USA C- Beijing Capital Airport, Beijing, China 2) Which of these airports uses a beach runway? A- Cibao International Airport, Santiago, Chile B- Frankfurt Airport, Frankfurt, Germany C- Barra Airport, Outer Hebrides, Scotland 3) How many airports are there in the world? A- 49,000 B- 172,000 C- 23,000 4) What are modern architects developing? A- floating airports B- space airports C- desert airports 5) What were the earliest takeoff and landing sites made of? A- grass B- concrete C- dirt 6) What is the world's oldest airport? A- College Park Airport, Maryland, USA B- Sydney Airport, Sydney, Australia C- Charles de Gaulle Airport, Paris, France 7) What was the first international airport? A- Chicago O'Hare International Airport, Chicago, US B- Croydon Airport, South London, UK C- Charles de Gaulle Airport, Paris, France 8) What is the use of grooves in the runway concrete surface? A- to slow down the aircraft after landing B- to draw off excess water in rainy conditions C- to help the aircraft stay parallel to the runway 9) When do airplanes produce their greatest load? A- during landing due to the impact B- when they move slowly on the runway C- during acceleration 5 10) What has been dramatically increased since September 11th, 2001? A- number of flights /day B- number of passengers /day C- airport security 11) All airports use a « trafic pattern » to assure a smooth traffic flow between arriving and departing aircrafts. What is the other name of the « traffic pattern »? A- flight circuit B- flight route C- traffic circuit 12) When does « Ground Control » stop and « Tower Control » start? A- when the plane has taken off B- when the plane leaves its parking place C- when the plane is ready to take off II- The airport environment : a) Look at the map below and say which parts of the airport you already know : 6 b) Look at the map above and then write the following words next to their definitions: maintenance hangar - access road - service road – service area - passenger terminal telescopic corridor - taxiway line - control tower ____________________________: Lane reserved for airport service vehicles. ____________________________: Glassed-in office where the air traffic controllers coordinate aircraft movement such as takeoff, landing and flight. ____________________________: Lane used by aircraft for entering or exiting a takeoff or landing runway. ____________________________: Structure through which passengers pass before or after their flight to pick up or leave their baggage and to go through customs. ____________________________: Structure where aircraft are maintained and repaired. ____________________________: Yellow line painted on the ground that shows aircraft the route to follow on the apron or the maneuvering area. ___________________________: Area around an aircraft that is reserved for service vehicles and ground crew attending to arriving or departing aircraft. ___________________________: Mobile corridor connecting the passenger loading area with the aircraft. c) Airport vehicles : c-1) Read the definitions below and write the correct words below the images : air start unit Vehicle that is equipped with an air compressor driven by a gas turbine; it pumps air into the aircraft’s jet engines to start them. 7 jet refueler Truck that pumps fuel from underground tanks into the aircraft’s tanks. tow bar Device that connects the tow tractor to the aircraft’s front landing gear. tow tractor Very heavy vehicle that pulls or pushes an aircraft onto the maneuvering area or the parking area. c-2) Reliez les mots à leur traduction : 1-Jet refueler Camion élévateur 2-Catering vehicle Camion citerne d'eau potable 3-Baggage trailer Véhicule de service technique 4-Tow tractor Camion avitailleur 5-Cargo vehicle Véhicule de service 6-Service vehicle Barre de tractage 7-Pasenger loading bridge Camion vide-toilette 8-Level floor vehicle Remorque à bagages 9-Lavatory/ toilet truck Tracteur de piste 10-Aircraft maintenance truck Camion de livraison de nourriture 11-Potable water truck Passerelle d'embarquement passagers 12-Tow bar Véhicule de fret 8 c-3) Write the names below the pictures : tank farm– apron or tarmac – flight pattern – parking lot - c-4) Airport codes : Which European airports do these codes correspond to? FRANCE CDG ORY BOD BSL CFE GNB MPL SXB LYS TLS NCE AJA EUROPE AMS VIE OSL BUD ATH GAT DUB HAM CPH MAD FCO ASIA BKK PVG PEK SVO NRT AFRICA TUN RBA ALG ABJ CAI CKY AMERICA LAX PHL YUL JFK CCS SFO EZE OCEANIA SYD NOU CGK 9 III- Inside the airport : Classify the following words in the grid below: newsagent – souvenirs shop – ATM – pharmacy – infirmary – bookshop – coffee shop – restaurant – clothes shop – immigration - shoe shop - toilets – bureau de change – showers – delicatessen – business lounge – information point – oversized luggage – left luggage – special assistance – check-in desks – X-ray machines – customs – Related to food Related to health and hygiene Related to shopping Related to money Related to travel Related to security What do the following pictograms represent: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 Now look at the map below and learn how to give directions to people : 1-Passenger terminal Contrôle de sécurité 2-Baggage cart / trolley Douane 3-Information desk / counter Hall 4-Security check Contrôle des passeports 5-Passport control Terminal 6-Customs Zone de duty-free 7-Lobby Comptoir d'enregistrement 8-Flight information board Zone de livraison bagages 9-Baggage claim area Chariot bagages 10-Duty-free shop area Comptoir d'informations 11-Check-in desk / counter Comptoir de ventes des billets 12-Ticket desk / counter Tableau d'informations IV- Airport Staff Classify the words below in the grid : captain – ramp agent – flight attendant – traffic agent – purser – cleaning agent – first officer – steward – stewardess – security officer – customs officer – police officer – immigration agent – serviceperson – check-in agent – reservation agent – assistance staff – baggage handler – air traffic controller – cabin crew – bar person – bus driver – supervisor – call centre travel agent Working outside Working in the terminal Working in the aircraft 11 ORAL COMPREHENSION : CUSTOMS AND IMMIGRATION : o Listen to Alan and Ernesto’s arrival in San Francisco and answer the questions : 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) What are the two documents that they must fill in? What are they made for? What do you do if you have goods less than $100 worth? Why does Alan go to Michigan? Where does he want to go sightseeing? How long will he stay? What does Alan mean by “just pulling your leg?” o Listen again and complete the following exercises : What do you call? - the control of the movement of goods : ______________________________ - the control of people’s movement across a border :______________________ - the announcement of goods you are taking to the country : ________________ What do you write if your goods do not exceed $100? ______________________ What do you call? - to use ink to make an impression on paper : ______________________________ - a small piece of metal used to hold papers together : _______________________ Complete with an expression meaning you are ready to do it : - You _________________________ go home. - He ____________________________ give it a try. - We _______________________________ take a picture of Micky Mouse. What is the common American expression for greeting? __________________________ How do you answer? ___________________________________ SAY THAT EVERYTHING WENT WELL How did it go? No problem. Write down the following informal expressions meaning that everything went well : o ___________________________________ o ___________________________________ o ___________________________________ o ___________________________________ o ___________________________________ o ________________________________________________________________. What do you call? - people who raise doubts in your mind, who are untrustworthy : ___________________ joking, teasing somebody : _______________________________ III- Now listen and practice. 12 Chapter 3- TRAFFIC AGENT : OPERATING AN AIRCRAFT A- THE TRAFFIC AGENT’S TASKS : 1) Say whether the sentences are right or wrong (if possible, correct the wrong sentences) : R W As an operator of aircraft, the traffic agent is responsible for the safe loading of your aircraft. He/ she is in charge of attending to airline customers. He/ she is in charge of storing the containers into the hold. Overloading the aircraft can have a consequence on the amount of fuel that will be used during the journey. Another consequence of overloading could be the damage of the landing gear and fuselage on landing. Because of overloading, take-off run necessary to become airborne could be shorter. If the center of gravity is too far forward, the aircraft will be tail heavy. If the center of gravity is too far aft, the aircraft will be nose heavy. An aircraft whose center of gravity is too far aft will be unstable and possess abnormal stall and spin characteristics. It is the purser's responsibility to see that the center of gravity lies within the recommended limits. As the flight progresses and fuel is consumed, the weight of the aircraft increases. The pilot must calculate the weight and balance not only for the beginning of the flight but also for the end of it. The aircraft weight and balance limits can be found in both the aircraft Weight and Balance Manual and the Flight Manual. If the weight exceeds the limits or if confidence in the numbers is lost, the aircraft must be reweighed. 13 B- USEFUL WORDS a) Link the following words to their definitions : Masse sans carburant Landing fuel Masse au décollage Trip fuel Masse à l’atterrissage Block fuel Carburant au bloc Zero fuel weight Carburant au roulage Landing weight Carburant au décollage Take off fuel Délestage Take off weight Carburant à l’atterrissage Taxi fuel WEIGHT TERMS b) Write the appropriate term next to the definition: Dry operating weight Landing weight Zero fuel weight Maximum zero fuel weight Ramp weight Maximum takeoff weight Takeoff weight Maximum landing weight Basic weight ___________________________: Empty weight including : aircraft structure, systems, engines, unremovable equipment, unusable liquids (fuel, oil and others), standard loose equipment. ___________________________: Basic weight plus operational items such as crew and pantry (equipment, food, beverages). ___________________________: Takeoff weight minus trip fuel. ___________________________: Weight limitation for landing, governed by structural and/ or operational requirements. ___________________________: Weight limitation for takeoff (brake release), governed by structural and/or operational requirements. ___________________________: Takeoff weight plus taxi fuel, i.e. weight of loaded aircraft before starting the engines. 14 ___________________________: Gross weight of aircraft at brake release for takeoff, i.e. actual zero fuel weight plus takeoff fuel. ___________________________: Dry operating weight plus total traffic load. ___________________________: Structural weight limitation. FUEL TERMS: b) Same exercise : Ballast fuel Block fuel Burn-off fuel Reserve fuel Taxi fuel Takeoff fuel Trip fuel __________________________: Non-usable fuel used for balancing purpose (only possible on some aircraft). The ballast fuel is separated from takeoff fuel (usable fuel) and loaded in a separate tank. The fuel must not be consumed or jettisoned during flight. __________________________: Weight of total amount of fuel on board before starting taxi. __________________________: Difference between takeoff fuel and trip fuel, consisting of route reserve, diversion, holding, and additional fuel. __________________________: Weight of fuel to cover APU consumption, engine start and ground maneuvers until start of takeoff. Standard weights are used which are, with a few exceptions, applicable at every airport. __________________________: Weight of total usable fuel onboard at the moment of takeoff (brake release). __________________________: Weight of the precalculated fuel consumption from takeoff to touchdown at the next point of landing. __________________________: Taxi fuel + trip fuel. 15 LOAD TERMS: Allowed traffic load Deadload Total traffic load (total payload) Underload ____________________________: total weight of baggage, cargo, mail. ____________________________: total weight of passengers, baggage, cargo, mail. ____________________________: difference between allowed traffic load and load actually carried. ____________________________: the weight remaining after the subtraction of the operating weight from the allowed takeoff weight. C- COMMUNICATING WITH THE CAPTAIN 1) Put the conversation in the right order : Number Captain: OK. What slot do we have? Captain: Thanks. Bye. Traffic agent: The refueler has just arrived. What are the fuel figures today? Traffic agent: OK. Thank you very much captain. And here is the weather report. The weather conditions are good today. The sky is clear and there are only light winds. Traffic agent: You have a slot at 6 pm. Captain: Here are the fuel figures: bloc fuel: 32,000 kgs, taxi fuel: 500 kgs, trip fuel: 29,000 kgs. The estimated elapse time is 3 hours forty-five minutes. There are 7 flight attendants in the cabin, and 2 pilots in the cockpit. The dry operating weight is 90,055 kgs, the dry operating index is 50.57. The maximum take-off weight is 171,700 kgs, the maximum zero fuel weight is 130,000 kgs and the maximum landing weight is 140,000 kgs. Traffic agent: Have a nice flight Sir. Captain: All right. How about refueling? Traffic agent: Good morning Captain. How are you today? Captain: OK. Thank you very much. Captain: Fine thanks. So, is the flight full today? Traffic agent: Yes, quite full. We have 311 passengers. There's one passenger in a wheelchair and we have two pets in the hold. 16 2) Now link these words to their translations : Braking action Indice Center of gravity Centre de gravité Flight level Niveau de vol Runway Freinage Sea level Niveau de la mer Loadsheet Feuille de chargement Flight plan Piste Index Plan de vol 3) Same exercise : Parking brake Bulletin météo Chocks Frein de stationnement GPU Groupe électrogène Handles Moteur Tow bar Portes de soute Weather report Poignées Engine Broche hydraulique Headset Cales Steering pin Casque Push back Barre de tractage Cargo doors Camion déplaçant l’avion 4) Write the appropriate sentences next to the appropriate situations : “You can disconnect your headset.” “ Show me the steering pin on your right side.” “ Engine number 1 is OK.” “GPU disconnected” “Doors closed”. “Handles checked” “Steering pin in place” “Parking brakes set” “ As soon as you’re ready we can go.” “Chocks removed.” “Ground check is completed.” “ Push back is completed.” 17 a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) k) l) Les freins de parking ont été mis en place : _________________________________ Le pilote est prêt à partir : _______________________________________________ Les portes des soutes sont fermées : _______________________________________ Les cales ont été retirées : _______________________________________________ Le groupe électrogène est débranché : _____________________________________ Le pilote demande à l’agent qu’il lui montre la broche hydraulique : ______________ _____________________________________________________________________ Le pilote dit à l’agent qu’il peut débrancher son casque : _______________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Les poignées des portes ont été vérifiées : ___________________________________ Le moteur est en bon état de fonctionnement : ________________________________ Toutes les vérifications au sol ont été effectuées : _____________________________ Le tractage de l’avion est terminé : _________________________________________ La broche hydraulique a été mise en place : __________________________________ D- COMMUNICATING WITH THE PURSER : Put the conversation in the right order : Traffic agent : All right. Well, have a nice flight to Cancun. Will you be staying there for a few days? Traffic agent : I wish I could go. Have a nice time. Purser : Five minutes? Fine. When will boarding take place? Purser : Thanks. Have a nice day. See you next time Purser : We are waiting for one flight attendant but he's on his way. He should be here in a few minutes. Traffic agent :How about your crew? Is everybody ready? Traffic agent : Boarding should start within fifteen minutes. Everything's on time today. Traffic agent: Well, we have 231 passengers today and 4 infants. Traffic agent : Hi, how are you today? Purser : So, is the flight full today? Purser : Fine thanks. How are you? Purser: OK. And where is the catering truck? Purser : Oh yes, three days. It's a great place. Nice hotel and beautiful beaches Traffic agent : It should be there within five minutes. Traffic agent : Good. E- USEFUL SENTENCES : a) Traduisez les phrases suivantes : 1234567- Combien de passagers y a-t-il aujourd’hui? Le vol est-il plein? Vide? Y a-t-il beaucoup de passagers? Combien y a-t-il d'enfants de moins de deux ans? Y a-t-il des animaux? Nous avons 512 passagers aujourd'hui. Le vol est presque plein. 18 8- Il y a beaucoup d'enfants sur ce vol. 9- Vous avez trois mineurs non accompagnés, deux bébés, un passager handicapé et un animal en cabine. 10- Le vol est presque vide. Il y a seulement 69 passagers. 11- Il n'y a plus de sièges disponibles. 12- Quand aura lieu l'embarquement? 13- A quelle heure arriveront les passagers? 14- L'embarquement commencera à 17h45. 15- Les passagers sont sur le point d'arriver. 16- Les passagers arriveront d'ici 20 minutes. 17- L'embarquement a pris du retard. 18- Où est le camion du catering? 19- Quels sont les poids de carburant? 20- Qu'en est-il du trip fuel? 21- Quel est le poids du taxi fuel? 22- Combien y a-t-il de membres d'équipage? 23- Combien de PNC? Combien de PNT? 24- Quels sont les poids de carburant? 25- Qu'en est-il du trip fuel? 26- Quel est le poids du taxi fuel? 27- Combien y a-t-il de membres d'équipage? 28- Combien de PNC? Combien de PNT? F- SALUER, PRENDRE DES NOUVELLES : Good morning Good afternoon Good evening Hello Hi How are you today? How are you doing? How have you doing recently? What's up? Fine, thanks. Pretty good. No problem. Excellent. Not too bad. Captain Sir Madam Mr Miller Mrs Johnson 19 Chapitre 4- THE AIRCRAFT I- Different types of airplanes: a) Write the names of these different sorts of aircrafts in the grid : taildraggers – helicopter – business jet – floatplane – biplane – glider – light sport – single engine - 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 b) Read the following texts and place the words in blue on the drawing: fuselage: The fuselage is that portion of the aircraft that usually contains the crew and payload, either passengers, cargo, or weapons. Most fuselages are long, cylindrical tubes or sometimes rectangular box shapes. Empennage is another term sometimes used. wing: The wing is the most important part of an aircraft since it produces the lift that allows a plane 20 to fly. The wing is made up of two halves, left and right, when viewed from behind. These halves are connected to each other by means of the fuselage. flap: Flaps are usually located along the edge of both the left and right wing, typically inboard of the ailerons and close to the fuselage. Flaps are most often used during takeoff and landing to increase the lift the wings generate at a given speed. This effect allows a plane to takeoff or land at a slower speed than would be possible without the flaps. elevator: The elevator is located on the horizontal stabilizer. It can be deflected up or down to produce a change in the downforce produced by the horizontal tail. It increases the downforce produced by the horizontal tail causing the nose to pitch upward. rudder: The rudder is located on the vertical stabilizer. It can be deflected to either side to produce a change in the side-force produced by the vertical tail. It creates a side-force to the left which causes the nose to yaw to the right. aileron: Ailerons are located on the tips of each wing. They are deflected in opposite directions (one goes trailing edge up, the other trailing edge down) to produce a change in the lift produced by each wing. The wing with more lift rolls upward causing the aircraft to go into a bank. cabin or cockpit: Most of the time the term cockpit is applied to a compartment at the front of the fuselage where the pilots and flight crew sit. Meanwhile, a cabin is typically a compartment within the fuselage where passengers are seated. nose & main gear: The landing gear is used during takeoff, landing, and to taxi on the ground. This system has two large main gear units located near the middle of the plane and a single smaller nose gear unit near the nose of the aircraft. c) Place the three following words on the drawing : YAW – PITCH - ROLL d) Now read the following definitions and write the appropriate words : rudder – aileron - fuel tank – flight deck - elevator – passenger cabin – baggage compartment – porthole – nose – wing – tail - navigation light – 1)_______________________: apparatus used to turn an aircraft. 2)_______________________: rear part of the fuselage. 3)_______________________: device used to regulate the altitude of an aircraft. 4)_______________________: section used aircraft travelers. 5)_______________________: container in which fuel is stored. 6)_______________________: movable flap on the trailing edge of the wing, operated by the control stick that allows an aircraft to bank. 7)_______________________: rear corner marker light. 8)_______________________: compartment where baggage is stored. 9)_______________________: front part of an aircraft. 21 10)_______________________: cubicle reserved for the operation of an aircraft. 11)_______________________: small, round, sealed window. 12)_______________________: each of two lateral planes of an aircraft, which provide lift and balance. f) Oral comprehension: ON BOARD ANNOUNCEMENT I- Listen to the text and answer the following questions : 1) What is the number of this flight? o 80 o 18 o 81 2) How long is the flight? o 2 hours and 40 minutes o 2 hours and 14 minutes o 2 hours and 4 minutes 3) What is the local time in Seattle? 1. 11.45 pm 2. 12.15 pm 3. 10.12 am 4) What is the current weather in Seattle? o Partly cloudy o Rainy o Sunny 5) Which gate will the plane arrive? o 13 o 3 o 30 II- Now listen again and complete: Hello everyone, this is the ____________________________, and I want to welcome you to _____________________ bound for ______________________. Our flight time today is ________________________________, and we will be __________________at an ________________________________________ of _______________________. The local time in Seattle is __________________________, and the ___________________________ is ___________________, but there is a ________________________ later in the day. We will be arriving at _________________, and we will be announcing ________________________ on our____________________ to the ______________________________. On ___________________________ Sky ________________ and the ______________, I want to wish you an _______________________________ in the Seattle ________________ or at your _____________________ destination. Sit back and _________________________. 22 AIRPORT ANNOUNCEMENT I- Listen to the text and answer the following questions: 1-Who is making the announcement? o A pilot o A flight attendant o A ticket agent o A ground crew member 2-What is the ultimate destination of the flight? o Atlanta o Miami o Caracas o Lima 3-What change has been announced? o The flight number o The gate number o The arrival time o The boarding time 4-What are the current weather conditions outside? o It’s raining o It’s cloudy o It’s hailing o It’s windy 5-What time will the plane depart? o 9.50 am o 12.15 pm o 4.05 pm o 8.45 pm II- Now listen again and complete : Hello. Passengers of _________________ bound for ________________, with __________________ in ___________________ and ________________. The departure gate _________________________ to ________________. Also, there will be a ____________________________________ due to _______________________________ outside. The ___________________ is in the process of ____________________________ in preparation for departure. It also looks like the flight is slightly _______________________ , so we are offering ________________________________________________ to a few passengers willing to take a ___________________________. We should be _________________ about a quarter to the hour. Thank you for your ________________________. 23 Chapter 5- PASSENGERS a) Look at the IATA codes below and say which types of passengers they refer to : CHD INF UMNR WCH BLND DEAF FQTV VIP PETC HUM b) What do you call the passengers below: Frequent traveller – infant – adults – deaf people – disabled people – pregnant women – children – elderly people – unaccompanied minors – blind people – 1 people over sixty years old : 2 children under 12 who travel alone 3 passengers aged 2 to 11 4 passengers under 2 years old 5 passengers over 12 years old 6 passengers who cannot see 7 passengers who cannot hear 8 women expecting a baby 9 passengers in a wheelchair 10 passengers who often travel a )Write the IATA codes next to the following passengers : PETC – DEAF – LANG – WCHS - AVIH – UMNR – WCHC - WCHR - MAAS - DEPA – FQTV DEPU – MEDA –INAD – OXYG – STCR –BLND –YP- ACCO Pet travelling in the cabin Animal travelling in the hold Blind passenger Deaf passenger Deported passenger escorted Deported passenger unaccompanied Frequent traveller Unaccompanied minor Passenger travelling in a wheelchair, able to climb stairs Passenger travelling in a wheelchair, unable to climb stairs Passenger unable to move and climb stairs Passenger needing oxygen Passenger needing medical assistance Passenger travelling on a stretcher Passenger unadmitted by immigration services Passenger aged 12 to 17 needing limited assistance Passenger needing assistance to make his/her way through the airport Person accompanying infant or passenger on a stretcher Passenger who does not know the language of the country 24 d) Boarding passengers : the check-in agent job : 1-Luggage belt / conveyor belt 2-Tag / sticker / label 3-Check-in desk / check-in counter 4-Carry-on luggage/ cabin luggage/ hand luggage 5-Hold luggage / checked luggage 6-Extra charge 7-Delayed flight 8-Postponed flight 9-Cancelled flight 10-Passport 11-ID 12-Luggage weight allowance 13-Excess baggage 14- To change a ticket 15- To upgrade 16-Check-in closing time Heure de fermeture de l’enregistrement Surpoids Vol différé Passeport Papiers d’identité Vol annulé Limite bagage autorisée Bagages cabine Bagage soute Comptoir d’enregistrement Surclasser Tapis bagage Modifier un billet Surcoût Etiquette Vol retardé e) Oral Comprehension: at the check-in desk 25 AT THE CHECK-IN COUNTER 1) Listen to the conversation at the check-in counter and complete the grid below : Passengers’s name Place of departure Destination Connection Departure time Delay? Documents Luggage Weight allowances Luggage weight Carry-on luggage Information about flight Seating preference Reason What he must go through in ¨Paris 2) Now listen again and fill in the blanks: - - - - - - Next in _____________, please. Check-in Sir and what’s your __________________ today? _______________, France. _________________ through Paris. Is departure still at _______________? Yes, indeed. Everything’s _______________ today. Can I have your _________________________________ please? Are you ______________ any __________________? Yes, just ____________________. But could you tell me what the _____________________________________ is? I think I might be _________________________. 35 kilos. Could you please _________________ your suitcase on the _________________ Mr Strauss ? OK. That’s just ______________ 35 kgs so you’ll be _____________. Oh, that’s a ________________. And I see you have one carry-on bag. Here is a ___________________ that are __________________ in your __________________ baggage. Please be sure you check before you go through this _____________________. Sure, could you tell me if the ________________ is very _________________? It’s almost _________________ but you’ll have ___________________________. Your reservation is __________________. Do you have a ______________________? ___________________________? Well, I’d just like an _____________________ near the ________________ so I can _________________________ in Paris. My connection is quite ________________ and I want to get through _________________________________ as quickly as possible. 48 I see but I don’t think it will __________________. Your luggage is checked through in Nice but you still have to __________________________ the customs in Paris yourself. So being first in line at immigration probably won’t ______________ you any _____________. 26 - - Well, I’ll ______________ it anyway. So, _________________________ if you could put me in an aisle seat ________________________________. We certainly can. Ok Sir, you’re in ______________________ on flight ______________ departing from ___________________ at 11.45. ___________________ your passport and boarding pass and the gate is over to your __________________. Thank you very much. _____________________________, Sir. Conversation : What do you know about the conditions for : travelling wih a pet travelling with a wheelchair travelling with an infant transporting one's musical instrument travelling as an unaccompanied minor 27 Chapter 6 - CARGO I- Useful words : Link the words to their definition : 1-Pound 2-Foot 3-Container 4-Airway bill 5-Unit Load Device 6-Pallet 7-Out of balance 8-Pitch 9-Tank 10-Cargo doors 11-Handles 12-Notification To Captain 13-Loadsheet 14-Trimsheet 15- Registration 16- Pantry load 17-Fly away kits II- Pied Lettre de transport aérien Déséquilibré Poignées Réservoir Livre Palette Feuille de chargement Feuille de centrage Note pour le commandant de bord Immatriculation Portes de soute Kits de sécurité avion Conteneur Provisions nourriture Dispositif de chargement Espacement (soute) Airport containers : A = Airbus; B = Boeing; L = Lockheed; MD = McDonnell-Douglas; F = freighter; ER = extended range var.; LR = long range var. 28 Air Freight Container Specifications Grid A : LD-1 IATA ULD Code: Also known as: Forkable: Classification: Rate Class: Suitable for: Internal volume: Maximum gross weight: AKC Contoured Container AVC, AVD, AVK, AVJ AVY LD-1 Type 8 B747, B767, B777, MD-11 4.8 cu.m 1588 kg LD-3 IATA ULD Code: Also known as: Forkable: Classification: Rate Class: Suitable for: Internal volume: Maximum gross weight: _______________________ AKE, AVA, AVB, AVC, AVK, DVA, DVE, DVP, XKS, XKG AKN, AVN, DKN, DVN, XKN LD-3 Type 8 ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ 29 The 88'' pallet Classification : 88'' pallet with net Suitable for : B747, B767, B777, DC-10 Maximum volume : 11.9 cu.m. Maximum gross weight: 747/ DC-10 : 6033kg 767 : 5103 kg 777/ DC-10 : 4626 kg Height : 162 cm Length : 317 cm Width : 223 cm The 96’’ pallet Classification : LD-9 Suitable for : A300, A310, A330, A340, B747, B767, B777, DC-10, MD-11, L1011 Maximum volume : 21.2 cu.m. Maximum gross weight: 6804kg Height : _________________ Length : _________________ Width : __________________ 30 Grid B : LD-1 IATA ULD Code: Also known as: Forkable: Classification: Rate Class: Suitable for (type of aircrafts): Internal volume: Maximum gross weight: ____________________ AVC, AVD, AVK, AVJ AVY LD-1 Type 8 _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ LD-3 IATA ULD Code: Also known as: Classification: Rate Class: Suitable for: Internal volume: Maximum gross weight: AKE AKE, AVA, AVB, AVC, AVK, DVA, DVE, DVP, XKS, XKG AKN, AVN, DKN, DVN, XKN LD-3 Type 8 A300, A310, A330, A340, B747, B767, B777, DC-10, MD-11, L1011 4.3 cu. m. 1588 kg 31 The 88'' pallet Classification : 88'' pallet with net Suitable for : B747, B767, B777, DC-10 Maximum volume : 11.9 cu.m. Maximum gross weight: 747/ DC-10 : 6033kg 767 : 5103 kg 777/ DC-10 : 4626 kg Height : _________________ Length : _________________ Width : __________________ The 96'' pallet Classification : LD-9 Suitable for : A300, A310, A330, A340, B747, B767, B777, DC-10, MD-11, L1011 Maximum volume : 21.2 cu.m. Maximum gross weight: 6804kg Height : 162 cm Length : 317 cm Width : 223 cm II- ORAL COMPREHENSION Listen to the text and tick the right number: 32 1.There are _____________ interesting museums throughout the country. A. 3 B. 13 C. 30 2. The bus fare to the capital is _______________ dollars. A. 15 B. 50 C. 55 3. This ________________ was constructed about ________________ years ago. A. 405 B. 415 C. 450 4. The _____________ for the trip to Europe will cost about _________ dollars. A. 708 B. 718 C. 780 5. We drove about ______________ miles on our trip. A. 1,100 B. 1,200 C. 1,300 6. She __________________ on _________ during her _______. A. 1,006 B. 1,016 C. 1,060 7. The mountain ______________________________________. A. 3,007 B. 3,017 C. 3,070 8. A total of ___________________ visited the __________________. A. 13,212 B. 30,222 C. 30,212 9. The population ___________________________ two years ago. A. 314,819 B. 314,890 C. 340,819 10. Over_____________________ people live in the capitol. A. 2,470,530 B. 2,417,530 C. 2,417,513 33 III- Weight and Measures Mesures de longueur Mesures de surface Mesures de volume 1 inch = 2,54 cm 1 foot = 12 inches = 30,48 cm 1 yard = 3 feet = 91,44 cm 1 mile = 1760 yards = 1,609 km 1 square inch = 6,45 cm2 1 square foot = 929,03 cm2 1 square yard = 0,836 m2 1 square mile = 2,59 km2 1 acre = 40,47 acres 1 cubic inch 1 cubic foot 1 cubic yard 1 cubic mile Mesures de capacité pour les liquides : 1 gill = 0,142 L (UK) = 0,118 L (US) 1 pint = 4 gills = 0,57 L (UK) = 0,472 L (US) 1 quart = 2 pints = 1,136 L (UK) = 0,944 L (US) 1 gallon = 4 quarts = 4,544 L (UK) = 3,776 (US) Mesures de poids : 1 grain = 0,0648 g 1 drachm/dram = 27,34 grains = 1,77g 1 ounce = 16 drachms = 28,35 g (abréviation : oz) 1 pound = 16 ounces = 0,453 kg (abréviation lb) 1 stone = 14 pounds = 6,349 kg 1 quarter = 28 pounds = 12,7 kg 1 hundredweight = 112 pounds (UK) = 50,8 kg / = 110 pounds (US) = 45,36 kg 1 ton = 20 hundredweights (UK) = 1016 kg / = 2000 pounds (US) = 907,18 kg 1) Convert the following measures : 1- 153 cm = ________________ '' 2- 79'' = _______________ cm 3- 3500 lb (pound) = _________________ kg 4- 4624 kg = __________________ lb 5- 300 m = ___________________ ft 6- 10,000 ft = ___________________m 7- 2.5 km = _____________________ yd 34 8- 3 l. = ___________________ gal 9- 3.79$ / gal = _________________ $ per liter 10- 3 lb = ___________________ grams 1. 2. 3. 4. 2) Convert : Two pints equal ________ quart. One gallon equals _______ quarts. Two gallons equal _______quarts. One-half gallon equals _____ quarts. 35 Chapter 7 - BAGGAGE I- Luggage description : 1)Definition of luggage. 2)What do you do if a bag is fragile or badly wrapped? 3)Why is it easy to trace a bag? 4)Where should you generally keep fragile items? 5)What are the maximum size and weight of cabin luggage? 6)What is the maximum weight of hold luggage? 7)What happens if the bag is overweight? 8)What sort of information can you find on a luggage tag? 9)What must be kept by the passenger? 10)What sort of other items can you check-in? Write the names under the different pieces of luggage : garment bag – flight bag – carry all – vanity case – suitcase - toilet bag – trunk – rucksack – 36 c) Find the questions to ask the following information about luggage : TYPE SIZE WEIGHT MATERIAL COLOUR SHAPE USE 37 Chapter 8 - DANGEROUS GOODS a) Write the type of dangerous goods under each drawing : toxic – environmental hazard – corrosive – harmful – explosive – oxidizing – flammable – Classify the following items in the grid below : fireworks – explosives – bats – knives – pesticides – flammable liquids – radioactive materials – guns – hockey sticks – ammunition (if declared) – poisons – guns (if unloaded, locked in a container and declared) – tools – swords – razors – liquids in containers >100ml – liquids in containers <100ml – Items allowed only in checked baggage Items banned from carry-on or checked baggage 38 Chapter 9- FLIGHT DISRUPTIONS I- Vocabulary : Link the words to their translation : 1- To take off 2- To land 3- Departure 4- Leaving from 5- Destination 6- To call at 7- To be due at 8- Non stop 9- Connecting flight 10- Domestic flight 11- International flight 12- Boarding area 13- To catch a flight 14- To catch the shuttle 15- Airfare 16- To miss 17- To be delayed 18- To be postponed 19- To be grounded 20- To be called off Etre annulé Faire escale Prendre la navette Tarif des billets Etre prévu à Vol intérieur Zone d’embarquement Rater Etre retardé Correspondance Vol direct Départ A destination de Etre différé Décoller Atterrir Partant de Prendre le vol Etre retenu au sol Vol international b) What time is the boarding ? Listen to the times and place the hands in the clocks : 39 Write down the times : 6 pm 5.05 10.55 7.20 am 11.45 6.50 pm e) Oral comprehension : TELLING THE TIME 1. Our class begins at __________________________________. A. 4:05 B. 4:15 C. 4:50 2. My mother left this morning at __________________________. A. 9:03 B. 9:13 C. 9:30 3. I'm going to catch my bus at ____________________________. A. 3:40 B. 4:20 C. 12:04 4. Let's get together at ___________________________________. A. 12:05 B. 5:12 C. 5:22 5. The store ____________________________________________. A. 4:06 B. 5:45 C. 6:15 6. The ____________ starts at _____________________________. A. 7:04 B. 7:14 C. 7:40 7. _____________________________________________________. A. 10:00 B. 10:05 C. 10:10 40 8. _____________________________________________________. A. 11:05 B. 4:12 C. 11:45 9. _____________________________________________________. A. 8:05 B. 8:15 C. 8:25 10._____________________________________________________. A.3:03 B.3:13 C. 3:30 f) Traduire : il y a une heure : la semaine dernière : hier matin : la nuit dernière : ce matin : dans l’après-midi : ce soir : toute la soirée : la nuit : demain soir : dans une semaine : le week-end prochain : aujourd’hui en huit : samedi : une fois par semaine : deux fois par jour : trois fois par mois : une semaine sur deux : nuit et jour : b) Imagine the passengers’ questions : 1- ____________________________________________________________________ _ I’m afraid it’s due to cold weather. The ground crew is deicing the wings. 2- ____________________________________________________________________ It shouldn’t be long. Just about half an hour. 3- ____________________________________________________________________ I’m sorry but your flight has been overbooked. I’ll rebook a ticket for you. 4- ____________________________________________________________________ The flight is due at 12.15 am. 5- ____________________________________________________________________ The shuttle will wait for you at entrance number 12. 41 c) Translate the following sentences : 1- Le vol est annulé en raison des conditions météorologiques. 2- Il arrive dans 5 minutes. 3- Il est en retard. 4- Il ne viendra pas. 5- Je suis désolé mais ils ont été retardés. 6- Est-ce que l'équipage est prêt? 7- Un PNC manque. 8- Tout le monde est là. 9- Nous embarquerons les passagers quand votre collègue sera là. 10- Tout est à l'heure aujourd’hui. 11- Nous procéderons à l'embarquement quand tout l'équipage sera là. 12- J'ai bien peur que nous n'ayons pris du retard. 42 Chapter 10 - WEATHER CONDITIONS a) Write the names next to the pictograms : b) Classify the words in the grid : ice- gale- black ice- flurries- breeze- drizzle- frost- fog- rainbow- thunder- cyclone- dog days- sunny intervals- snowflakes- shower- snowdrift- downpour- blizzard- mist- flash of lightning- storm- draught- drought- hurricane- typhoon- COLD WEATHER HOT WEATHER WIND SNOW RAIN CLOUD 43 c) Now link the words to their translation : 1-Mild 2-Changeable 3-Unsettled 4-Fair 5-Biting 6-Damp 7-Wet 8-Chilly 9-Icy Beau Glacial Piquant, mordant Mouillé Humide Frais Changeant Doux Incertain d) Do the same with these verbs : 1-To shine, shone, shone 2-To blow, blew, blown 3-To roar 4-To break out 5-To whirl 6-To cloud over 7-To clear away 8-To pour 9-To drizzle 10-To thicken 11-To dissipate 12-To melt 13-To freeze Tourbillonner Gronder S’éclaircir Souffler Pleuvoir à verse Geler Bruiner S’épaissir Se dissiper Fonder Se couvrir Briller Éclater e) Link the sentences to their meaning : 1-It was boiling hot, so we all jumped into the lake. 2-It's supposed to go below freezing before the week-end. 3-It's a bit chilly so I think you should wear a coat. 4-They're calling for a cold spell so we put off our camping trip. 5-I think I'll take the dog for a walk. It's only drizzling now. 6-Forest fires are a serious danger during a drought. 7-The flood was so bad, our basement was full of water. 8-We couldn't see the bridge because there was too much fog. 9-According to the 5 day forecast, it's going to rain on our wedding day. 10-It was a freezing cold day for the Santa Claus parade. 11-Some flowers are so strong they can withstand frost. 12- There are a few flurries but the snow isn’t sticking to the ground. Overflow of rainwater. A long period with no rainfall. Raining slightly. Cold. It was a very hot day. A period of colder than average weather. A covering of ice needles. Under than 0°C (32°F) A very cold day. A cloudlike mass that covers the earth and reduces visibility. Very light snowfall. Prediction, estimation in advance. 44 Oral Comprehension THE WEATHER FORECAST Adams, Tennessee Johannesburg, South Africa Papeete, Tahiti The Weather today in Adams, Tennesse Through 3 AM you can _________________ an ______________ of scattered to ______________ showers ... and isolated __________________ to expand ___________________. This rain should ________________ the Nashville _________________ around 2AM and reach the Kentucky _______________ around 3 AM or 4AM. Most of the _________________ will produce _____________ to ________________ rainfalls ________________ __________________ will produce brief _______________ _______________. Then on Friday showers and ___________________ will be ________________ in the morning. It will be ___________________ with ______________ around 80 and a ___________ ________ from 10 to 20 ________________________________. At night ________ will be around 70. The weather in Johannesburg today It will be partly _______________ along the ______________. ______________ to ____________ conditions are ________________ countrywide but _________ in places in the west and in the Gordonia _________________. These _______________ are expected to __________________ until tomorrow, when a cold front will be _______________ south of the country, bringing some _______________ to the __________________ parts. The weather today in Papeete The weather today will be ____________ to ____________ __________. Lows will be around 73F and _____________ ____________ will blow at 5 to 10 mph. Tomorrow there will be ____________ ______ ____________ and sunshine with _____________ around 84 F and west winds at 5 to 10 mph. At night you can expect a few clouds _______ ________ ___ ___________ with ______________ winds. 45 13) Write the words from the text next to their definitions : 11) dispersed : ___________________ 12) to increase in extent, to spread out : ________________________ 13) heavy, drenching rain : _______________________ 14) probably destined : ________________________ 15) extending accross the whole nation : _______________________ CONVERSATION o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o What's your favorite season and why? Do you think weather patterns are changing? If so, why do you think this is? Do you have many disasters in you country which are caused by weather? Do you like snow? Which do you like better hot weather or cold weather? What's the average temperature in your country in the summer time? o How about in the winter? How does weather affect your attitude? How to you depend on the weather reports on TV? When would knowing tomorrow's weather change you plans? Have you ever checked the weather for your city on the Internet? What time of year is the best weather where you live? Have you ever been in a typhoon? Where do you get your weather information? What is your favorite winter activity? What is the hottest natural temperature (not in a sauna) you have experienced? Where and when was it and what did it feel like? 46 The weather Find fifteen adjectives related to the weather : D N U L W A Y U N S E T T L E D E I E A M Y O L F B R S I T M Y Y I C Y W C E L F T C D S I S S I D C Y Y T S I M E A S E Z C H I L L Y L W I H H C I L D D O R A R L M B D T I F O Y N E A M Y T I I T E M U H F V Q R D W D R E Y A I I D O F O I E L Y L R Y C D S E O N T L D D Z C E Y G G O F I T S U A W M T Y F F A Y Y H L E I D T A Y D N I W S U H S D W L E F W U Y D U O L C I A E F Y I H H L I W E B Y U T L C E C M E H S E L A E G N A H C B I S 47 Chapter 11 – S’ENTRAINER A L’ENTRETIEN ORAL I- Find the words corresponding to the definitions : strength – research – achievement – references – weakness – competition – proof – resume/CV – up-to-date – interview – goal o something very good and difficult that you have succeeded in doing: ______________ o an aim or purpose: _______________________ 3) a meeting in which someone asks you questions to see if you are suitable for a job or course: ________________________ 4) a detailed study of a subject, especially in order to discover (new) information or reach a (new) understanding: _________________________ 5) when someone is trying to win something or be more successful than someone else: ___________________________ 6) a letter that is written by someone who knows you, to describe you and say if you are suitable for a job or course, etc: _________________________ 7) when someone or something is not strong or powerful: ______________________ 8) the ability to do things that need a lot of physical or mental effort: _________________ 9) a short written description of your education, qualifications, previous employment and sometimes also your personal interests, which you send to an employer when you are trying to get a job : _______________________ 10) a fact or piece of information which shows that something exists or is true: _____________________ 11) modern, recent, or containing the latest information: ______________________ 48 questions to avoid asking 1- "How many weeks holiday do I get?.." 2- "When would I get a pay-rise?.." 3- "What are the lunch times?.." 4- "What sort of car do I get?. 5- "What other perks are there?.." 6- "What are the pension arrangements?.." 7- "Do you have a grievance procedure?.." 8- "What expenses can I claim for?.." 9- "How soon before I could get promoted?.." 10- "When is going-home time?.." III- Read the following advice and say to which question they apply best : Anger to me means loss of control. I do not lose control. When I get stressed, I step back, take a deep breath, thoughtfully think through the situation and then begin to formulate a plan of action. I do not have a pet peeve. If something is bothering me, I step back, analyze "why" and find a good solution. If you asked my teenage daughter she would tell you my pet peeve is the volume on her radio! I've learned from each boss I've had. From the good ones, what to do, from the challenging ones - what not to do. The company was cutting back and, unfortunately, my job was one of those eliminated. I spent time being a stayat-home mom and volunteering at my daughter's school. I found myself bored with the work and looking for more challenges. I am an excellent employee and I didn't want my unhappiness to have any impact on the job I was doing for my employer. 49 IV- Now prepare yourself to these job interview questions : - Tell me about yourself. Why did you leave your last job? What experience do you have in this field? What do co-workers say about you? What do you know about our company? What have you done to improve your knowledge in the last year? Are you applying for other jobs? Why do you want to work for us? Do you have a team spirit? What is your philosophy towards work? Have you ever been asked to leave a position? Why should we hire you? How would you be an asset to this company? What irritates you about co-workers? What are your greatest strengths? Tell me about your dream job. Why do you think you’d do well in a job? What has disappointed you about a job? Tell me about your ability to work under pressure? What qualities do you look for in a boss? Tell me about a time you resolved a conflict with others? What motivates you to do your best on the job? Would you be willing to relocate? What have you learnt from your mistake? Do you have blind spots? How do you propose to compensate for your lack of experience? Do you have any questions? 50 V- A useful list of words Verbs to apply for to set goals to achieve to improve to be eager to to complete to conceive to classify to solve to graduate to attend a school to meet your expectations to be in charge of + ING to be responsible for + ING to be able to + BV Nouns ability to prioritize problem-solving skills focus on projects positive attitude leadership skills loyalty energy initiative hard work sense of humor holder of high standards a benefit an asset Adjectives fair loyal accurate active adaptable adept broad-minded competent conscientious creative dependable determined diplomatic discreet efficient energetic enterprising enthusiastic experienced tactful trustworthy firm genuine honest innovative logical mature methodical motivated objective outgoing personable pleasant positive practical productive reliable resourceful self disciplined sensitive sincere successful VI- Translate using the right tense : Traduisez les phrases suivantes après avoir réfléchi au temps (ou au modal) approprié : 1) J’ai étudié au lycée Jacques Prévert de 2000 à 2003 . Temps à employer : ________________________ Pourquoi ? Traduction : ____________________________________________________________ 2) Je suis actuellement un stage d’agents d’escale chez Aéroform. Temps à employer : ________________________ Pourquoi ? Traduction : _____________________________________________________________ 3) Depuis six mois, je travaille en tant qu’agent de sécurité à l’aéroport de Roissy. Temps à employer : ________________________ Pourquoi ? Traduction : _____________________________________________________________ 4) J’ai été employé par Air France de mai 2004 à juin 2005. Temps à employer : ________________________ Pourquoi ? Traduction : _____________________________________________________________ 5) Je ferai de mon mieux pour satisfaire à vos exigences. Modal à employer : ________________________ Pourquoi ? Traduction : _____________________________________________________________ 51 CV / RESUME Jerome ANDREW 111 Mt. Aberdeen Close SE Calgary, AB T27 Phone : (403) 401- 1356 OBJECTIVE : To work for a progressive and reputable airline that offers opportunity for growth. PROFESSIONAL PROFILE : - Strong customer service and interpersonal skills - Excellent communication skills - Strong organizational skills and ability to multi-task - Effective time management skills in determining priorities, scheduling and meeting deadlines - Remains calm under pressure, used to working to deadlines - Experience working in an airport environment in a variety of roles - Positive attitude, hard working team player CERTIFICATIONS AND EDUCATION - First Aid Certification - Finance Clerk, Inventory control, Aircraft Groomer, Ramp Agent and Baggage Agent course work - Restricted Radio Operators certificate - Flight Dispatcher certificate PROFESSIONAL EXPERIENCE Aircraft Groomer Calgary International Airport, Calgary, AB - Provided First Aid support - Managed ramp agent, baggage agent and inventory control duties 1989-2008 Infantry Person 1973-1989 Canadian Armed Forces (Various locations) - Performed electrical generating systems technician, pay clerk and electrician duties VOLUNTEER EXPERIENCE 2006-present Member services – Potential Place 1997-1999 Scouts Leader – Scouts Canada REFERENCES AVAILABLE UPON REQUEST 52 VOCABULAIRE AGENT DE TRAFIC 1) The Airport 2) Airport staff 3) Traffic 4) The aircraft 5) Passengers 6) Check-in and boarding 7) Flight disruptions 8) Baggage 9) Weather 53 THE AIRPORT Runway Service area Terminal Taxiway Control tower Air start unit Jet refueler Tow bar Tow tractor Catering vehicle Baggage trailer Cargo vehicle Level floor vehicle Toilet truck Maintenance truck Potable water truck Tarmac Parking lot Newsagent Souvenirs shop ATM, cash machine Pharmacy /chemist/ drugstore Infirmary Bookshop Coffee shop Restaurant Clothes shop Immigration Customs Showers Check-in desk X-ray machines Business lounge VIP lounge Foreign exchange office Lift / elevator Disabled facilities Baggage cart/ baggage trolley Information desk / information counter Security checkpoint Lobby Baggage claim area Duty-free shop Flight information board Piste Zone de service Terminal Taxiway, zone de roulage Tour de contrôle ASU Camion avitailleur Barre de tractage Tracteur de piste, « tracma » Véhicule de transport de nourriture Remorque à bagages Véhicule de fret Véhicule élévateur Camion vidange toilettes Véhicule de service technique Camion d’eau potable Tarmac Parking Marchand de journaux Magasin de souvenirs Distributeur d’argent Pharmacie Infirmerie Librairie Café Restaurant Magasin de vêtement Immigration Douane Douches Comptoir d’enregistrement Rayons X Salon business Salon VIP Bureau de change Ascenseur Aménagements handicapés Chariot bagages Comptoir d’informations Point de contrôle sécurité Hall Zone de livraison bagages Duty-free Tableau d’informations 54 AIRPORT STAFF Captain Ramp agent Flight attendant Traffic agent/ flight dispatcher Purser Cleaning staff First officer, co-pilot Steward, stewardess Security officer Customs officer Police officer Immigration officer Cabin crew Service person / assistance staff Reservation agent Check-in agent Baggage handler Air traffic controller Bus driver Supervisor Call center travel agent Commandant de bord Agent de piste Personnel Navigant Commercial Agent de trafic Chef de cabine Personnel de nettoyage Co-pilote Steward, stewardess Agent de sécurité Agent des douanes Policier Agent d’immigration Equipage de cabine Personnel d’assistance Agent de réservation Agent d’enregistrement, agent d’escale Bagagiste Contrôleur aérien Chauffeur de bus Superviseur Agent de call center TRAFFIC Landing fuel Trip fuel Block fuel Zero fuel weight Landing weight Take off fuel Take off weight Taxi fuel Maximum zero fuel weight Maximum takeoff weight Maximum landing weight Ballast fuel Burn-off fuel Reserve fuel/ remaining fuel Allowed traffic load Deadload Total traffic load Underload (before LMC) Brakes Centre of gravity Flight level Sea level Loadsheet Carburant à l’atterrissage Délestage Carburant au bloc Masse sans carburant Masse à l’atterrissage Carburant au décollage Masse au décollage Carburant au roulage Masse maximum sans carburant Masse maximum au décollage Masse maximum à l’atterrissage Carburant de ballast Carburant consommé Carburant de réserve Charge offerte Masse en soute Charge transportée Charge offerte résiduelle Freins Centre de gravité Niveau de vol Niveau de la mer Feuille de chargement 55 Flight plan Index Parking brake Chocks GPU Handles Weather report Engine Headset Steering pin Push back Cargo doors Plan de vol Indice Frein de parking Cales Groupe électrogène Poignées Bulletin météo Moteur, réacteur Casque Broche hydraulique Tracteur avion Portes de soute THE AIRCRAFT Wing Aileron Flap Elevator Fuselage /body Cabin Cockpit Rudder Nose Tail Nose gear Main gear Fuel tank Navigation light Porthole Aile Aileron Volet Elévateur Fuselage Cabine Poste de pilotage Gouvernail Nez Queue Train avant Train d’atterrissage principal Réservoir Lumière de navigation Hublot PASSENGERS Child (pl. children) Infant Unaccompanied minor Wheelchair Blind Deaf Frequent traveller VIP (Very important Person) Pet Pet crate Elderly people Pregnant woman Stretcher Adult Disabled person Enfant Enfant de moins de deux ans Mineur non accompagné Fauteuil roulant Aveugle Sourd Voyageur abonné VIP Animal de compagnie Caisse de transport d’animal Personnes âgées Femme enceinte Civière Adulte Handicapé 56 CHECK-IN AND BOARDING Luggage belt/ conveyor belt Tag/ sticker/ label Check-in desk/ check-in counter Carry-on luggage/ cabin luggage/ hand luggage Hold luggage/ checked luggage Extra charge Overweight / excess baggage Passport ID Luggage weight allowance To change a ticket To upgrade Check-in closing time Boarding gate Boarding pass Boarding area Airfare Tapis bagage Etiquette Comptoir d’enregistrement Bagages à main Bagages soute Surcoût Surpoids, excédent bagages Passeport Papiers d’identité Poids baggage autorisé Modifier un billet Surclasser Heure de fermeture d’enregistrement Porte d’embarquement Carte d’embarquement Zone d’embarquement Tarifs des billets FLIGHT DISRUPTIONS To take off To land Departure Leaving from Destination …/ bound for… To call at To be due at/ to be scheduled at Stopover/ layover Connecting flight Non stop/ direct flight Domestic flight International flight To catch a flight To catch the shuttle To miss To be delayed To be cancelled/ to be called off To be postponed To be grounded Décoller Atterrir Depart Partant de À destination de Faire escale Être prévu à Escale Correspondance Vol direct Vol intérieur Vol international Prendre un vol Prendre la navette Rater Être retardé Être annulé Être différé Être retenu au sol BAGGAGE Luggage / baggage (indénombrable) Carry-on luggage / hand luggage/ cabin luggage Checked luggage/ hold luggage Bagage Bagage à main Baggage soute 57 Trunk Flight bag Garment bag Vanity case Backpack/ rucksack Suitcase Carry-all Toilet case Prohibited items Dangerous goods To wrap To trace To check To check in Flammable Corrosive Harmful Environmental hazard Explosive Toxic Oxidizing Containers To load To unload Pallet ULD Malle Sac cabine Housse à vêtements Vanity case Sac à dos Valise Sac fourre-tout Trousse de toilette Objets interdits Matières dangereuses Emballer Suivre la trace 1-Vérifier ; 2- Enregistrer Enregistrer Inflammable Corrosive Nuisible Dangereux pour l’environnement Explosive Toxique Inoxydable Conteneurs Charger Décharger Palette ULD WEATHER Snow Snowflake Flurries Snowdrift Fog Mist Rain Rainfall Downpour Rainbow Drizzle Wind Storm Thunderstorm Flash of lightning Sunny intervals Blizzard Breeze Cyclone Tornado Neige Flocon de neige Rafale (vent, neige) Conger Brouillard Brume Pluie Chute de pluie Averse Arc en ciel Bruine Vent Tempête, orage Orage Éclair Éclaircies Blizzard Brise Cyclone Tornade 58 Hurricane Typhoon Draught Ice Frost Black ice Sun Coldness Coolness Heat wave/ dog days Drought Heat Warmth Spell Forecast Weather Weather report Hot Warm Cool Chilly Mild Changeable Unsettled Fair Biting Wet Humid/ damp Icy To shine, shone, shone To blow, blew, blown To roar To break out, broke out, broken out To whirl To cloud over To clear away To pour To drizzle To thicken To dissipate To melt To freeze, froze, frozen Ouragan Typhon Courant d’air Glace Givre Verglas Soleil Froid Fraîcheur Canicule Sécheresse Chaleur Chaleur Période, vague Prevision Temps Bulletin météorologique Chaud Chaud Frais Frais Doux Changeant Incertain Beau Piquant, mordant Mouillé Humide Glacial Briller Souffler Gronder Éclater Tourbillonner Se couvrir S’éclaircir Tomber à verse Bruiner S’épaissir Se dissiper Fonder Geler 59 FICHES GRAMMATICALES 1) Le présent simple 2) Le présent en BE+ING 2) Le prétérit simple 3) Liste des verbes irréguliers 4) Le prétérit en BE+ING 5) Le present perfect simple 6) Le present perfect en BE+ING 7) Les auxiliaires modaux 8) Les équivalents des modaux 9) Les auxiliaires modaux au passé 10) Expressions du futur et du conditionnel 11) Subordonnées en IF 12) Pronoms et adjectifs personnels, possessifs et réfléchis 13) SOME et ANY 14) Les quantifieurs : MUCH, MANY, LITTLE et FEW 15) Les comparatifs et les superlatifs 16) Corrections des exercices 60 1- LE PRESENT SIMPLE a) Formation : -A la forme affirmative, on met la base verbale à toutes les personnes et on rajoute un S à la troisième personne : -Aux formes interrogatives et négatives, on utilise l’auxiliaire DO. Forme affirmative I work You work He / She / It workS We work You Work They work Forme interrogative Do I work ? Do you work ? DoES he / she / it work? Do we work? Do you work? Do they work? Forme négative I don’t work ( I do not work) You don’t work He / she / it doESn’t work We don’t work You don’t work They don’t work Attention ! Aux formes interrogatives et négatives, le S se reporte sur l’auxiliaire DO (qui devient DOES). Il disparaît donc de la base verbale. Une seule marque suffit. b) Prononciation : [s] it takes, she thinks, he checks [z] she flies, it weighs, he knows [iz] it catches, he watches, she misses c) Emploi : Le présent simple sert à : - parler de vérités générales : Water boils at 100° Celcius. - parler de caractéristiques du sujet : She doesn’t like flying. - parler d’habitudes : British people drink a lot of tea. - parler d’un état présent (avec les verbes d’état comme be, have, know, seem, believe,... pour exprimer des sentiments, croyances, etc…) : She knows it will happen. 61 2- LE PRESENT EN BE+ING Formation : Le présent en BE + ING se forme à l’aide de l’auxiliaire BE au présent suivi du verbe en ING. Forme affirmative I am travelling You are travelling He / she / it is travelling We are travelling You are travelling They are travelling Forme interrogative Am I travelling ? Are you travelling ? Is he travelling? Are we travelling? Are you travelling? Are they travelling? Forme négative I am not travelling You are not/ aren’t travelling He is not/ isn’t travelling We are not/ aren’t travelling You are not/ aren’t travelling They are not/ aren’t travelling b) Emploi : Le présent en BE + ing sert à : - parler d’actions en cours : The boy is sleeping right now. - parler d’un futur proche : He is leaving tomorrow. Remarque : Certains verbes exprimant une activité mentale sont peu compatibles avec la forme en ING : believe, doubt, know, like, love, hate, wish, seem, suppose, want... EXERCICE 1 : Choisissez entre présent simple et présent en ING : o French people _______________________ (drink) a lot of wine. o I hope she will be there soon. I _________________ (depend) on her. o Could you come here, I ___________________ (want) to talk to you. o He ________________ (look) like her father. o What _____________________ (think) about at the moment? o The sun ______________________ (rise) at 5.50 tomorrow morning. o The price of the holiday ___________________ (include) the cost of excursions. o _________________________ (you/ study) French at the moment? o I always _____________________ (stay) on duty until six o’clock. o I ___________________________ (not make) a lot of money these days. 62 3- LE PRETERIT SIMPLE a) Formation : On distingue les verbes réguliers des verbes irréguliers. Verbes réguliers : - A la forme affirmative, on met ED à toutes les personnes. - Aux formes interrogatives et négatives, on utilise l’auxiliaire DID. Forme affirmative I travelled You travelled He/ she / it travelled We travelled You travelled They travelled Forme interrogative Did I travel? Did you travel? Did he/ she/ it travel? Did we travel? Did you travel? Did they travel? Forme négative I didn’t (did not) travel You didn’t travel He/ she/ it didn’t travel We didn’t travel You didn’t travel They didn’t travel Verbes irréguliers : Il faut les connaître par cœur. (Se référer au tableau ci-après) A la forme affirmative, on emploie la forme irrégulière (2ème colonne du tableau). Aux formes interrogatives et négatives, on emploie l’auxiliaire DID (l’irrégularité disparaît). Forme affirmative I flew You flew He/ she/ it flew We flew You flew They flew Forme interrogative Did I fly? Did you fly? Did he/ she/ it fly? Did we fly? Did you fly? Did they fly? Forme négative I didn’t (did not) fly You didn’t fly He/ she/ it didn’t fly We didn’t fly You didn’t fly They didn’t fly b) Prononciation de ED : [d] I played, she weighed, they opened [t] He worked, you checked, they watched [id] They started, we waited, I succeeded c) Emploi : Le prétérit sert à parler d’actions datées, terminées appartenant à une période du passé révolue. Ex : He often travelled on business. Le prétérit modal s’emploie aussi dans les phrases en IF et après certaines expressions. Ex : If I had more time, I would travel more I wish he called more often. 63 4- LISTE DE VERBES IRREGULIERS INFINITIF PRETERIT PARTICIPE PASSE TRADUCTION bear Bore borne supporter beat Beat beaten battre become Became become devenir begin Began begun commencer bend Bent bent (se) courber bet Bet bet parier bite Bit bitten mordre blow blew blown souffler break broke broken casser bring brought brought apporter build built built construire burn burnt burnt brûler burst burst burst éclater buy bought bought acheter catch caught caught attraper choose chose chosen choisir come came come venir cost cost cost coûter cut cut cut couper deal dealt dealt distribuer do did done faire draw drew drawn dessiner dream dreamt dreamt rêver drink drank drunk boire drive drove driven conduire eat ate eaten manger fall fell fallen tomber feed fed fed nourrir feel felt felt sentir, éprouver fight fought fought combattre find found found trouver flee fled fled s'enfuir fly flew flown voler forbid forbade forbidden interdire forget forgot forgotten oublier forgive forgave forgiven pardonner freeze froze frozen geler 64 get got got obtenir give gave given donner go went gone aller grow grew grown grandir hang hung hung pendre, accrocher have had had avoir hear heard heard entendre hide hid hidden (se) cacher hit hit hit frapper, atteindre hold held held tenir hurt hurt hurt blesser keep kept kept garder kneel knelt knelt s'agenouiller know knew known savoir, connaître lay laid laid poser à plat lead led led mener lean leant leant s'appuyer learn learnt learnt apprendre leave left left laisser, quitter lend lent lent prêter let let let permettre, louer lie lay lain être étendu light lit lit allumer lose lost lost perdre make made made faire, fabriquer mean meant meant signifier meet met met (se) rencontrer overcome overcame overcome surmonter, vaincre pay paid paid payer put put put mettre quit quit quit cesser (de) read read read lire rid rid rid débarrasser ride rode ridden chevaucher ring rang rung sonner rise rose risen s'élever, se lever run ran run courir say said said dire see saw seen voir seek sought sought chercher sell sold sold vendre 65 send sent sent envoyer set set set fixer shake shook shaken secouer shed shed shed verser (des larmes) shine shone shone briller shoot shot shot tirer show showed shown montrer shrink shrank shrunk rétrécir shut shut shut fermer sing sang sung chanter sit sat sat être assis sleep slept slept dormir smell smelt smelt sentir (odorat) speak spoke spoken parler spell spelt spelt épeler spend spent spent dépenser spill spilt spilt renverser (un liquide) spit spat spat cracher spoil spoilt spoilt gâcher, gâter spread spread spread répandre stand stood stood être debout steal stole stolen voler, dérober stick stuck stuck coller sting stung stung piquer stink stank stunk puer strike struck struck frapper swear swore sworn jurer swim swam swum nager take took taken prendre teach taught taught enseigner tell told told dire, raconter think thought thought penser throw threw thrown jeter understand understood understood comprendre wake woke woken (se) réveiller wear wore worn porter (des vêtements) win won won gagner withdraw withdrew withdrawn (se) retirer write wrote written écrire 66 5- LE PRETERIT EN BE+ING a) Formation : Le prétérit en ING se forme à l’aide de l’auxiliaire BE au passé suivi du verbe en ING. Forme affirmative I was travelling You were travelling He/ she/ it was travelling We were travelling You were travelling They were travelling Forme interrogative Was I travelling Were you travelling Was he/ she/ it travelling Were we travelling Were you travelling Were they travelling Forme négative I wasn’t (was not) travelling You weren’t travelling He/she/it wasn’t travelling We weren’t travelling You weren’t travelling They weren’t travelling b) Emploi : Le prétérit en BE +ING sert à parler d’une action qui était en cours dans le passé. Ex :Yesterday at 11 pm, she was sleeping. Parfois dans une même phrase au passé, on trouve deux actions : l’une se déroule quand soudainement l’autre vient l’interrompre. L’action qui se déroule est au prétérit en BE + ING, l’action brève au prétérit simple. Ex : They were eating dinner when the agent called them. EXERCICE 2 : Complétez avec le prétérit simple ou le prétérit en BE+ING : 2) This time last week, I _______________________ (cycle) along a country road. 3) When I _________________ (get) to the cinema, Jack was waiting for me. 4) What ______________________ (you/ do) at the moment of the explosion? 5) When you arrived, ______________________(you/ notice) what time it was? 6) I __________________ (manage) to talk to her just before she left. 7) I ____________________ (have) a bath so I _______________ (not hear) the bell. 8) I’m sorry I ____________________ (forget) to call you. 9) Someone ______________________ (know) she had been working there before. 10) I ______________________ (not understand) what ___________________ (go on). 11) It was only later that I _________________ (find out) I had been taken in.* * to take someone in : rouler qqn USED TO Used to suivi d’une base verbale exprime un contraste entre passé et présent et sert à parler d’une habitude dans le passé. Ex : I used to travel a lot when I was younger. I didn’t use to travel in business class. Did you use to watch cartoons as a child? 67 Attention! Il ne faut pas confondre USED TO + BV et BE USED TO + verbe en ING. BE USED TO suivi d’un verbe en ING sert à parler d’une habitude présente. Exemple : I am used to working a lot. Is she used to travelling? I am not used to smoking. 68 6- LE PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE a) Formation : Le present perfect se forme à l’aide de l’auxiliaire HAVE au présent (donc HAVE ou HAS à la 3ème personne) suivi d’un verbe au participe passé.* (* Le participe passé des verbes réguliers est en ED, celui des verbes irréguliers est à connaître par cœur et correspond à la 3ème colonne du tableau). Forme affirmative I have travelled You have travelled He/ she/ it has travelled We have travelled You have travelled They have travelled Forme interrogative Have I travelled? Have you travelled? Has he/ she/ it travelled? Have we travelled? Have you travelled? Have they travelled? Forme négative I haven’t (have not) travelled You haven’t travelled He/ she/ it hasn’t travelled We haven’t travelled You haven’t travelled They haven’t travelled Verbes irréguliers : Forme affirmative I have flown You have flown He/ she/ it has flown We have flown You have flown They have flown Forme interrogative Have I flown? Have you flown? Has he/ she/ it flown? Have we flown? Have you flown? Have they flown? Forme négative I haven’t (have not) flown You haven’t flown He/ she/ it hasn’t flown We haven’t flown You haven’t flown They haven’t flown b) Emploi : Le present perfect sert à mettre en rapport une action passée et le moment présent. Il n’existe pas de temps équivalent en français. Le present perfect sert à : - faire un bilan de ses expériences passées : Exemple : I have been to China and I have seen the Great Wall. Peu importe la date, il s’agit juste de se remémorer au présent ses expériences passées. On parle de passé indéterminé. C’est le souvenir présent de l’expérience qui compte. - parler d’événements très récents (avec JUST) : Exemple : She has just left. Ici, avec l’adverbe “just”, passé et présent s’entremêlent. - parler de la conséquence d’une action passée sur le présent : Exemple : She can’t fly. She has forgotten her passport at home. 69 L’incident s’est produit dans le passé mais la conséquence présente est qu’elle ne peut pas travailler. - parler d’une action commencée dans le passé et qui se poursuit dans le présent : Exemple : They have worked here for 15 years. Dès que l’on veut traduire la notion française de « depuis » qui exprime qu’une action a commencé dans le passé et se poursuit dans le présent, on a besoin du present perfect en anglais. Attention ! FOR et SINCE servent tous deux à traduire « depuis ». FOR s’utilise avec une durée et SINCE avec un point de départ. Exemples : for 10 years / since 1998 for one hour / since 11 o’clock EXERCICE 3 : Choisir entre prétérit simple et present perfect simple. 11- I ____________________ (not listen) to this CD since last year. 12- My colleague ___________________ (not come) yesterday. 13- She _________________ (put) the roast into the oven. We’ll eat soon. 14- We __________________ (get married) twenty years ago and _________________ (be) happy ever since. 15- They __________________(love) each other since the day when they met. 16- I think that people __________________ (become) tired of the poor quality of services. 17- They _______________________ (buy) their new house two years ago. 18- Neil Armstrong _____________________ (set) foot on the moon in 1969. 19- Our reporters ______________________ (be) on the scene since dawn. 20- How long _____________________ (they/ live) here? 70 7- LE PRESENT PERFECT EN BE+ING o Formation : Le present perfect en BE +ING se forme à l’aide de HAVE BEEN (ou HAS BEEN à la 3ème personne) suivi du verbe en ING. Forme affirmative I have been travelling You have been travelling Forme interrogative Have I been travelling? Have you been travelling? Forme négative I haven’t been travelling You haven’t been travelling He/ she/ it has been travelling Has he/ she/ it been travelling? He/ she/ it hasn’t been travelling We have been travelling You have been travelling They have been travelling Have we been travelling? Have you been travelling? Have they been travelling? We haven’t been travelling You haven’t been travelling They haven’t been travelling b)Emploi : Il sert à parler d’une action commencée dans le passé et qui se poursuit dans le présent tout en insistant sur son déroulement. Comparer : She has worked for two hours. (1) She has been working for two hours. (2) (1) Fait énoncé de façon neutre. On insiste sur le résultat de l’action. (2) Fait énoncé avec insistance. On insiste sur le déroulement de l’action. EXERCICE 4 : Choisissez entre present perfect simple et present perfect en ING : 12345- I _______________________ (always want) to live in a big city. She __________________________ (wait) for three hours. She is very angry. He is suffering from jetlag. He ___________________ (sleep) since last night. Don’t forget your pills. _____________________ (you / take) them? I ____________________ (phone) all evening but there’s no reply. 71 8- LES AUXILIAIRES MODAUX Les auxiliaires modaux sont au nombre de cinq et quatre d’entre eux ont une forme passée. CAN MAY MUST WILL SHALL (COULD) (MIGHT) (WOULD) (SHOULD) Les caractéristiques des modaux sont qu’ils sont toujours invariables et toujours suivis d’une base verbale. On ne pourra donc pas les conjuguer, ni les utiliser à tous les temps français. Le modal… CAN (COULD) CAN’T (COULDN’T) MAY (MIGHT) MUST MUSTN’T WILL (WOULD) SHALL SHOULD Exprime : La capacité La perception involontaire La permission La probabilité L’incapacité L’interdiction La probabilité La permission L’obligation Une forte probabilité L’interdiction Le futur Une forte volonté Consignes, réglements Proposition Conseil Exemple : I can speak English I can see / hear/ feel… Can I ask you to...? It can be your brother I can’t carry this weight You can’t smoke here It may rain May I see your boarding pass? You must stop smoking You must be out of your mind! You mustn’t smoke She will become a pilot. Will you marry me? We shall be landing at 7.05 Shall we dance? You should work harder Les auxiliaires modaux ne pouvant être conjugués, il faut avoir recours à d’autres expressions équivalentes pour exprimer l’obligation, la capacité ou leurs contraires. 72 9- LES EQUIVALENTS DES MODAUX HAVE TO : - A la forme affirmative, sert à exprimer l’obligation : You will have to work harder. They had to move. - A la forme négative, sert à exprimer l’absence d’obligation : You don’t have to pay to register your wheelchair = It is not necessary for you to pay. BE ABLE TO - A la forme affirmative, sert à exprimer la capacité : You will be able to speak English when you return from your trip. - A la forme négative, sert à exprimer l’incapacité : He hasn’t been able to keep his temper. BE ALLOWED TO - A la forme affirmative, sert à exprimer l’autorisation : He will be allowed to enter the duty free zone. - A la forme négative, sert à exprimer l’interdiction : You won’t be allowed to smoke in that area. Exercice 5- Complétez les phrases suivantes à l’aide d’un modal : 1- You ________________ at least have left a message ! 2- ____________n’t you see how upset your mother is? She __________________ have had a heart attack. 3- Mother, _____________ I leave the table? 4- They ______________ have thought you were joking when you asked them. 5- Don’t lean over this balcony! You _______________ fall! 6- They ______________n’t find your seats at the opera last night with all the people. 7- ______________ we all go to that horrible party? 8- You _________________ have had a hard time finding our place! 9- You ______________n’t have gone out with this cold. You wouldn’t have had a cold. 10- I’m afraid we really _________________ go now. 73 10- LES MODAUX AU PASSE Tous les modaux peuvent exister à la forme MODAL + HAVE + PARTICIPE PASSE CAN (COULD) HAVE + p. passé MUST HAVE + p. passé exemple He can have escaped. He must have failed. MAY (MIGHT) HAVE + p. passé WILL (WOULD) HAVE + p. passé He may have been ill. SHALL (SHOULD) HAVE + p. passé She should have worked more. I would have accepted if I had known français Possibilité : il a pu s’échapper. Forte probabilité : il a dû échouer. Probabilité : il se peut qu’il ait été malade. Futur antérieur ou conditionnel passé : j’aurais accepté si j’avais su. Avec should, exprime un reproche : elle aurait dû travailler plus. Exercice 6- Complétez en utilisant un modal au passé : 1- Thank you very much but you _______________________ bought me flowers. 2- You _______________________ lost your keys again. 3- She got home at 4 o’clock in the morning. The party __________________ been great! 4- He wasn’t here so he ________________________ broken your vase. 5- If it had been cheaper, I ______________________ bought another one. 74 11-EXPRESSIONS DU FUTUR ET DU CONDITIONNEL EXPRESSION DU FUTUR 1) WILL + BV WILL sert souvent à exprimer le futur ; il a une valeur de prédiction. Exemple : The company will serve new destinations next year. 2) BE GOING TO Il sert à exprimer un futur proche ou une intention. Exemple : It’s going to rain. 3) BE + ING La forme en ING sert à exprimer une action prévue à l’avance et est souvent employée avec un marqueur de temps. Exemple : The plane is leaving at 5.45. 4) WILL + BE + ING Comme toujours la forme en ING prend en compte le déroulement de l’action. Souvent et notamment dans les annonces aéroportuaires, il sert à exprimer des actions anticipées, prévues. De plus, la forme en ING permet d’atténuer, donc donne un côté plus poli. Exemple : The plane will be landing at 3.05. EXPRESSION DU CONDITIONNEL 1) WOULD + BV Le conditionnel français se forme généralement en anglais à l’aide de l’auxiliaire WOULD + BV Exemple : I would appreciate if you could give me a help. 2) WOULD BE + ING Même chose que pour WILL + BE+ING mais avec valeur de conditionnel. 75 12- SUBORDONNEES EN IF On trouve souvent les différents cas suivants : A) Conditionnel zéro : présent dans la subordonnée en IF + présent dans la principale [ If I work a lot], [I get tired.] Sert à exprimer une situation réelle. B) Conditionnel 1 : présent dans la subordonnée en IF + WILL dans la principale [If the plane is delayed], [I will be late for my appointment]. Sert à exprimer une situation possible dont le résultat est envisageable. C) Conditionnel 2 : prétérit dans la principale + WOULD dans la principale [If the tickets were cheaper], [I would travel more]. Sert à exprimer des situations imaginaires, à formuler des hypothèses. En général, avec BE, on utilise dans ce type de phrases WERE à toutes les personnes. Ex : If I were you, I would not answer. D) Conditionnel 3 : past perfect* dans la subordonnée + WOULD HAVE dans la principale. * past perfect = have + participe passé [If I had known], [I would have cancelled my flight.] Sert à parler de situations hypothétiques mais lorsqu’il est trop tard pour les réaliser. EXERCICE 7- Complétez avec le temps qui convient : 1- We are lost. If you (write) ____________________ the directions, this (happen) ____________________________. 2- Why don’t we leave the country? If we (live) _______________________ in Australia, at least the weather (be) _________________________ better. 3- Don’t be afraid. If you (touch) _______________________ the dog, it (not bite) ___________________________. 4- If we (not miss) ____________________________ the plane, we (kill) _____________________________ in the crash and we wouldn’t be here today. 5- If only I (work) ________________________ more, I (pass) ____________________ the exam. 6- Hurry up! You still have time. If you (hurry up) ________________________, you (not miss) __________________________ your plane. 76 13- LES PRONOMS ET ADJECTIFS Les pronoms remplacent le nom. Exemples : Pronoms sujets : The plane is taking off. / It is taking off. Pronoms compléments : I saw Kate. / I saw her. Pronoms possessifs : This bag is Jenny’s. / This bag is hers. Pronoms réfléchis : He is looking at himself in the mirror. Pronoms réciproques : They are talking to each other. PRONOMS PRONOMS PRONOMS PRONOMS PERSONNELS PERSONNELS POSSESSIFS REFLECHIS SUJETS COMPLEMENTS I ME MINE MYSELF YOU YOU YOURS YOURSELF HE HIM HIS HIMSELF SHE HER HERS HERSELF IT IT ITS ITSELF WE US OURS OURSELVES YOU YOU YOURS YOURSELVES THEY THEM THEIRS THEMSELVES PRONOMS RECIPROQUES EACH OTHER / ONE ANOTHER Les adjectifs précèdent le nom. Exemples : Adjectifs possessifs : Her bag is too heavy. ADJECTIFS POSSESSIFS MY YOUR HIS HER ITS OUR YOUR THEIR 77 14- SOME ET ANY 1) SOME ET ANY Observez : There are some passengers in the lobby. Are they any window seats left? There aren’t any tags. Some et Any signifient “du, de la, des...”. On emploie généralement SOME dans les phrases affirmatives et ANY dans les phrases négatives et interrogatives. Attention : Would you like some tea or coffee ? Lorsque l’on demande quelque chose à quelqu’un, on emploie SOME même dans les phrases interrogatives. En fait, on emploie SOME lorsque l’on est certain d’avoir la quantité et ANY lorsqu’elle est nulle ou lorsque l’on interroge sur l’existence de cette quantité (phrases négatives et interrogatives). 2) NO NOT ANY = NO Exemple : There aren’t any passengers = there are no passengers. 3) Les composés : SOMEBODY / ANYBODY (quelqu’un) ou NOBODY (personne) SOMEONE / ANYONE (quelqu’un) ou NOBODY (personne) SOMETHING/ ANYTHING (quelque chose) ou NOTHING (rien) suivent la même règle. 4) Traduction de « plus de… » There is no more milk = there is not anymore milk. Ou “il ne reste plus...” There is no milk left = there is not any milk left. EXERCICE 8- Complétez avec SOME ou ANY Is there ______________ chocolate left ? ______________ day, I will buy myself a new jacket. Would you like __________________ labels for your bags? I can’t speak ______________ louder. I haven’t seen _____________thing. 78 15- MUCH, MANY – LITTLE, FEW 1) MUCH et MANY : Observez : I don’t have much luggage/ time/ money. There aren’t many passengers today. MUCH et MANY signifient « beaucoup de ». On emploie MUCH devant les indénombrables et MANY devant les dénombrables pluriels. 2) LITTLE et FEW : I have little time. There are few passengers. LITTLE et FEW signifient “peu de”. On emploie LITTLE devant les indénombrables et FEW devant les dénombrables pluriels. Attention : A LITTLE et A FEW ont un sens différent. Ils signifient « UN peu de » (ou « quelques » pour « a few »). Exemple : I have a little time (un peu de temps) I have a few books (quelques livres) EXERCICE 9- Complétez avec MUCH, MANY, LITTLE ou FEW : o There were so _________________ tourists on the beach that we changed our plans. o We don’t have _______________ choice. We have to leave at once. o I was a _______________ scared but nobody noticed it. o A ________________ passengers have decided to complain to the manager. 79 16 - LES COMPARATIFS ET LES SUPERLATIFS 8) Le comparatif : - Comparatif de supériorité : On distingue les adjectifs courts des adjectifs longs. Adjectifs courts : ADJ+ ER + THAN Exemple : She is taller than her sister. Adjectifs longs : MORE + ADJ + THAN Exemple : She is more talkative than her sister. - Comparatif d’égalité : Pour tous les adjectifs : AS + ADJ + AS Exemple : She is as talkative as her sister. She is as tall as her sister. - Comparatif d’infériorité : Pour tous les adjectifs : LESS+ ADJ + THAN ou NOT AS + ADJ + AS Exemple : She is less tall than her sister. She is not as tall as her sister. 2) Le superlatif : Adjectifs courts : THE + ADJ + EST Exemple : She is the tallest girl in the group. Adjectifs longs : THE MOST + ADJ Exemple : She is the most talkative girl in the group. 3) Exceptions : GOOD BAD FAR COMPARATIF BETTER THAN WORSE THAN FARTHER THAN FURTHER THAN SUPERLATIF THE BEST THE WORST THE FARTHEST THE FURTHEST EXERCICE 10- Mettre au comparatif ou au superlatif selon le cas : 1- The hotel is (expensive) _____________________________ a bed and breakfast. 2- Wet roads are (dangerous) ______________________________ icy ones. 3- The bakery down the road is (good) __________________________ the one downtown. 4- Indian cuisine is (hot) ______________________________ Chinese cuisine. 5- Turner is one of England’s (famous) ________________________ painters. 6- The (rich) __________________ people are not necessarily the (happy) _____________. 7- It’s the (spicy) _____________________ fish I’ve ever eaten. 8- He does so much exercise that he is certainly the (strong) _______________ of us all. 80 17- SCRIPT DES CONVERSATIONS: CONVERSATION WITH THE PURSER Purser : Good morning. Traffic agent : Hi, how are you today? Purser : Fine thanks. How are you? Traffic agent : Good. Purser : So, is the flight full today? Traffic agent: Well, we have 231 passengers today and 4 infants. Purser: OK. And where is the catering truck? Traffic agent : It should be there within five minutes. Purser : Five minutes? Fine. When will boarding take place? Traffic agent : Boarding should start within fifteen minutes. Everything's on time today. How about your crew? Is everybody ready? Purser : We are waiting for one flight attendant but he's on his way. He should be here in a few minutes. Traffic agent : All right. Well, have a nice flight to Cancun. Will you be staying there for a few days? Purser : Oh yes, three days. It's a great place. Nice hotel and beautiful beaches. Traffic agent : I wish I could go. Have a nice time. Purser : Thanks. Have a nice day. See you next time. CONVERSATION WITH THE CAPTAIN Traffic agent: Good morning Captain. How are you today? Captain: Fine thanks. So, is the flight full today? Traffic agent: Yes, quite full. We have 311 passengers. There's one passenger in a wheelchair and we have two pets in the hold. Captain: OK. What slot do we have? Traffic agent: You have a slot at 6 pm. Captain: All right. How about refueling? Traffic agent: The refueler has just arrived. What are the fuel figures today? Captain: Here are the fuel figures: bloc fuel: 32,000 kgs, taxi fuel: 500 kgs, trip fuel: 29,000 kgs. The estimated elapse time is 3 hours forty-five minutes. There are 7 flight attendants in the cabin, and 2 pilots in the cockpit. The dry operating weight is 90,055 kgs, the dry operating index is 50.57. The maximum take-off weight is 171,700 kgs, the maximum zero fuel weight is 130,000 kgs and the maximum landing weight is 140,000 kgs. Traffic agent: OK. Thank you very much captain. And here is the weather report. The weather conditions are good today. The sky is clear and there are only light winds. Captain: OK. Thank you very much. Traffic agent: Have a nice flight Sir. Captain: Thanks. Bye. 81 18- Correction des exercices de grammaire : Exercice 1: 1- drink ; 2- am depending ; 3- want ; 4- looks ; 5-are you thinking ; 6- is rising ; 7- includes ; 8are you studying ; 9- stay ; 10- don’t make. Exercice 2 : 1- was cycling; 2- got; 3- were you doing; 4- did you notice; 5- managed; 6- was having : didn’t hear; 7- forgot; 8- knew; 9- did not understand; was going; 10- found out. Exercice 3 : 1- haven’t listened; 2-did not come; 3-has put; 4-got married; have been; 5- have loved; 6-have become; 7-bought; 8-set; 9-have been; 10- have they lived. Exercice 4 : 1- have always wanted; 2-has been waiting, 3- has been sleeping; 4- have you taken; 5- have been phoning. Exercice 5 : 1-could; 2-can; could; 3-may; 4-must; may; 5-may; 6-couldn’t; 7-must; 8- must; 9- shouldn’t; 10must. Exercice 6 : 1-shouldn’t have; 2- can’t have; 3-must have; 4-can’t have; 5-would have Exercice 7 : 1- had written / wouldn’t have happened ; 2-lived / would be ; 3- touch / won’t bite ; 4- had not missed / would have been killed ; 5- had worked / would have passed ; 6- hurry up / will not miss. Exercice 8 : 1-any; 2-some; 3-some; 4-any; 5-any Exercice 9 : 1-many; 2-much; 3-little; 4-few Exercice 10 : 1-more expensive than; 2- less dangerous than; 3-better than; 4-hotter than; 5-most famous; 6richest/ happiest; 7-spiciest; 8-strongest 82



